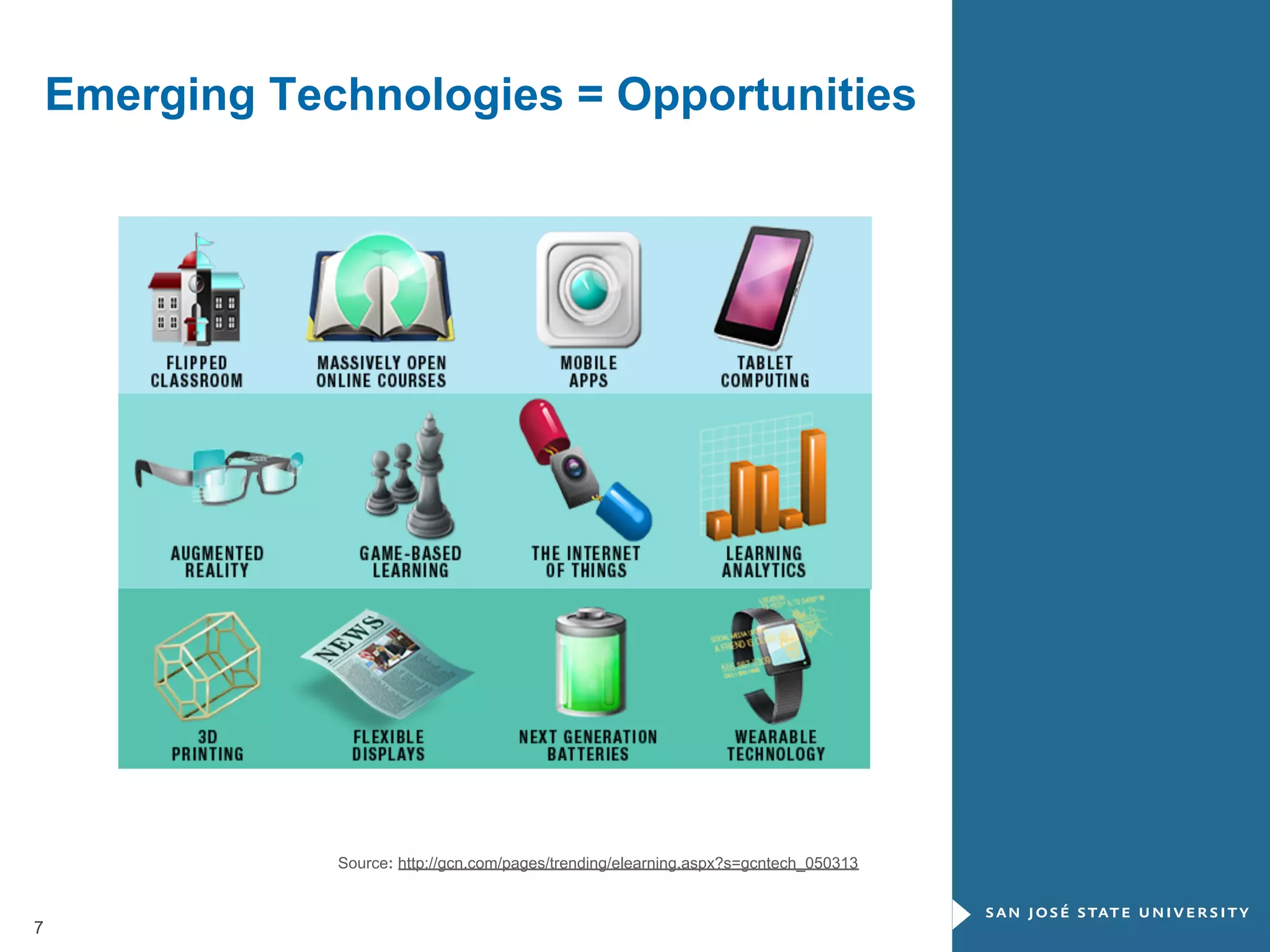
