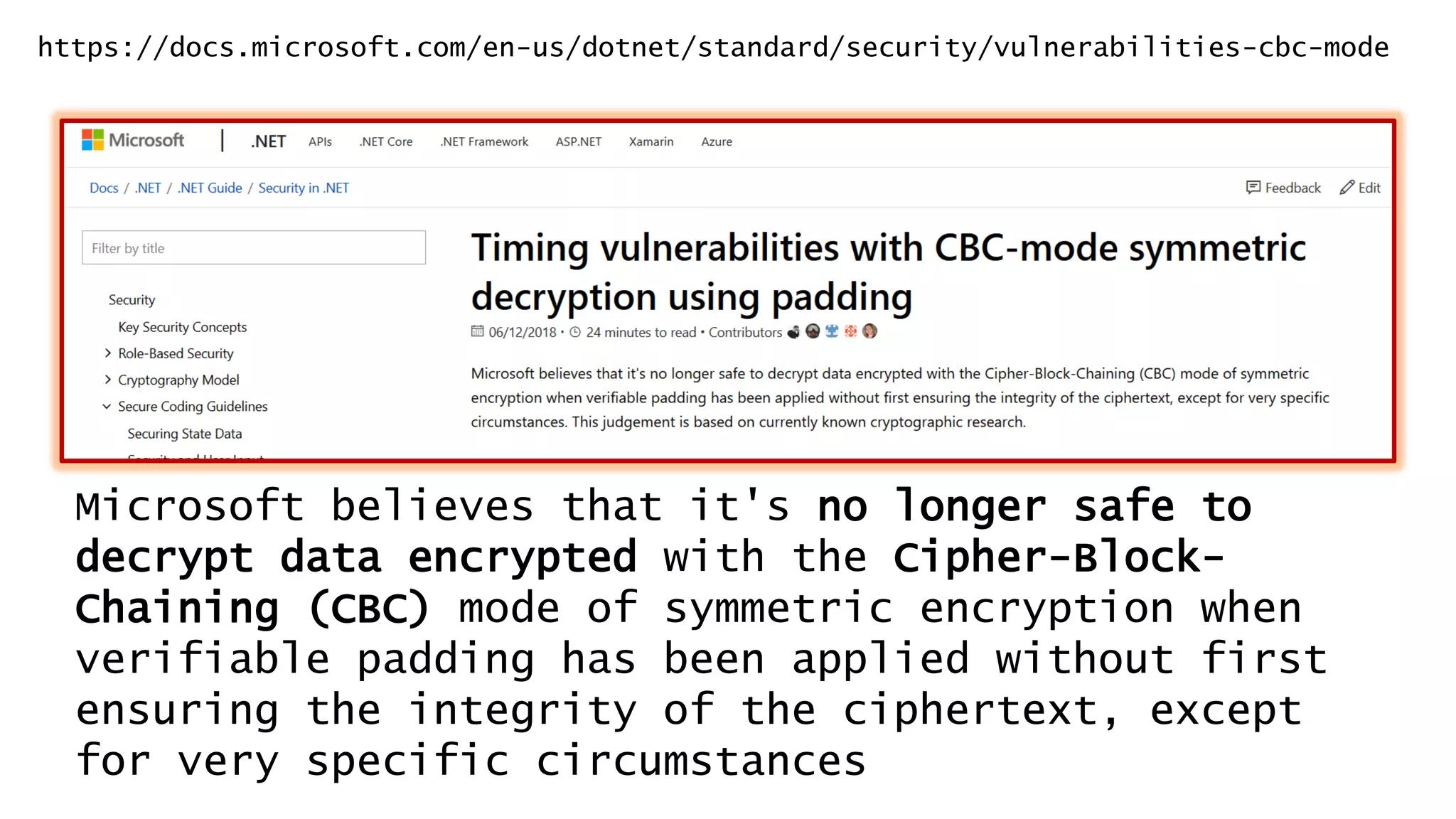
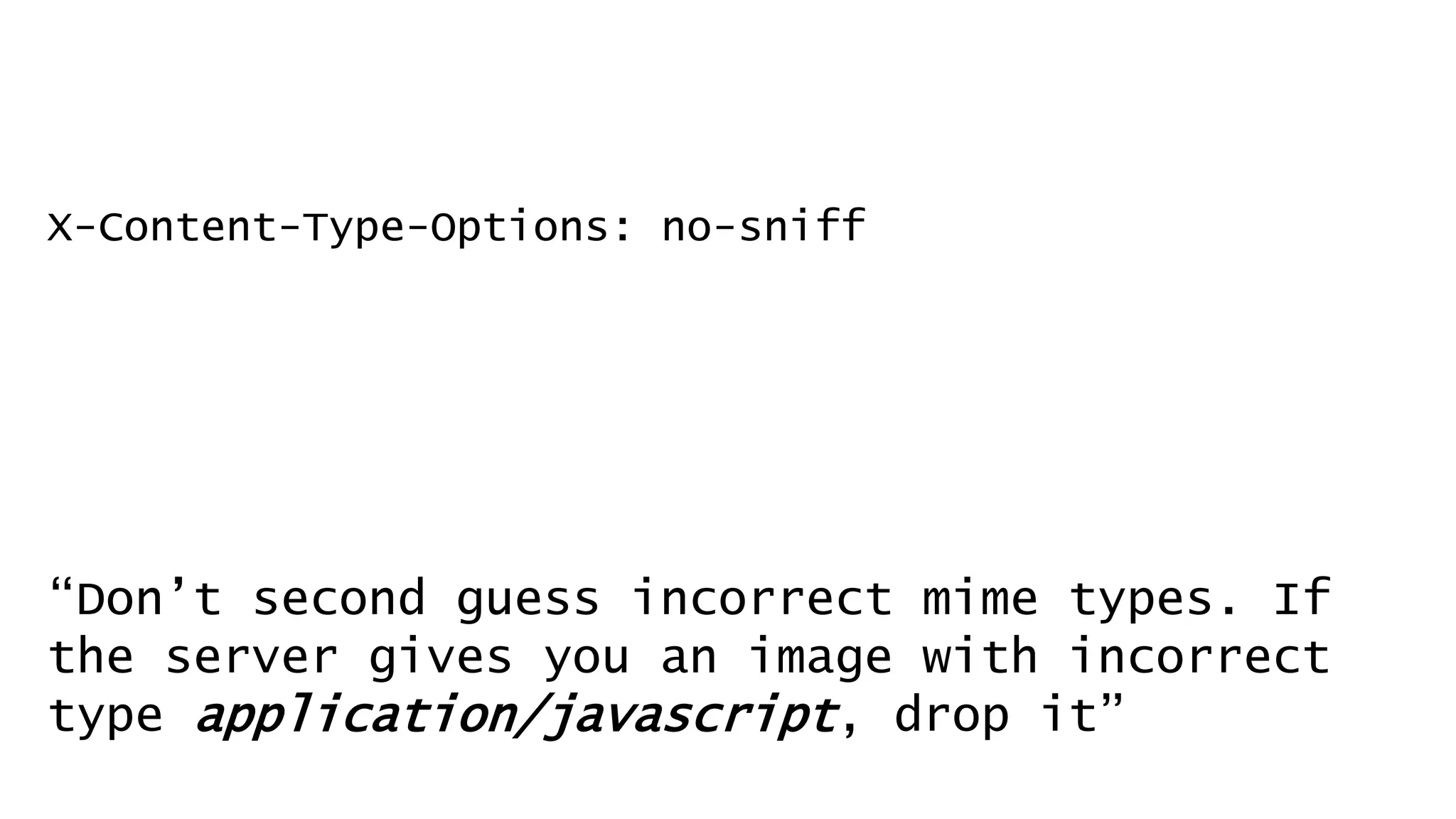
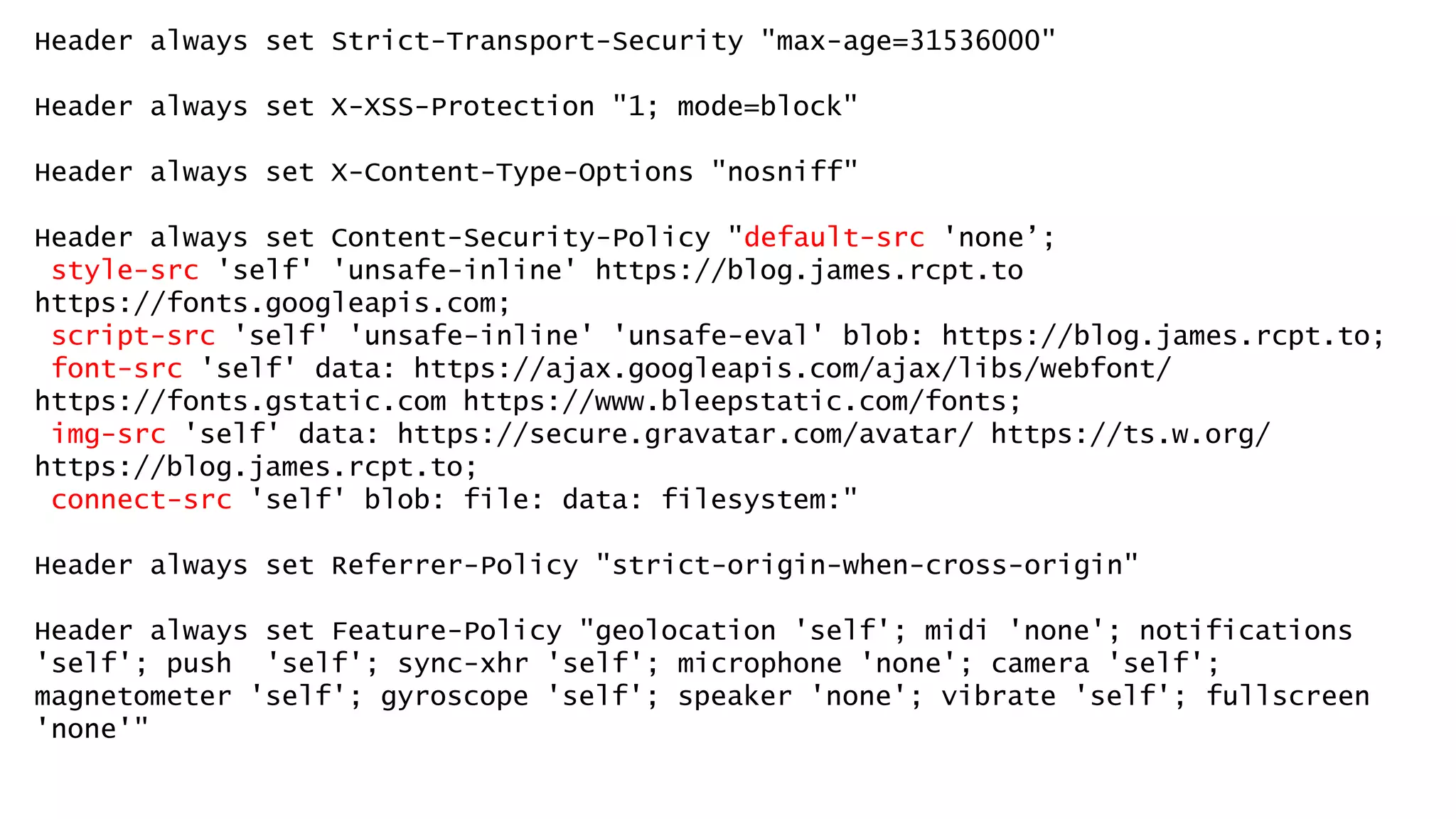
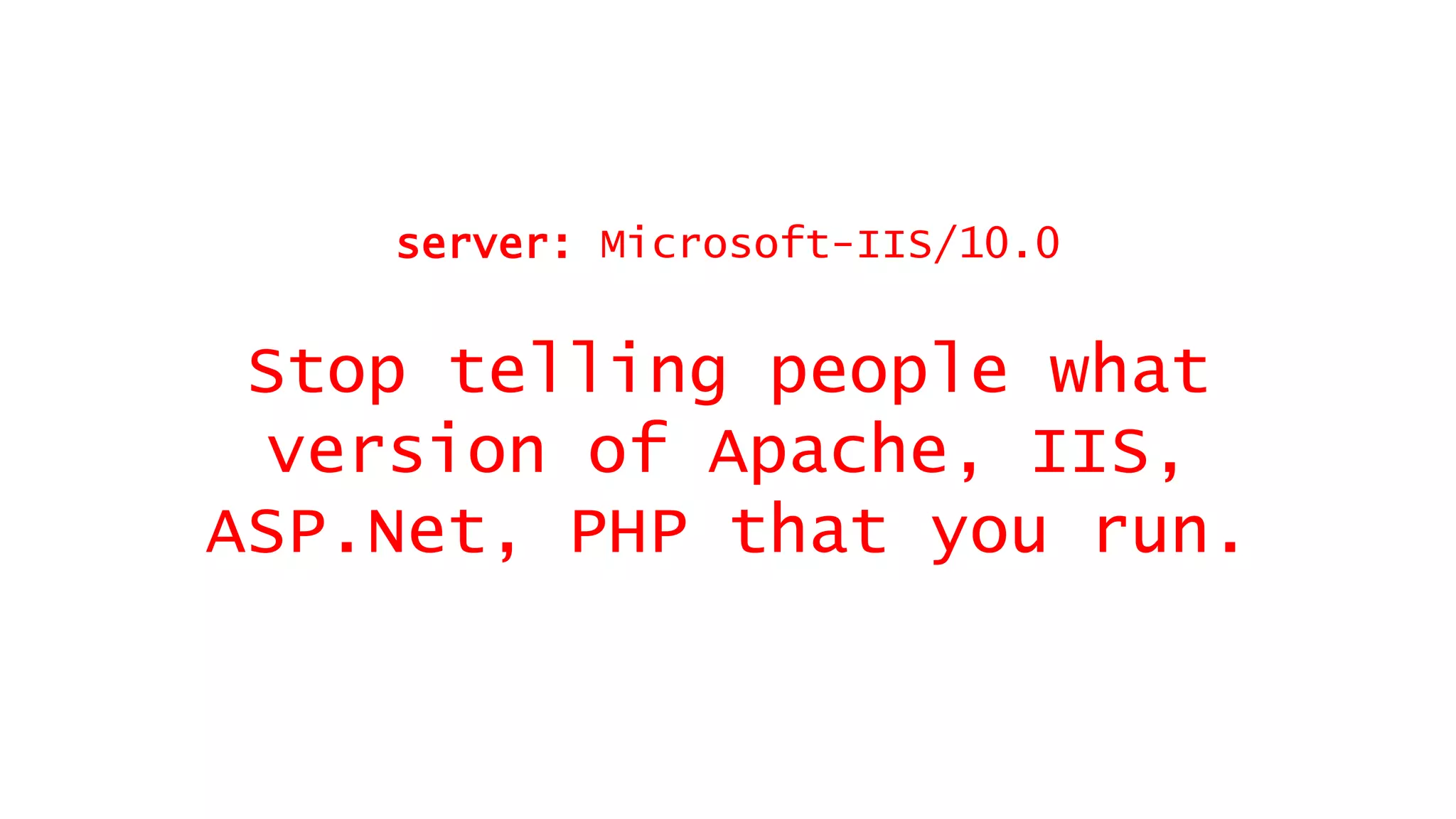
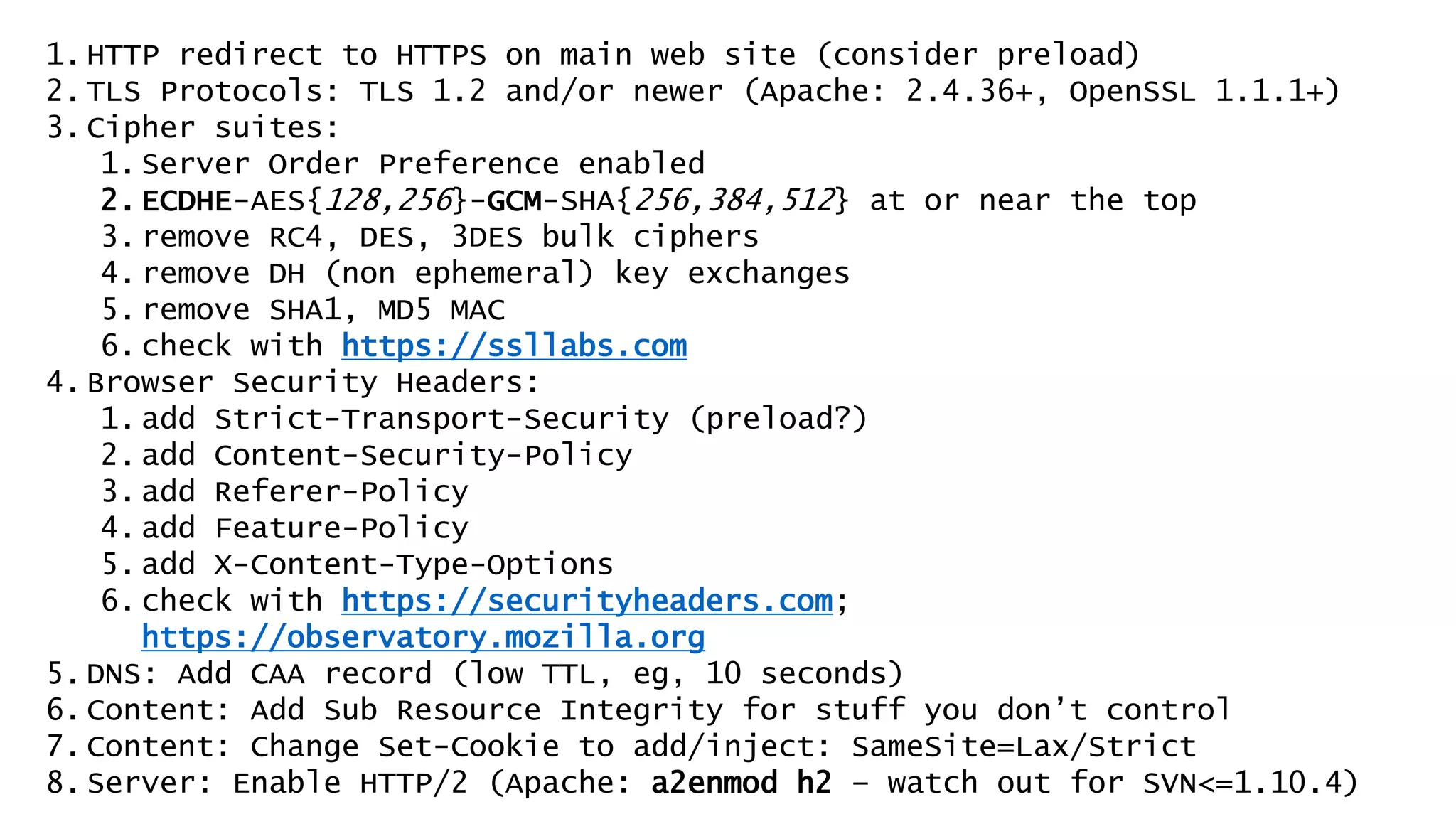
This document discusses recommendations for improving web security in 2019. It recommends: 1) Redirecting all sites to HTTPS; 2) Using TLS protocols 1.2 or newer and disabling legacy protocols; 3) Optimizing cipher suites to use perfect forward secrecy and disable weak ciphers; and 4) Adding security headers to browsers to restrict content and functionality. Following these recommendations will help sites adopt modern encryption standards and security best practices.

