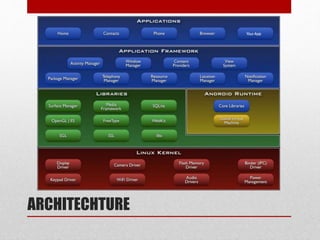
This document provides an overview of the Android operating system. It discusses that Android is a Linux-based OS designed for touchscreen mobile devices. It then describes the different versions of Android, the layered architecture including the Linux kernel, application framework, libraries, and applications. It also briefly discusses Android's memory management, security and privacy features, and potential future developments beyond smartphones and tablets.