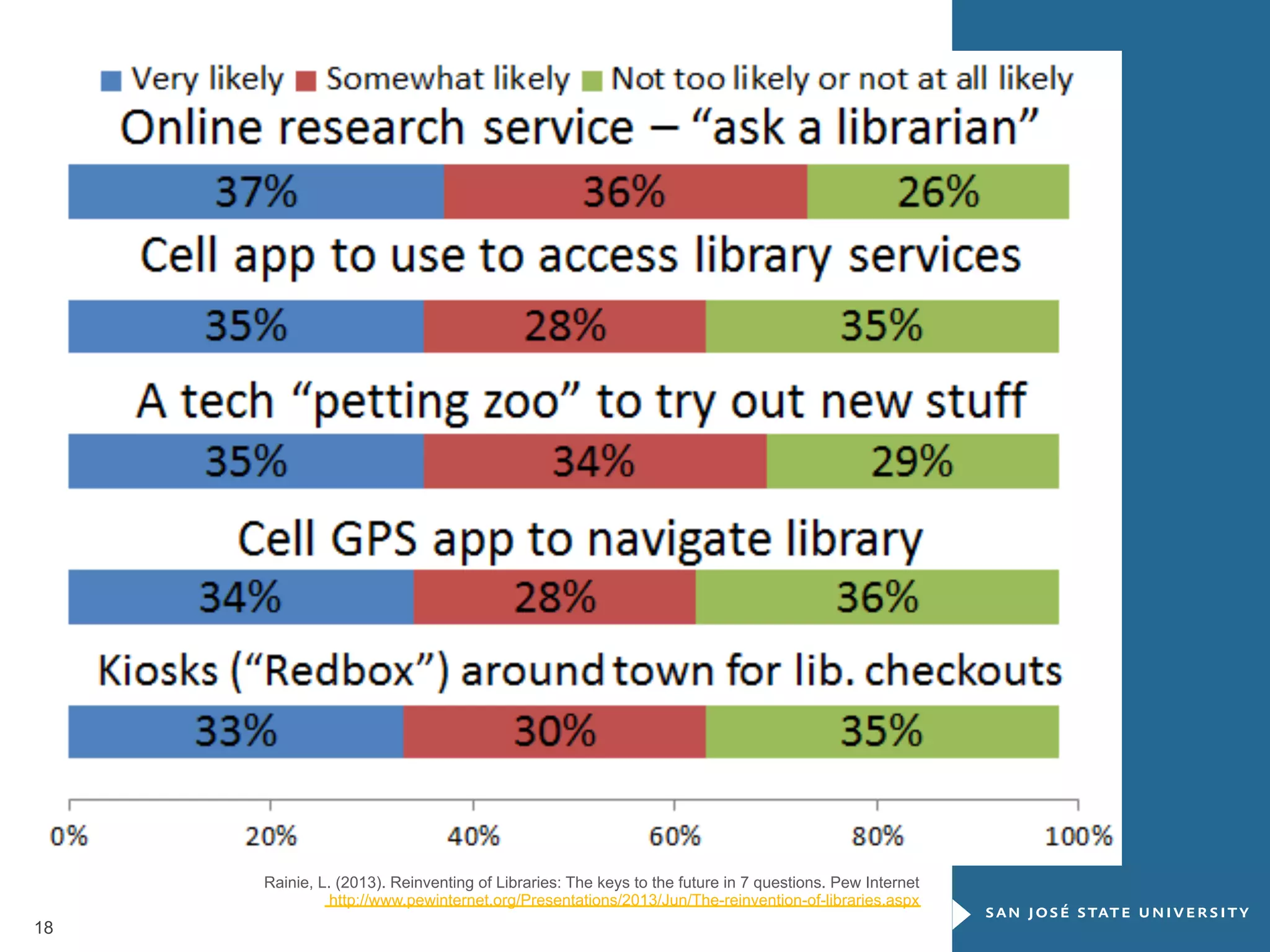
