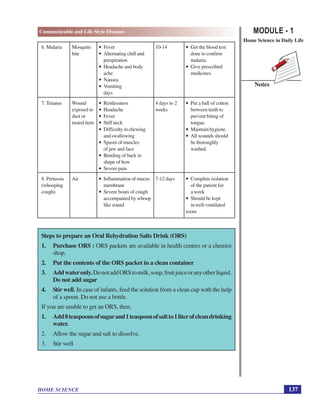
This document discusses communicable and lifestyle diseases. It defines communicable diseases as those that spread from one person to another through contact, air, food, water or insects. Examples include influenza, tuberculosis, and sexually transmitted infections. Lifestyle diseases do not spread between people but rather develop due to faulty habits like obesity, diabetes, and hypertension. The document outlines the causes and symptoms of communicable diseases and measures to prevent their spread, such as hand washing, vaccination, and avoiding crowded places when sick.