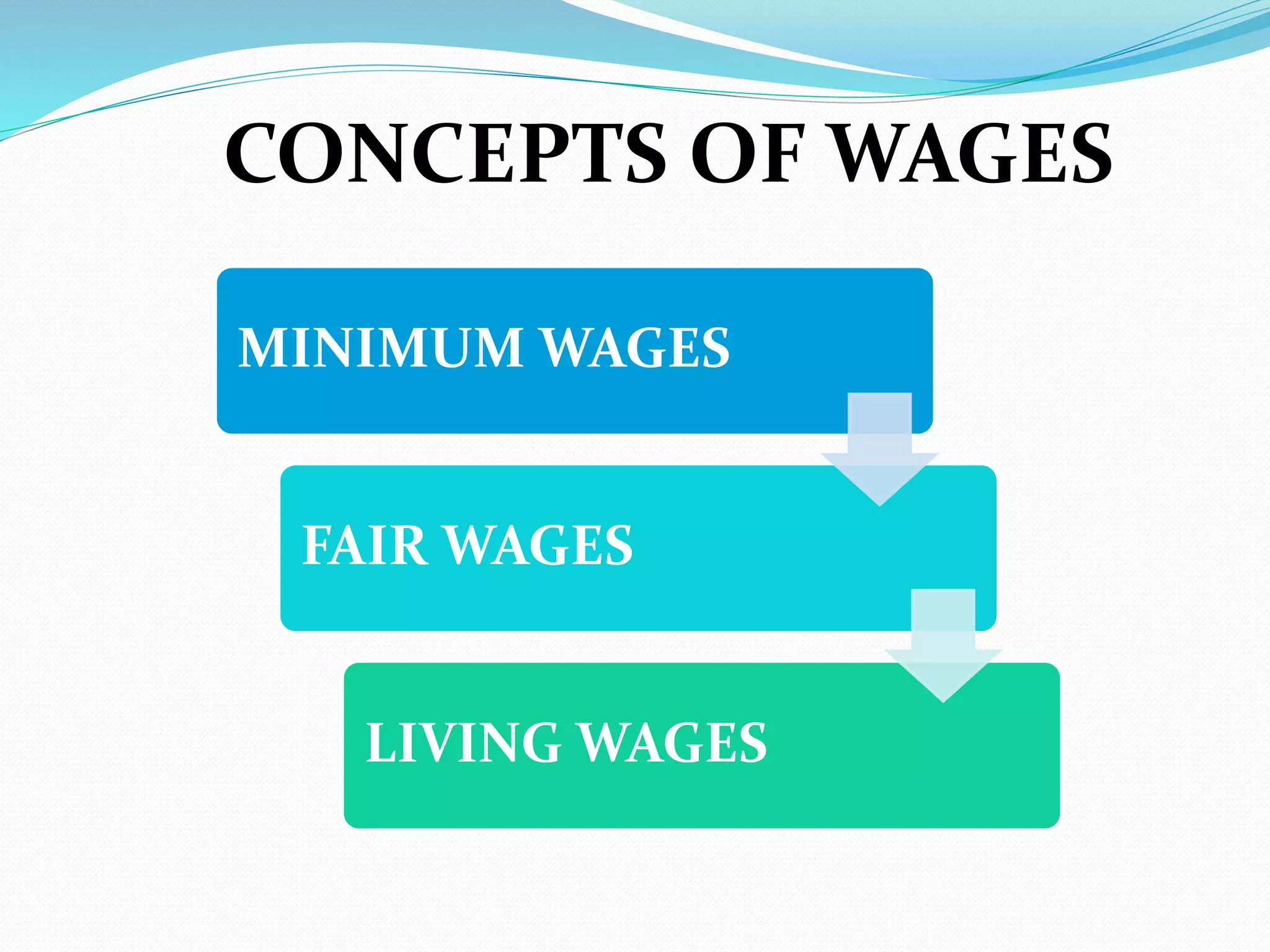
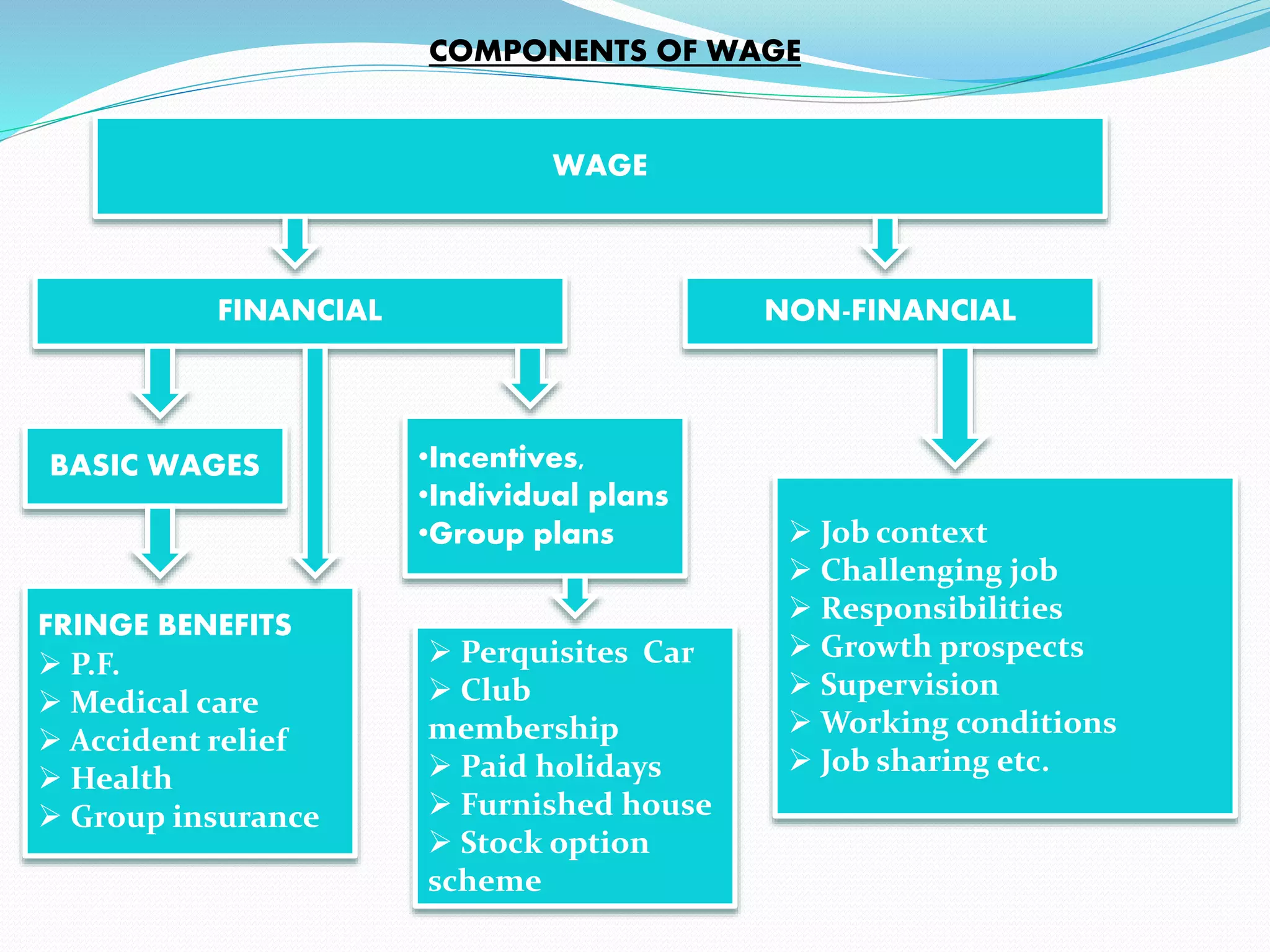
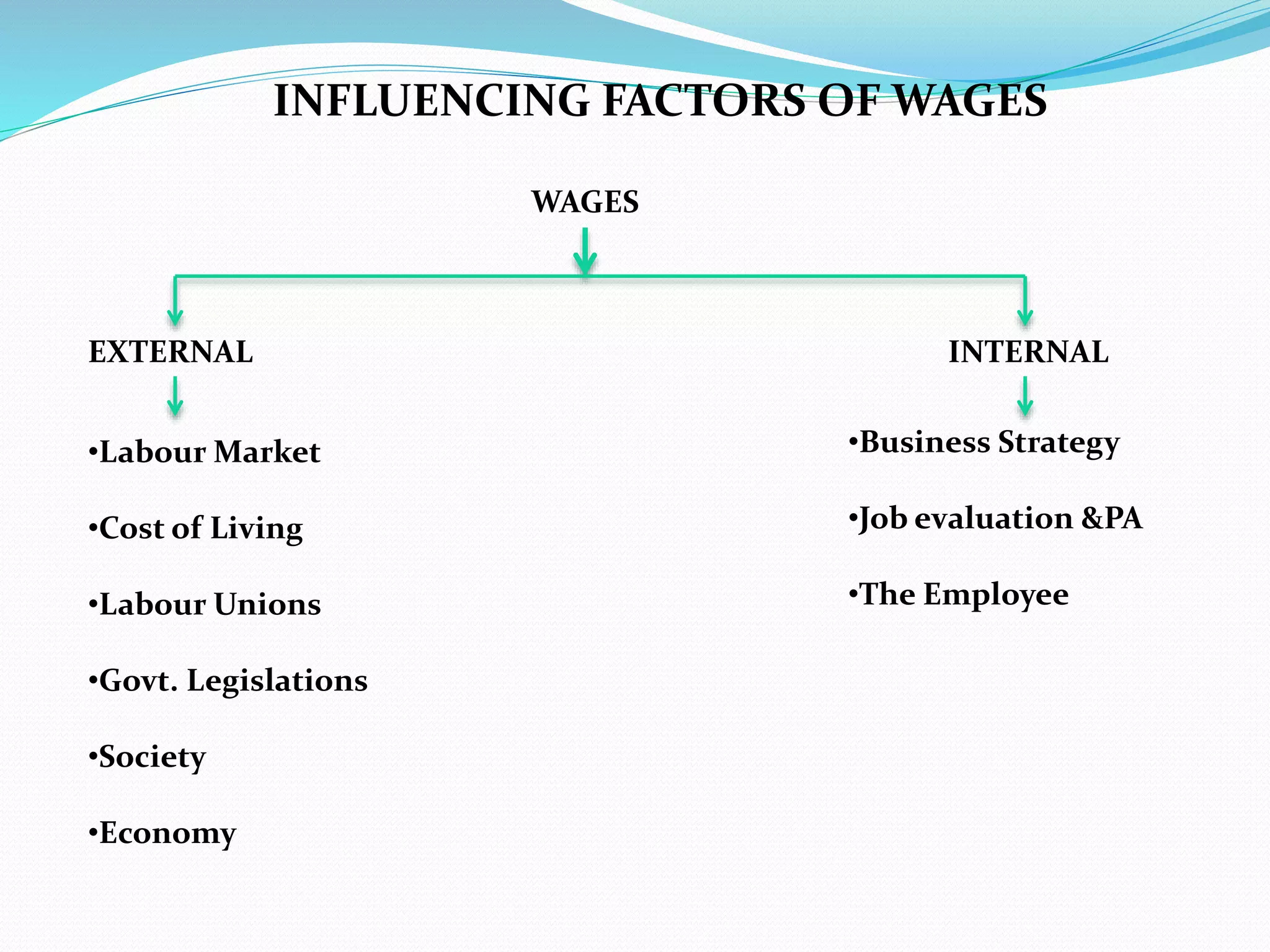
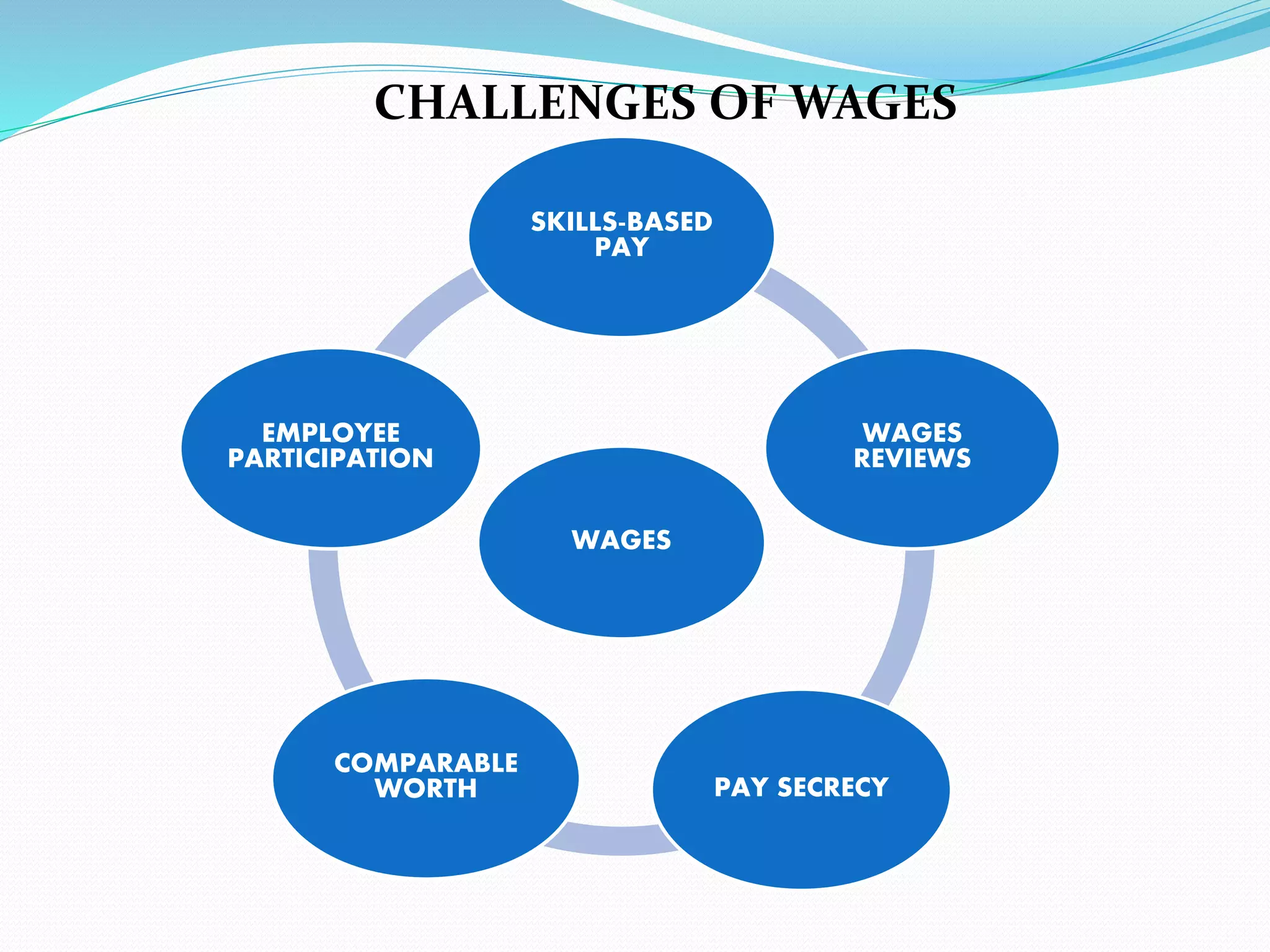
