The Linux booting process involves 6 main stages:
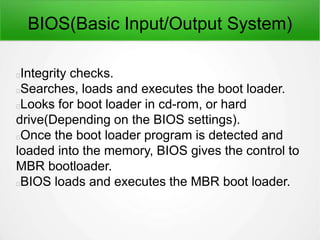
1. BIOS performs integrity checks and loads the MBR bootloader.
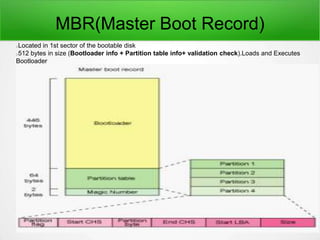
2. The MBR bootloader loads the Linux bootloader (GRUB).
3. GRUB loads and initializes the Linux kernel.
4. The kernel initializes memory and hardware before starting init.
5. Init reads /etc/inittab to determine the default runlevel and starts programs to launch that runlevel.
6. Each runlevel directory (/etc/rc.d/rc#.d/) contains programs starting with S and K that control services for that runlevel.