![• First paid-for web content 1995 (still online!)
• UWA Webmaster, 1997 – 2000 [1] (AusWeb Ballina 1999?)
• Debian/GNU Linux Developer 2001 – present
• Hartley’s/JDV online ShareTrading
• Linux.conf.au chair 2003 w/Linus [2]
• Fotango=Canon Europe (UK)/Vibrant Media (UK) 2003-2010
• AWS Security Soln Arch. Aus & New Zealand 2012-2014 [3]
• Modis CD National Cloud & Cyber Security Lead [4]
[1]
[2] [3]
[4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxconfau2019websecurity2019-190125020312/75/Linux-confau-2019-Web-Security-2019-2-2048.jpg)

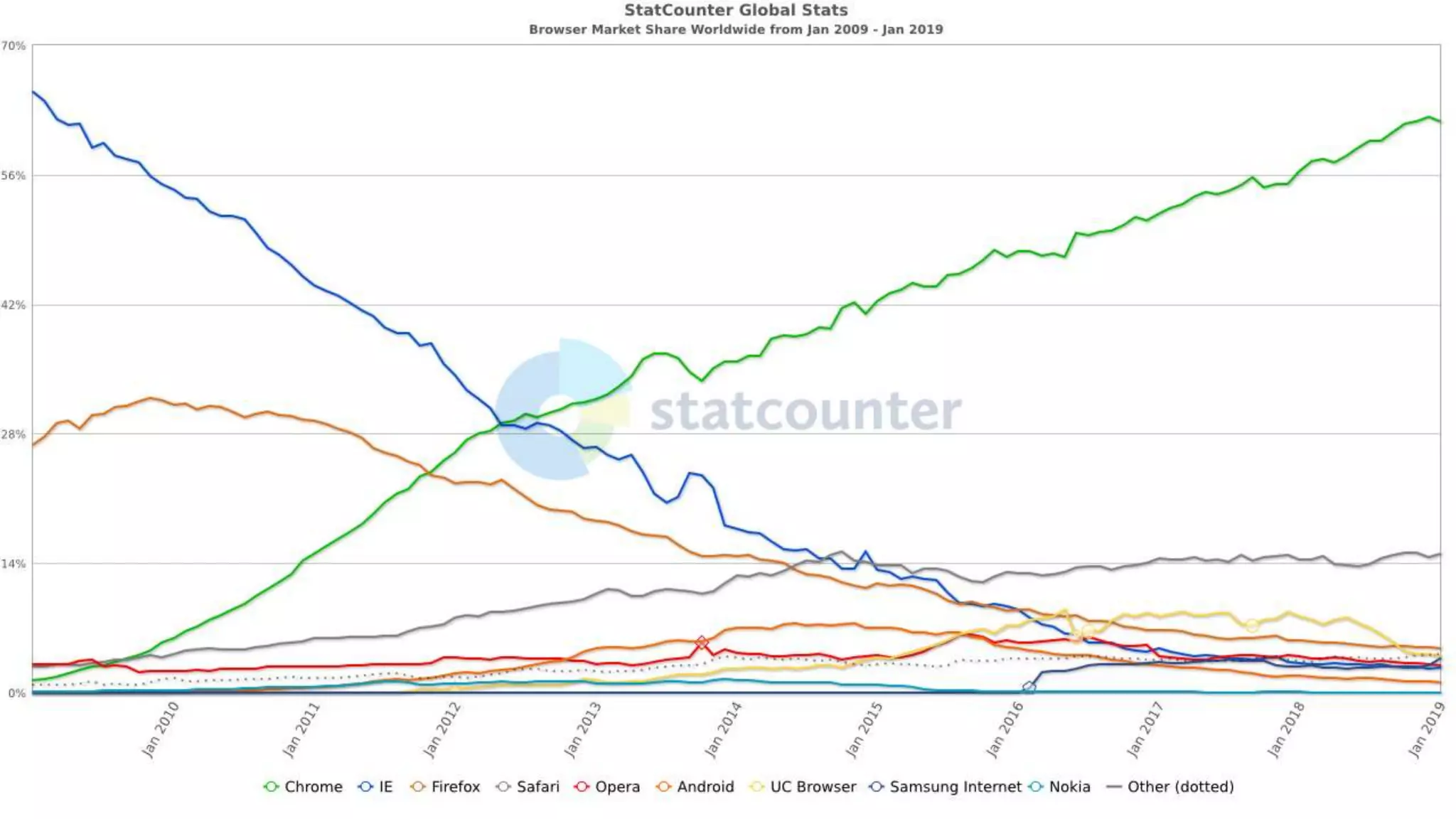
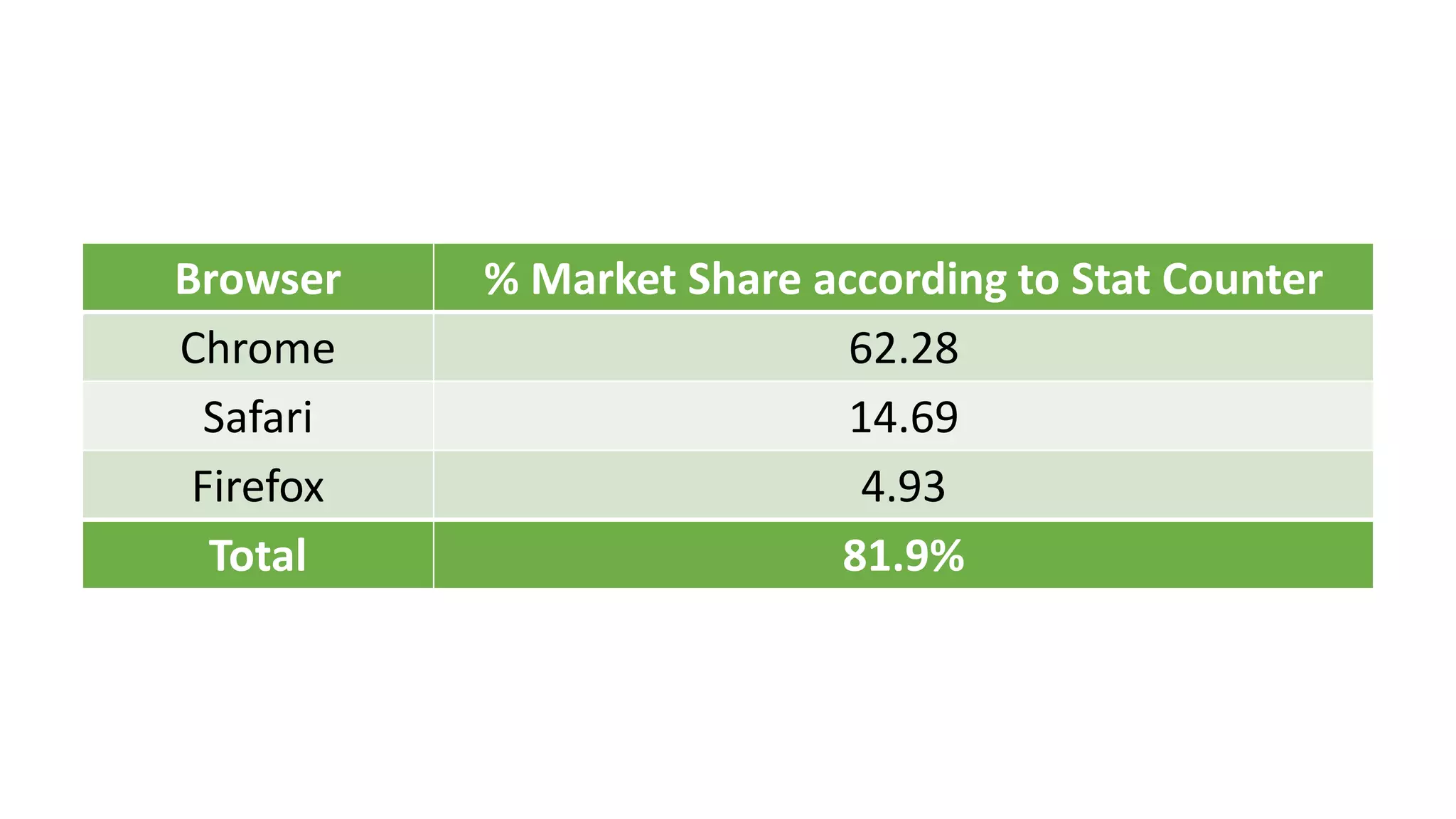
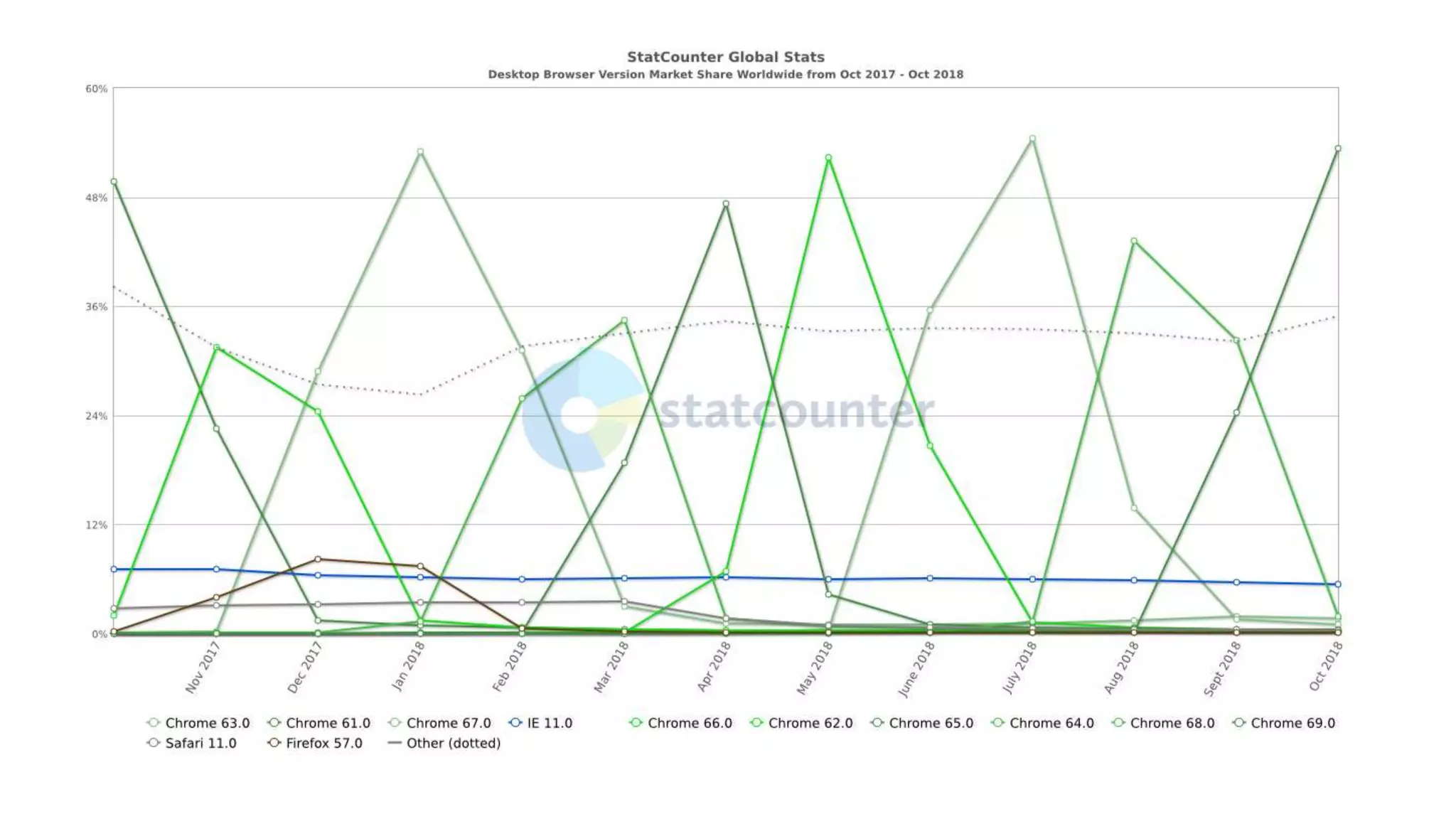





![Use HTTPS!
It’s not [just] about how much you value your content.
It’s about how much you value your visitors (customers,
staff, self) not being intercepted.
Internet, internal, everywhere.