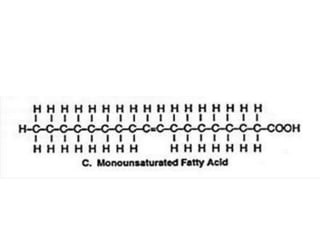
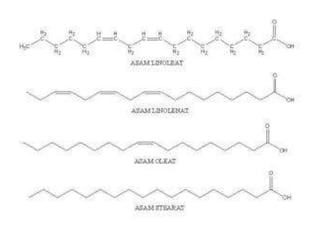
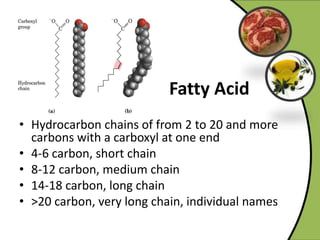
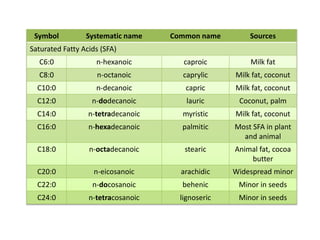
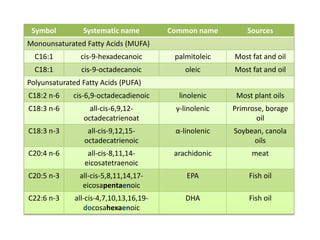
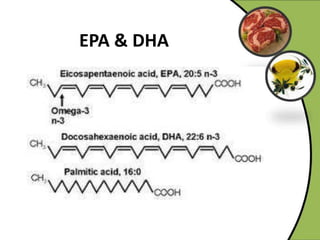
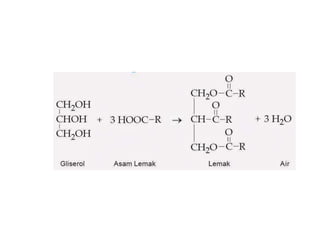
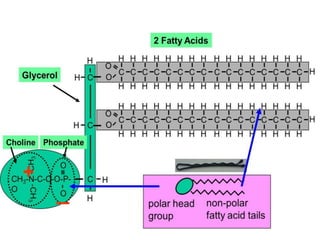
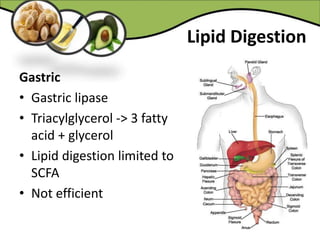
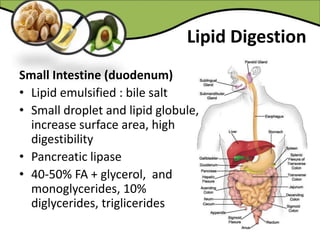
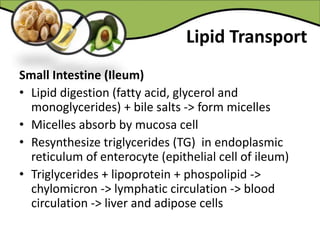
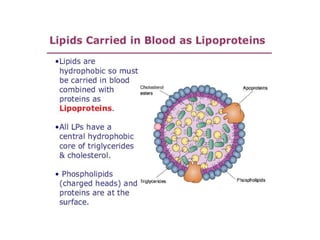
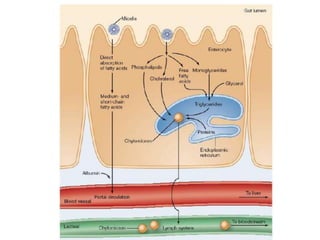
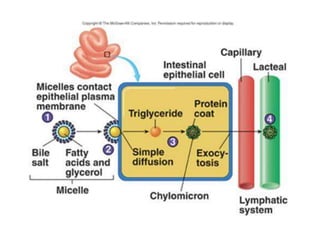
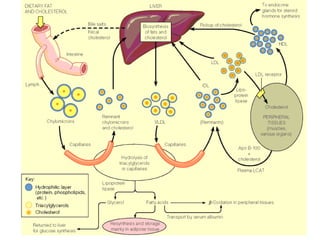
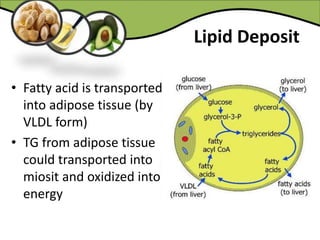
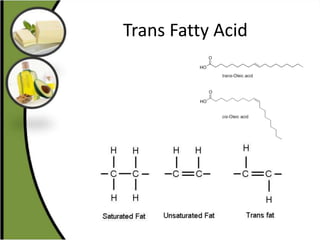
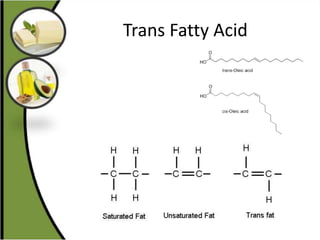
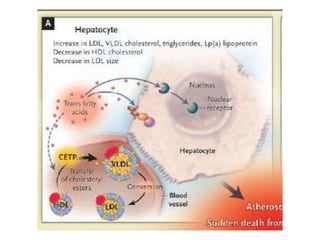
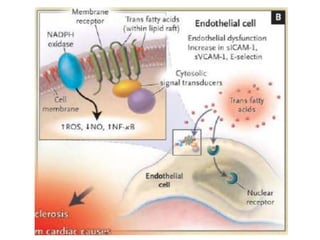
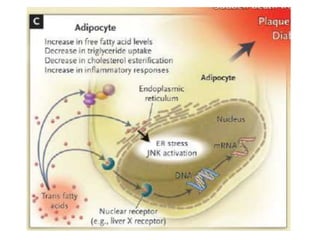
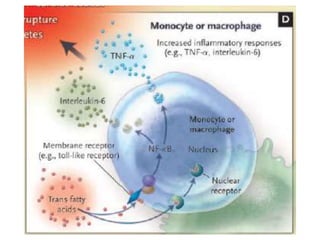
