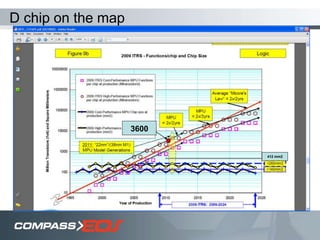
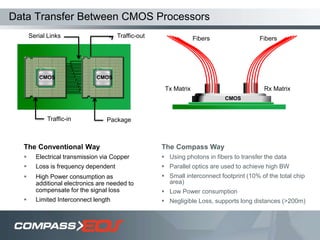
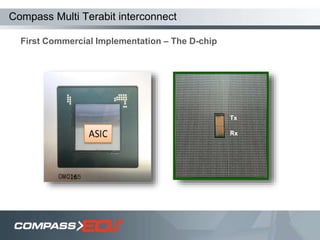
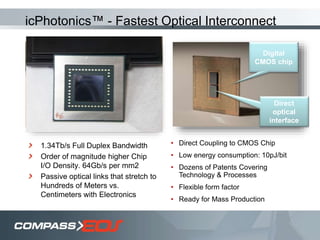
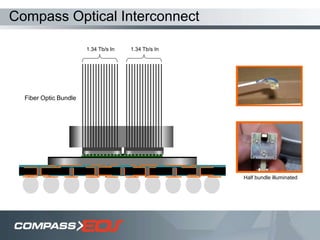
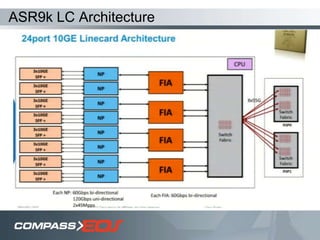
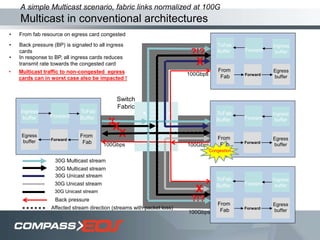
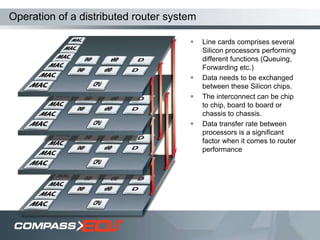
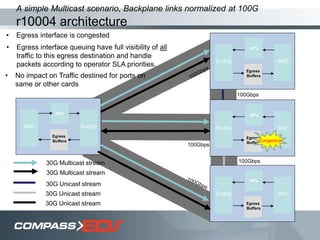
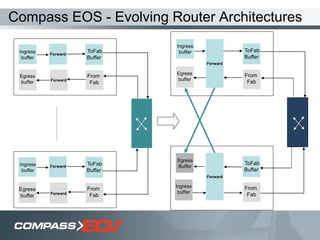
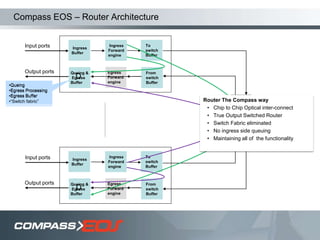
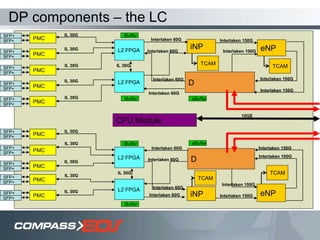
The document discusses optical interconnect technology for routers. It describes how conventional copper interconnects have limitations like power consumption and distance, while optical interconnects using fibers can transfer data over longer distances with lower power. The D-chip is presented as the first commercial router product using optical interconnect between silicon chips. It provides over 1 terabit per second bandwidth density and can scale to support future networking needs. The document also outlines how an output queued router architecture using optical interconnects between line cards improves performance for multicast traffic compared to a conventional router design.