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxconfau2019websecurity2019-190125020312/75/Linux-confau-2019-Web-Security-2019-15-2048.jpg)


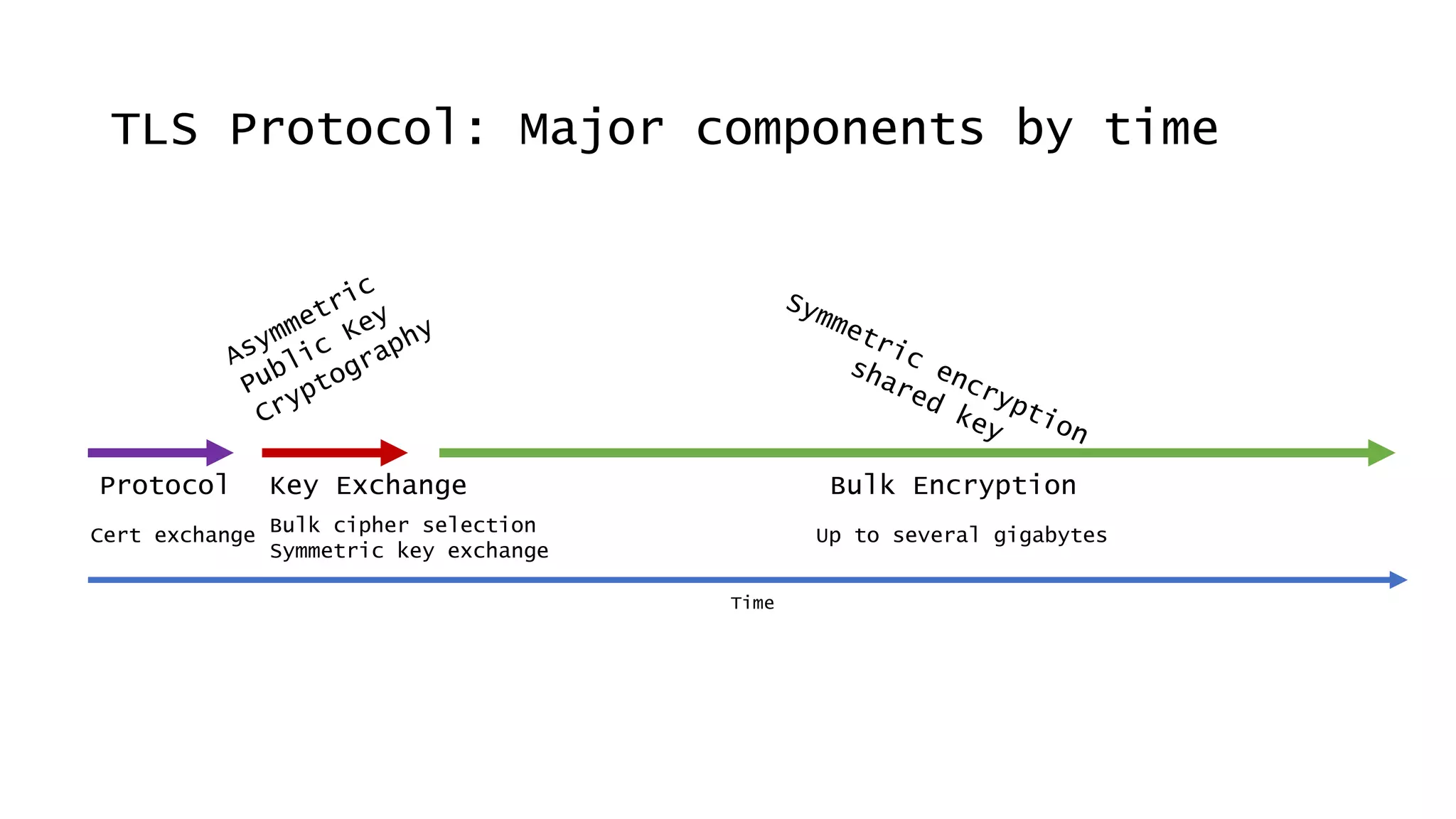

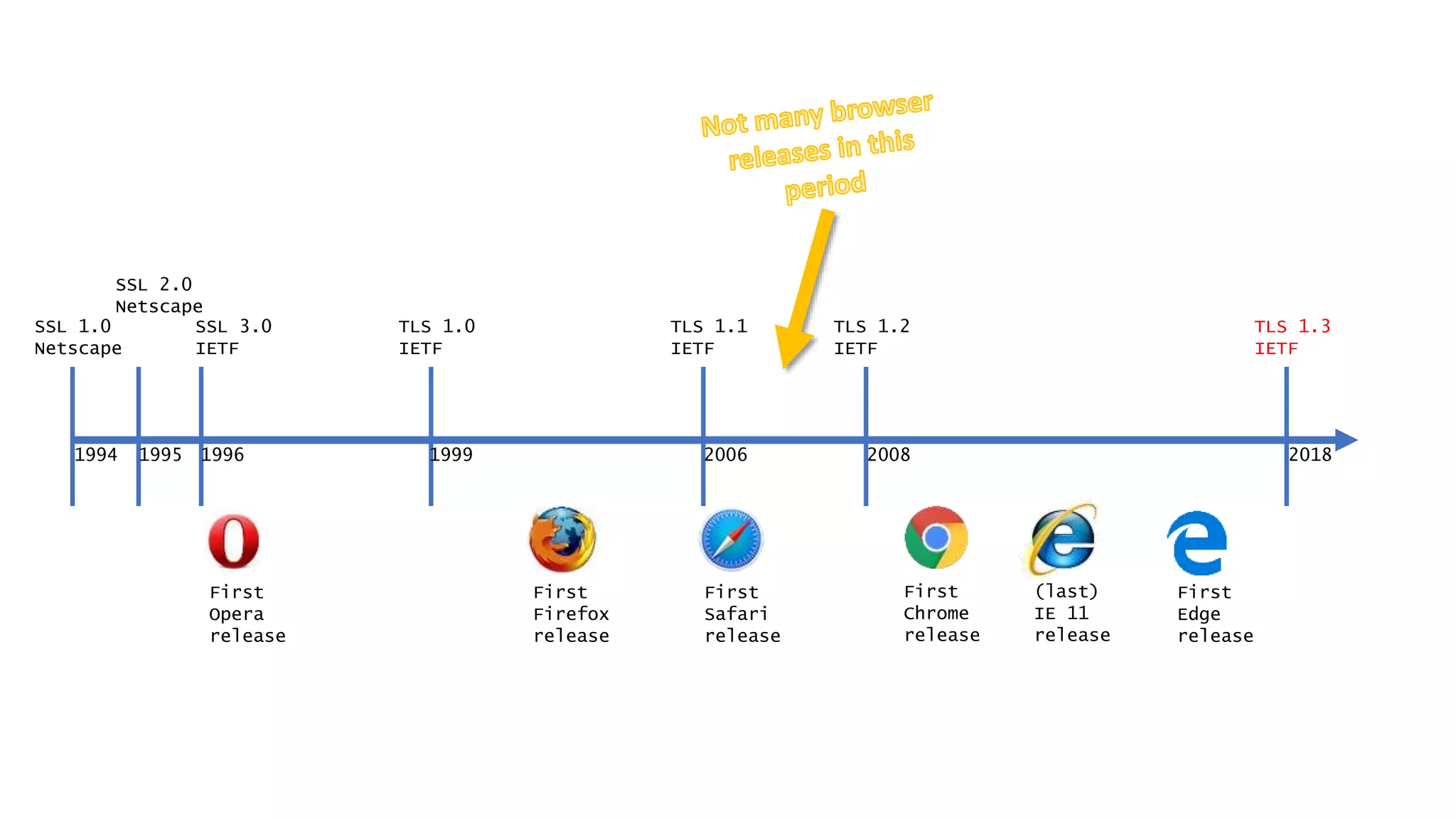


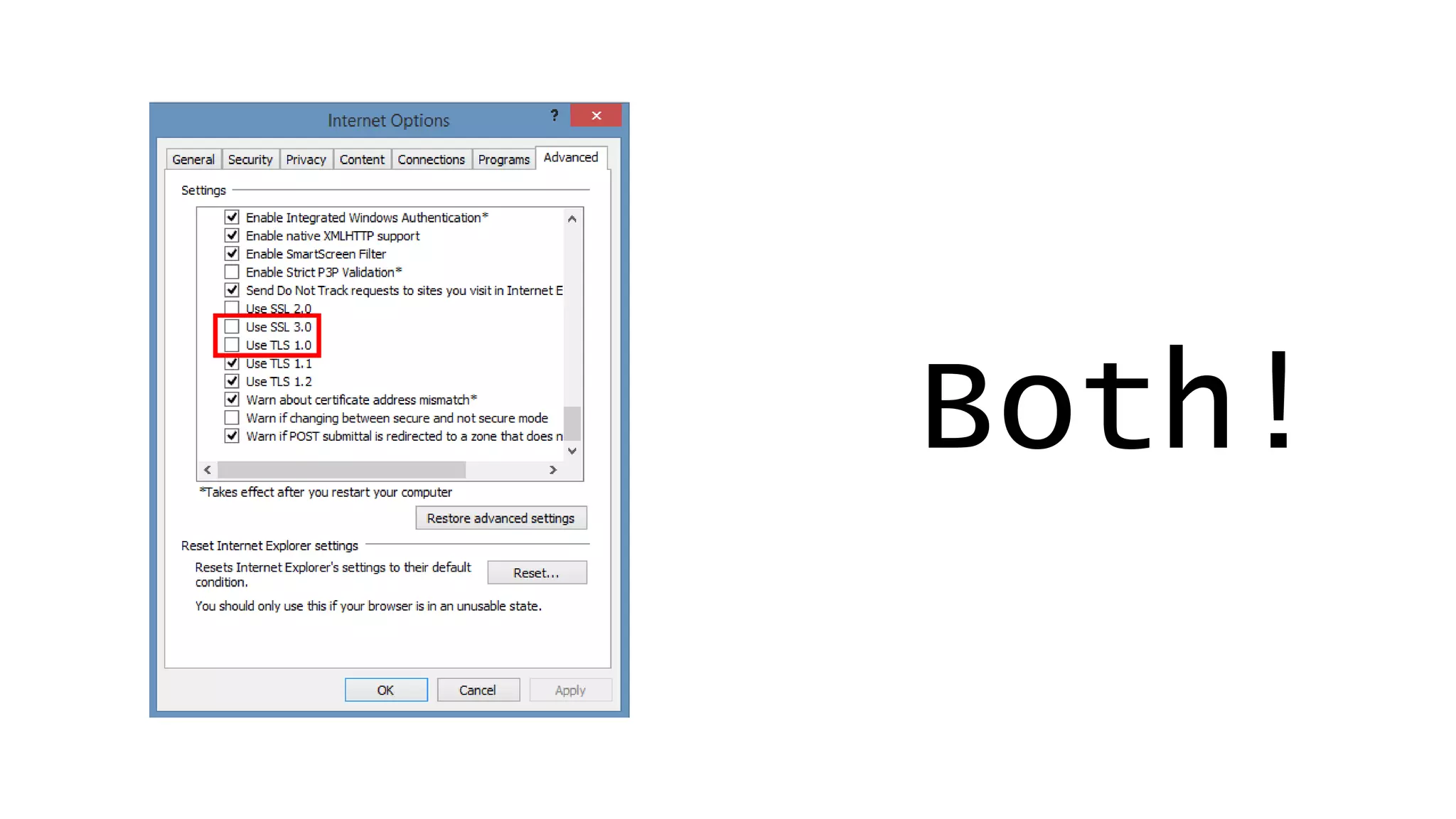
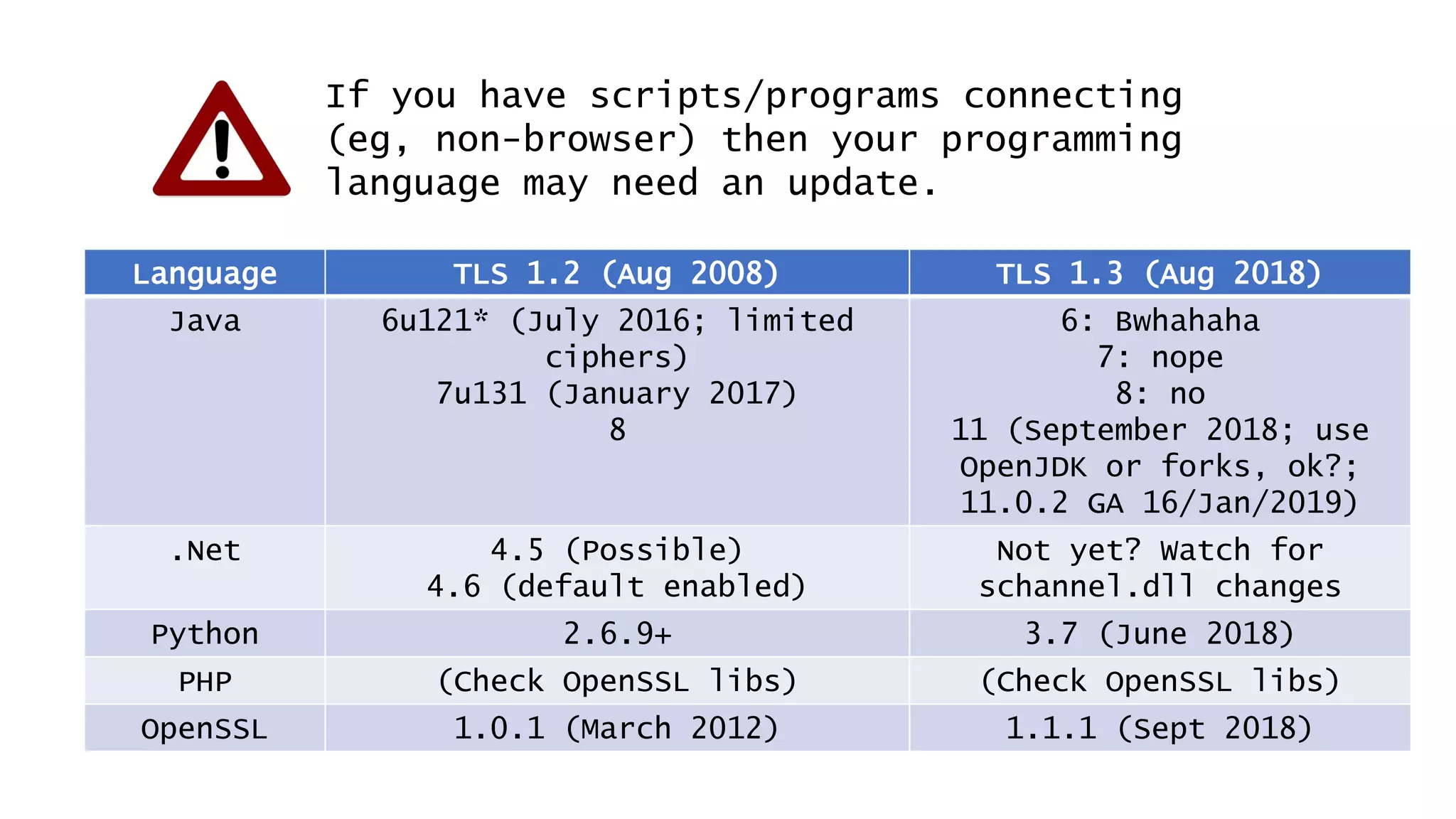
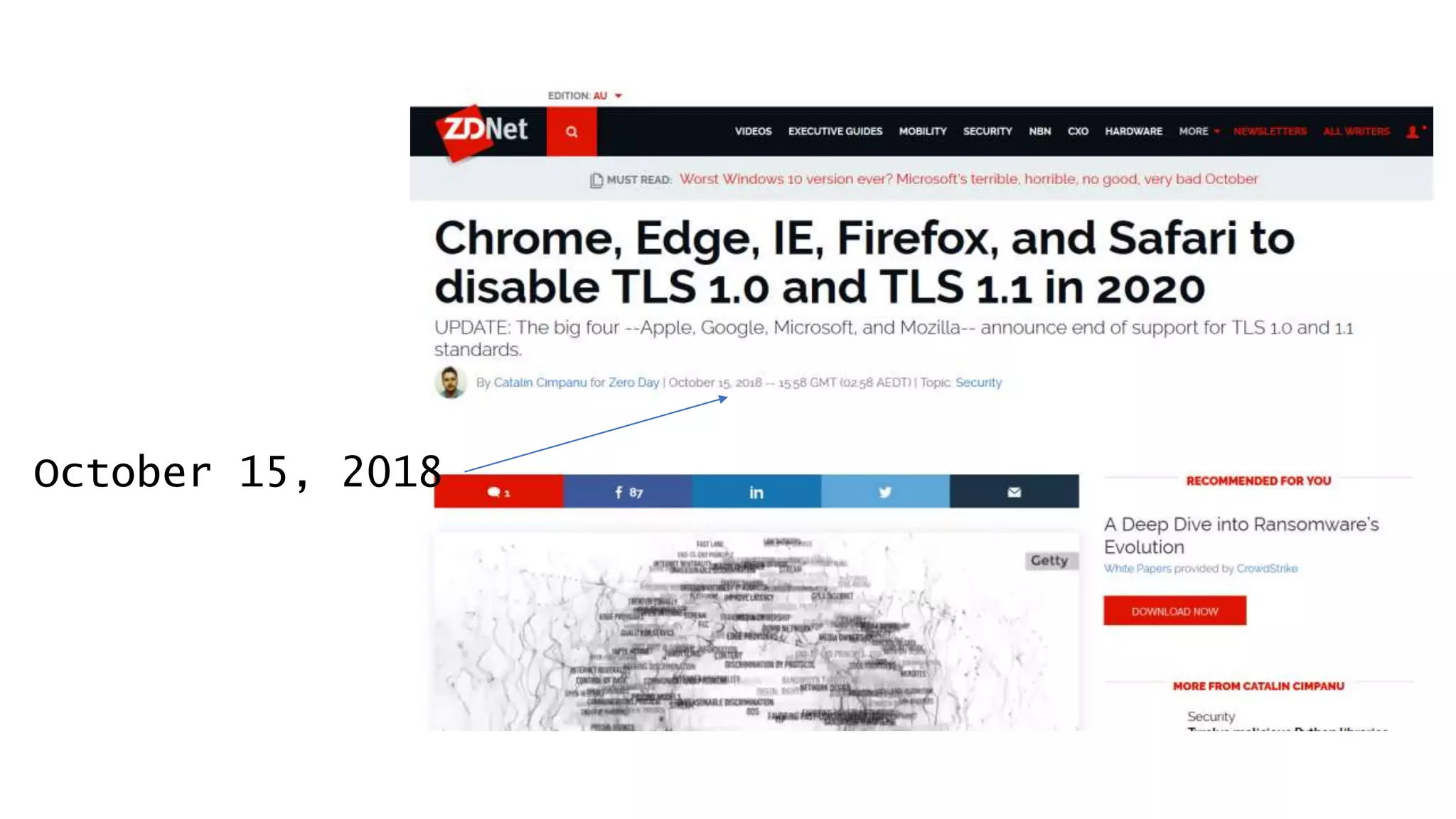
![Today’s Protocols Winners:
• TLS 1.2 [RFC 5246; August 2008]
• TLS 1.3 [RFC 8446; August 2018]
You should:
• Determine TLS version and ciphers actively