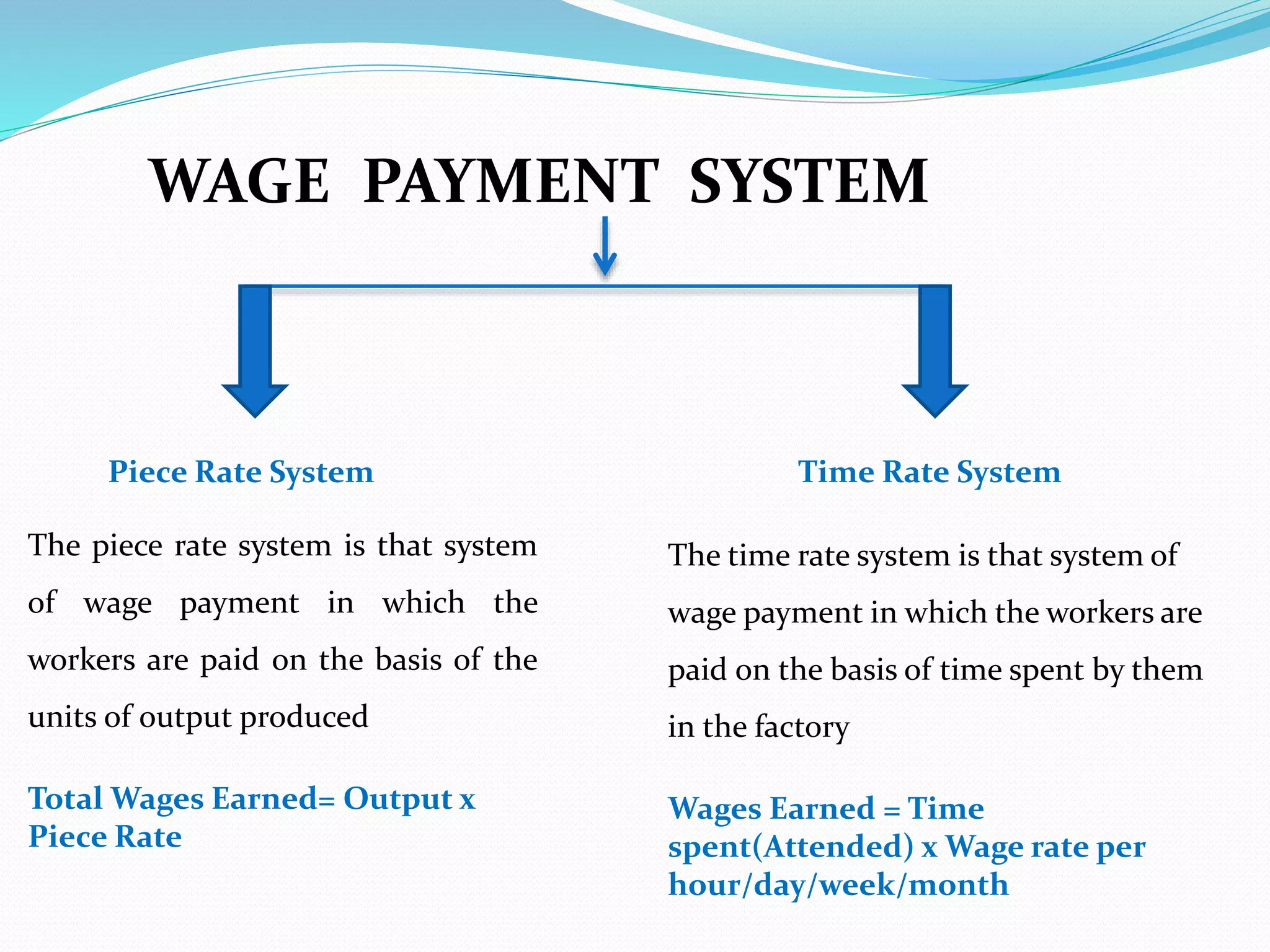
This document discusses factors to consider when formulating a wage policy. It covers definitions of key wage concepts like minimum wage, living wage, and fair wage. It also outlines influences on wages like the labor market, cost of living, unions, and government legislation. The objectives of wage administration include recruiting employees, controlling payroll costs, motivating performance, and maintaining fair wage standards. Wage policies aim to guide wage structures and determine relative shares for workers, management, and other stakeholders in an industry or economy.