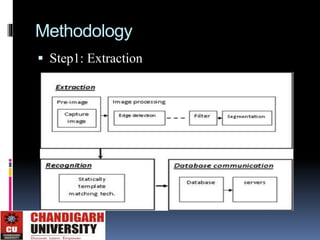
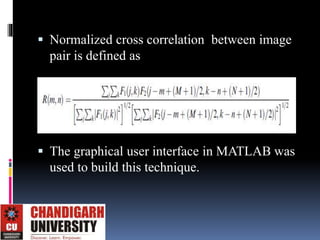
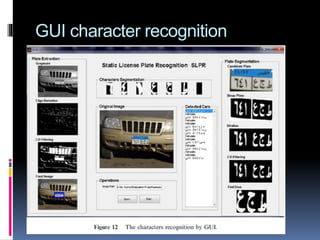
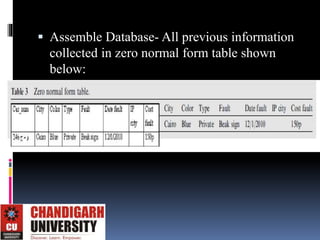
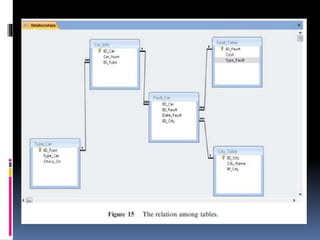
This document describes an automated license plate recognition system developed for Egypt. The system uses image processing techniques to extract license plates from images, recognizes the characters on the plates, and communicates with a database. It consists of three main parts: plate extraction, character recognition, and database communication. The system was tested on 100 plates and achieved a 91% accuracy rate. Future work could improve the system's ability to handle motion blurred or overlapped plates.