used from logs (turn on this logging)
• Turn off the unused legacy protocols](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxconfau2019websecurity2019-190125020312/75/Linux-confau-2019-Web-Security-2019-24-2048.jpg)






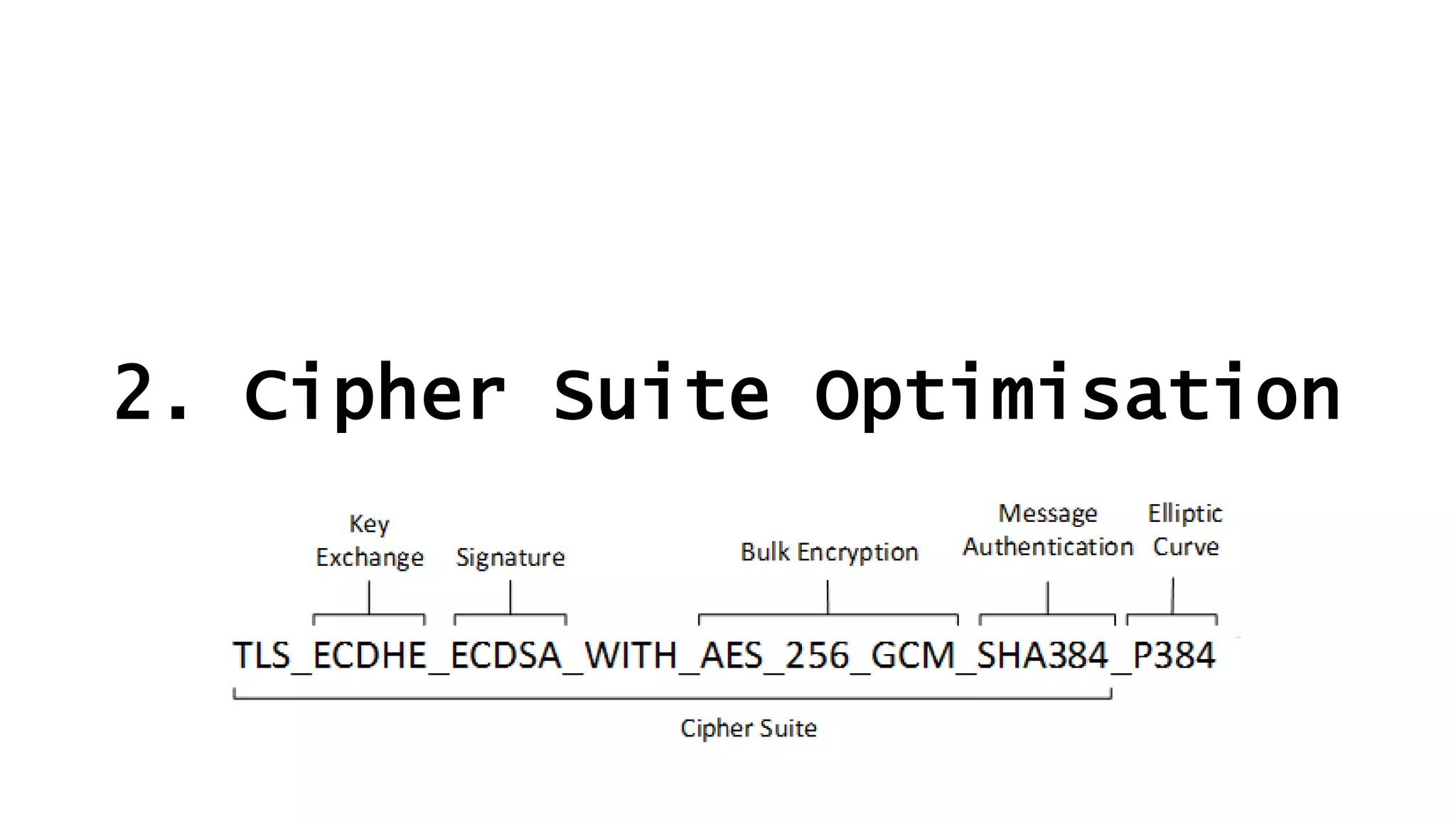
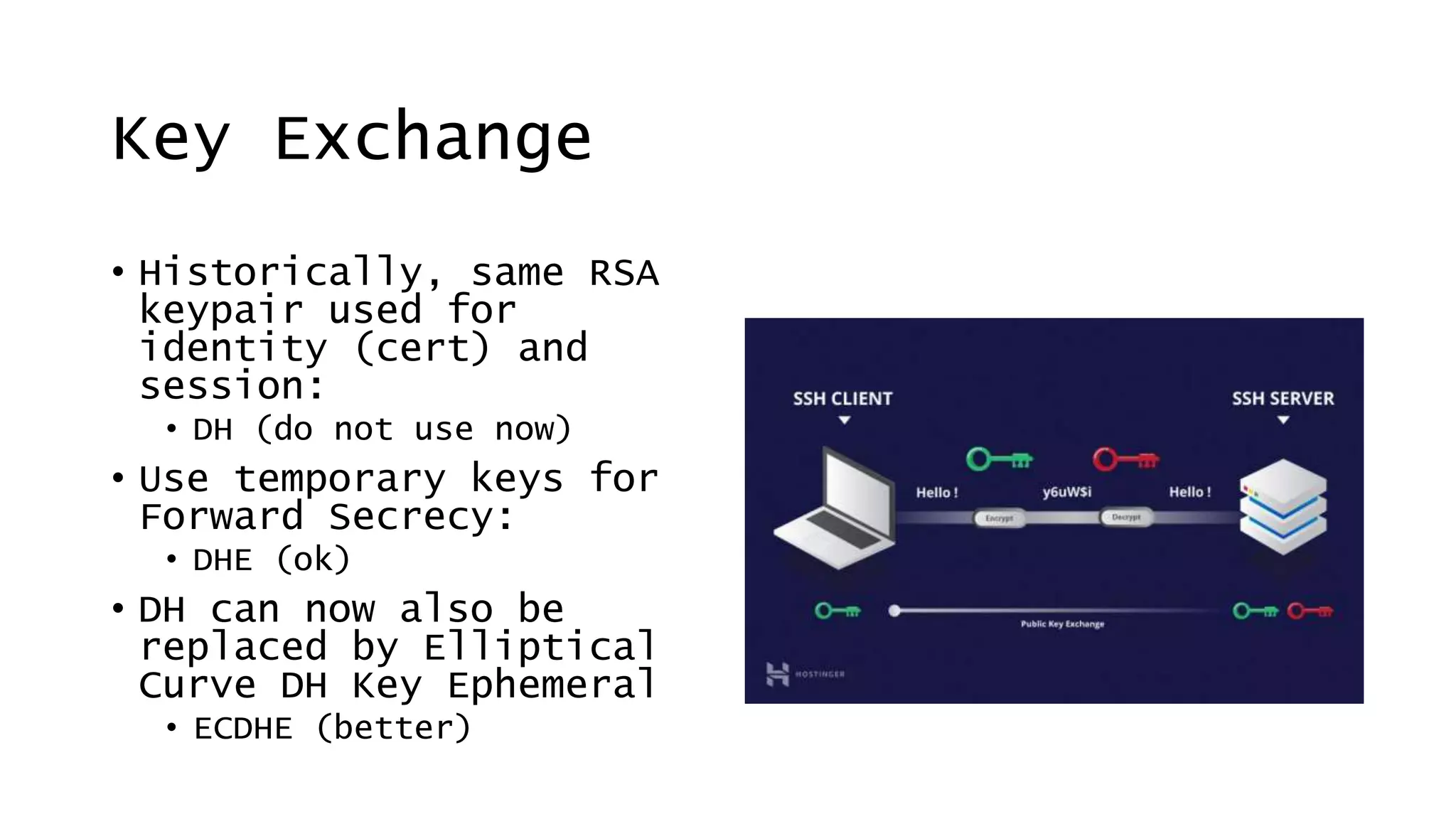

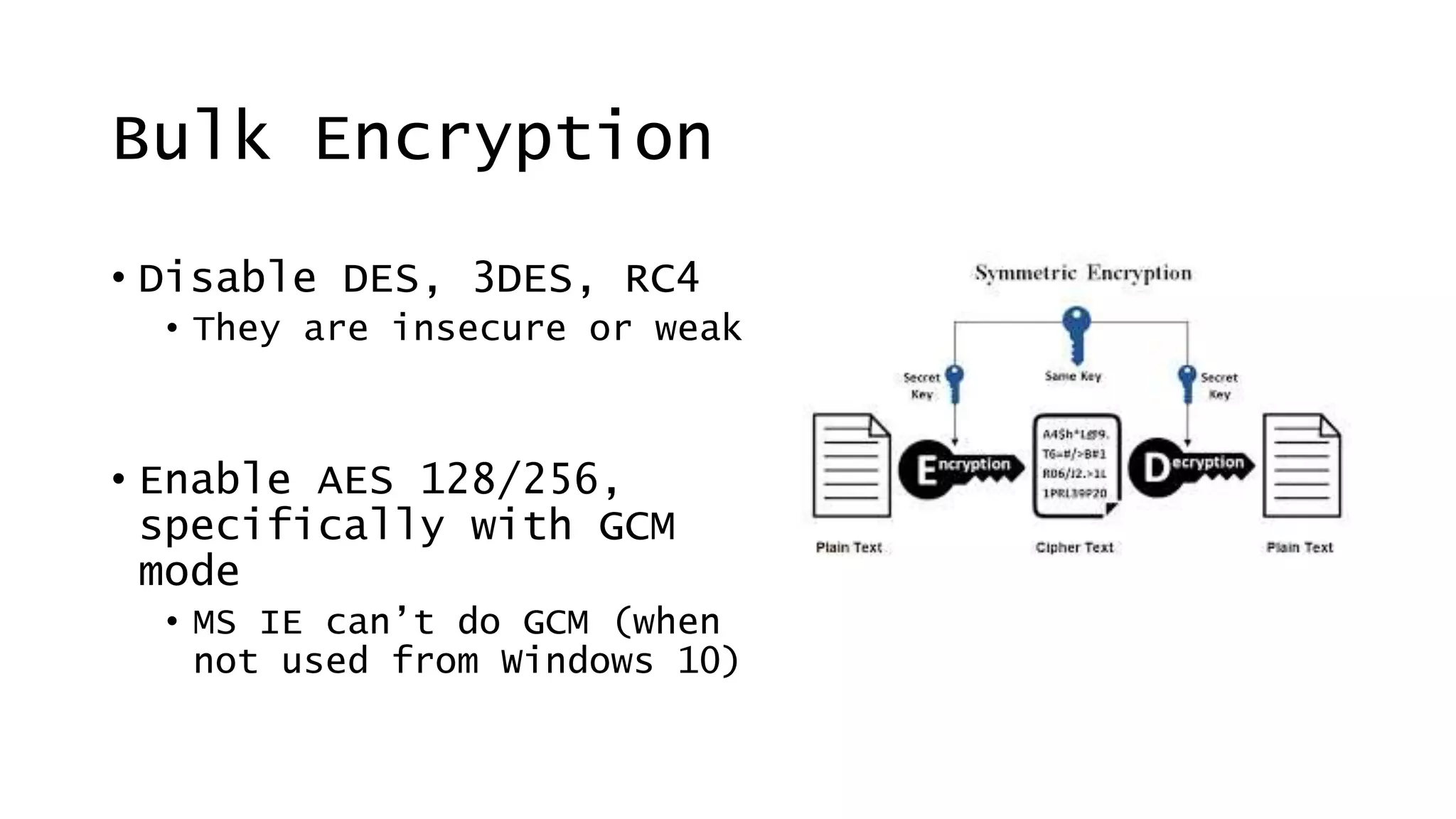














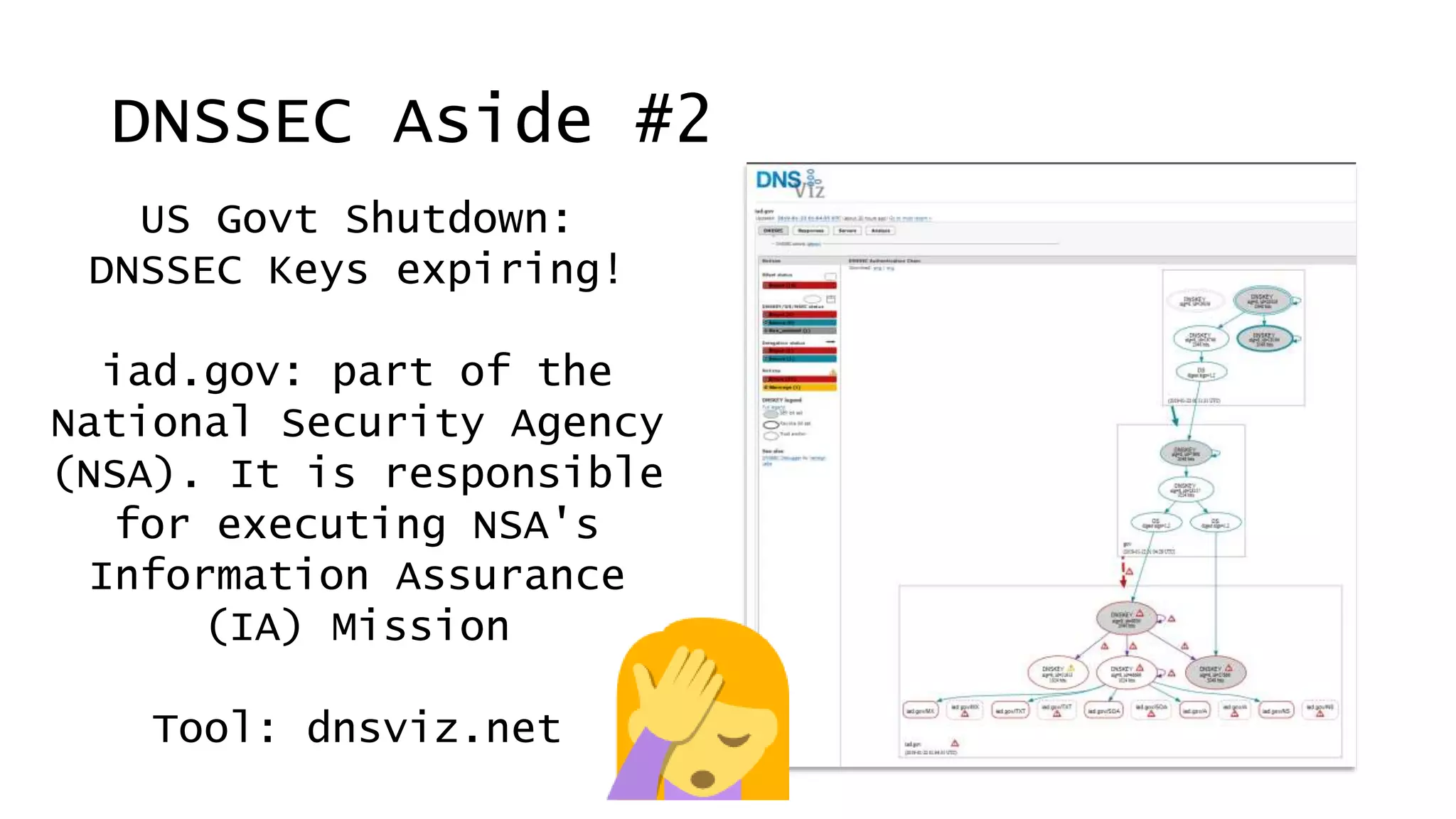
![Don’t mention the lack of DNS Sec on gov.au.