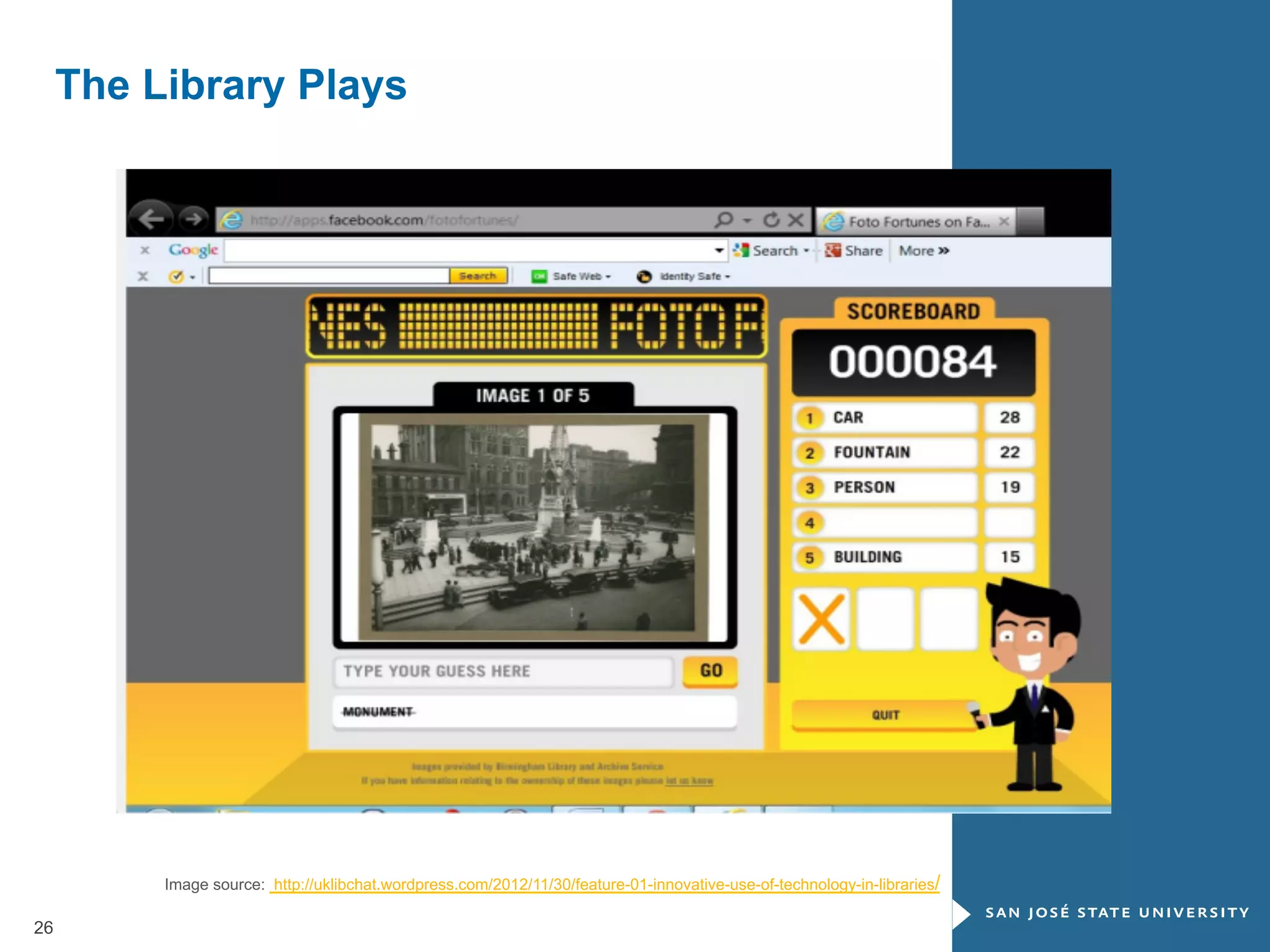
