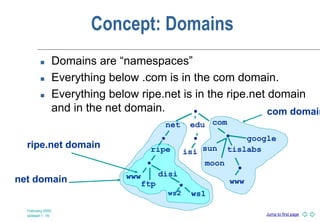
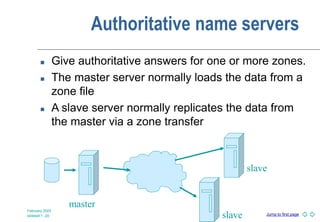
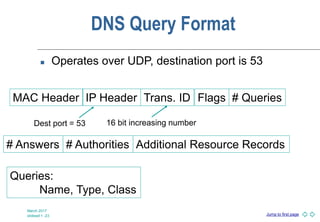
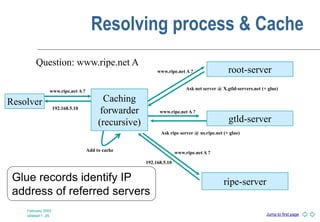
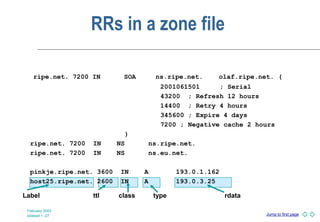
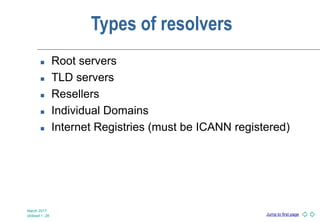
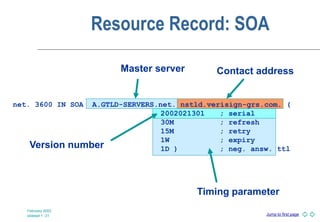
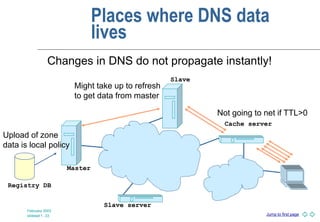
DNS is a globally distributed naming system that translates domain names to IP addresses. It consists of a hierarchical namespace, servers that store information in the namespace, and resolvers that query servers to translate names to addresses. The root servers contain information on top-level domains, which then delegate authority to other name servers lower in the hierarchy. Resource records containing information like IP addresses and name servers are distributed across authoritative name servers for each domain.