BTW, well done NZ on signing [govt|co|org].nz.
in 2012
6 years ago
DNSSEC Aside #1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxconfau2019websecurity2019-190125020312/75/Linux-confau-2019-Web-Security-2019-56-2048.jpg)

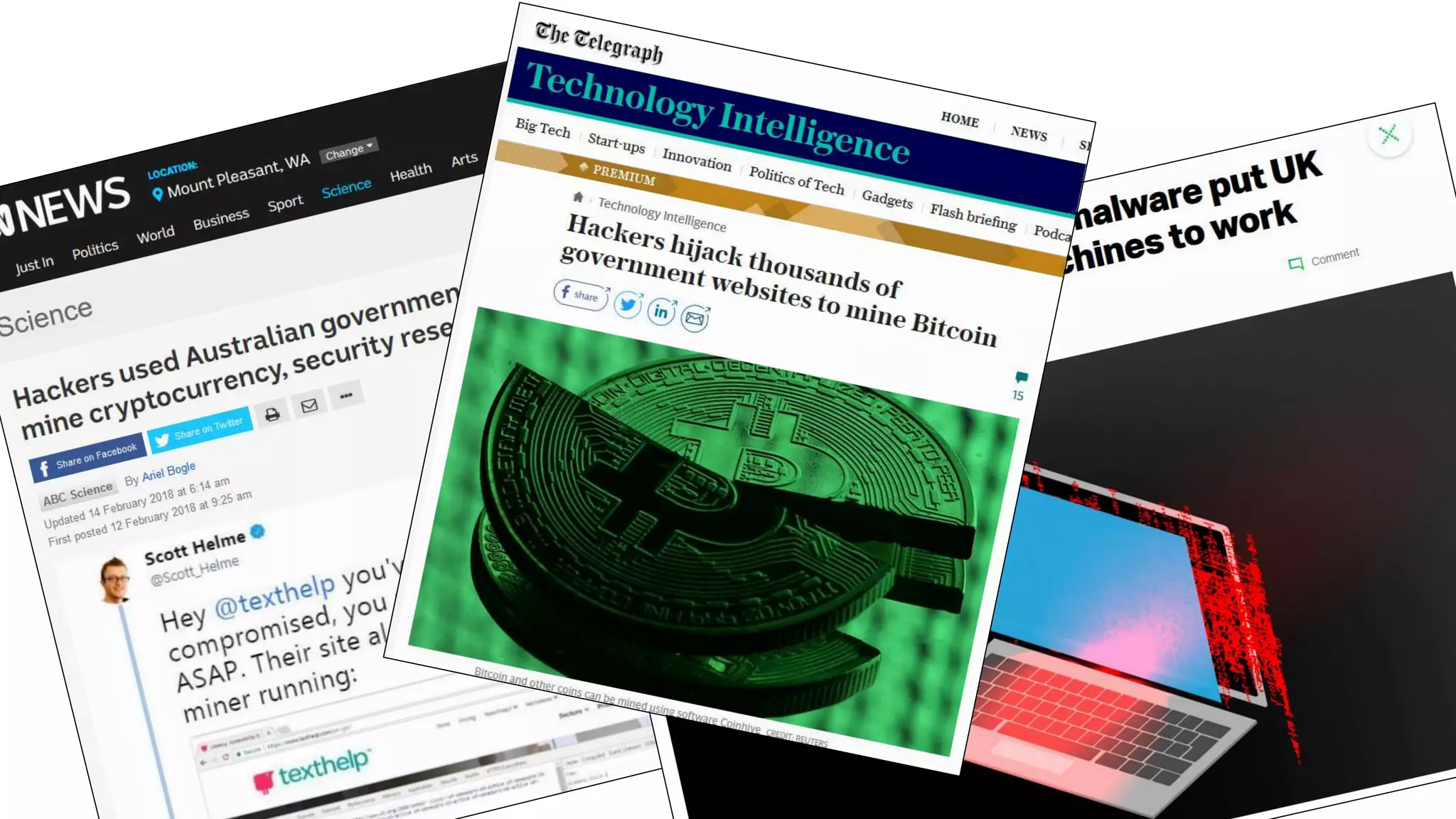















![[US] Emergency Directive 19-01
• Date: Wed 23/Jan/2019
• Reason: Iran takeover of six [6] US govt dept DNS
domains
• Issued by: US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure
Security Agency director Chris Krebs (no, not that
Krebs)
• Actions demanded of US agencies:
1. Audit DNS Records
2. Change DNS Account Passwords
3. Add Multi-Factor Authentication to DNS Accounts
4. Monitor Certificate Transparency Logs
• https://developers.facebook.com/tools/ct/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxconfau2019websecurity2019-190125020312/75/Linux-confau-2019-Web-Security-2019-77-2048.jpg)