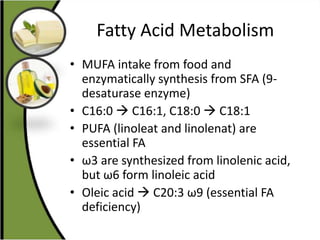
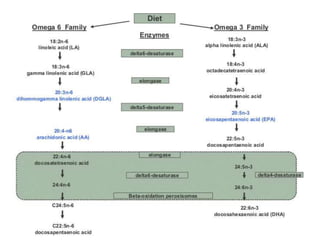
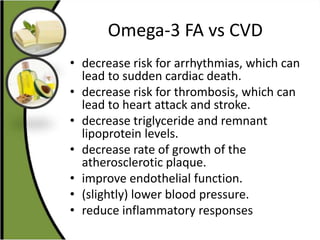
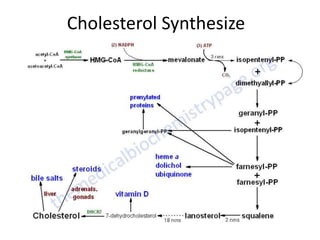
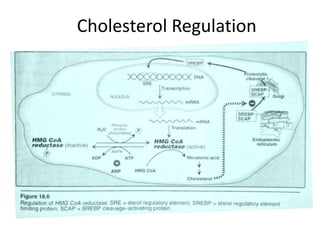
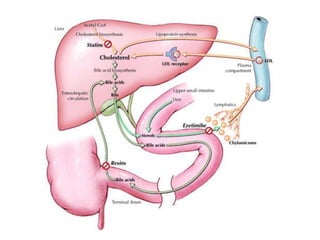
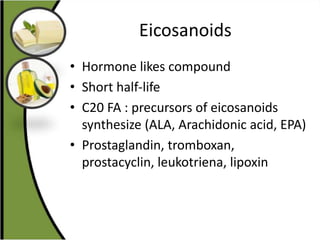
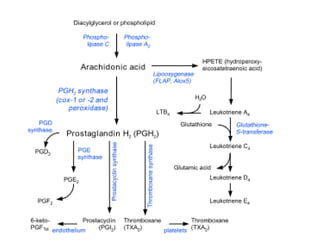
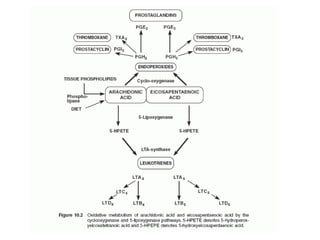
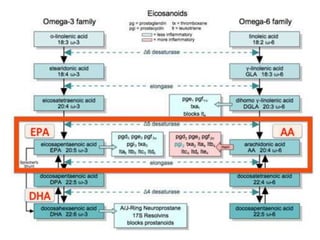
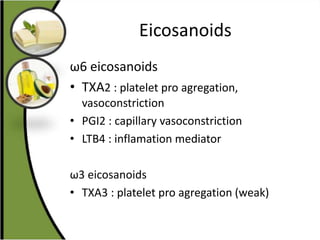
The document discusses various aspects of lipids, including their classification, digestion, metabolism, and health impacts. It details the role of different fatty acids, their sources, and the physiological processes involved in lipid digestion and absorption. Additionally, it covers the implications of trans fatty acids and omega-3 fatty acids on health, particularly regarding cardiovascular disease and metabolic functions.