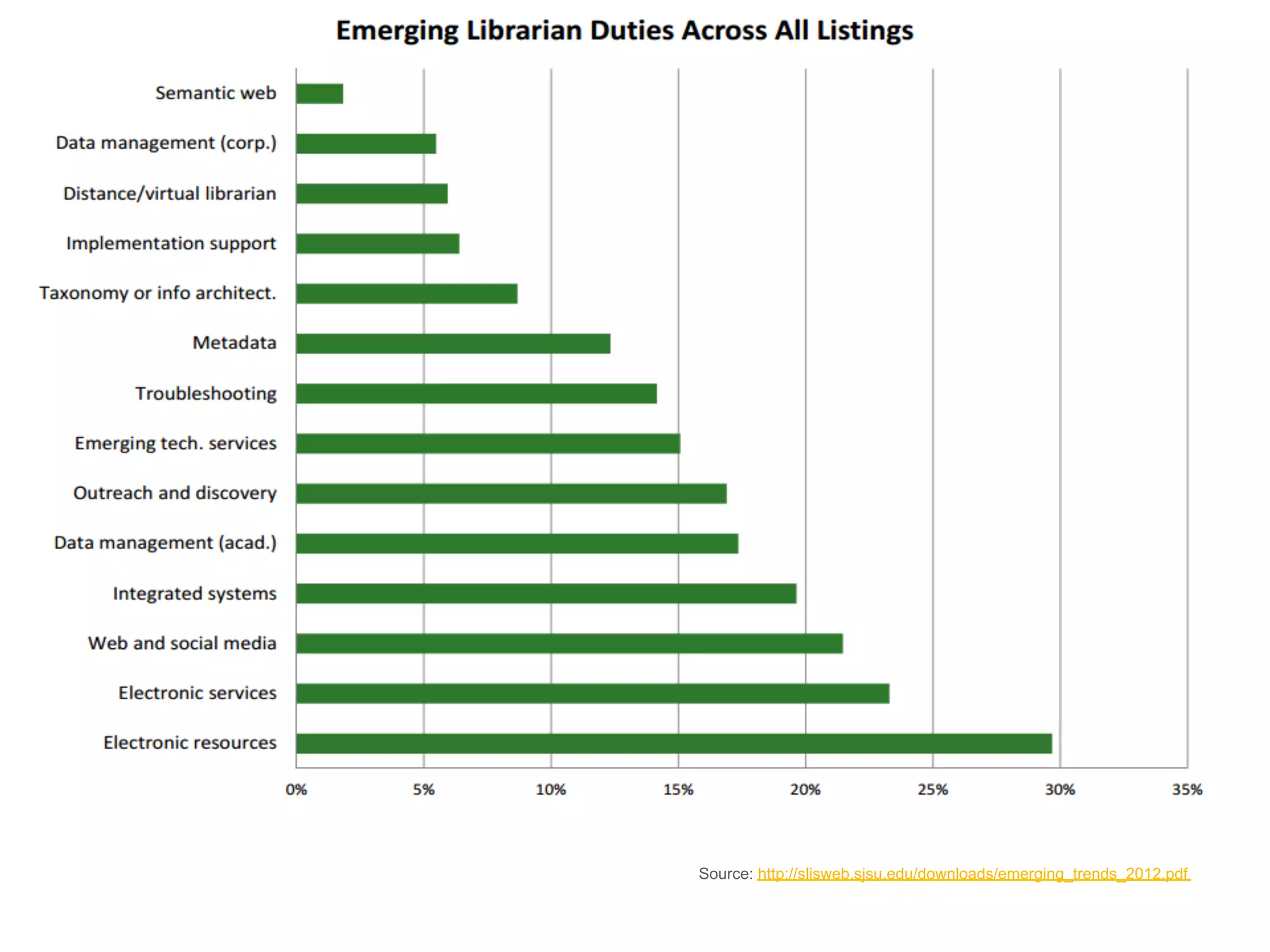
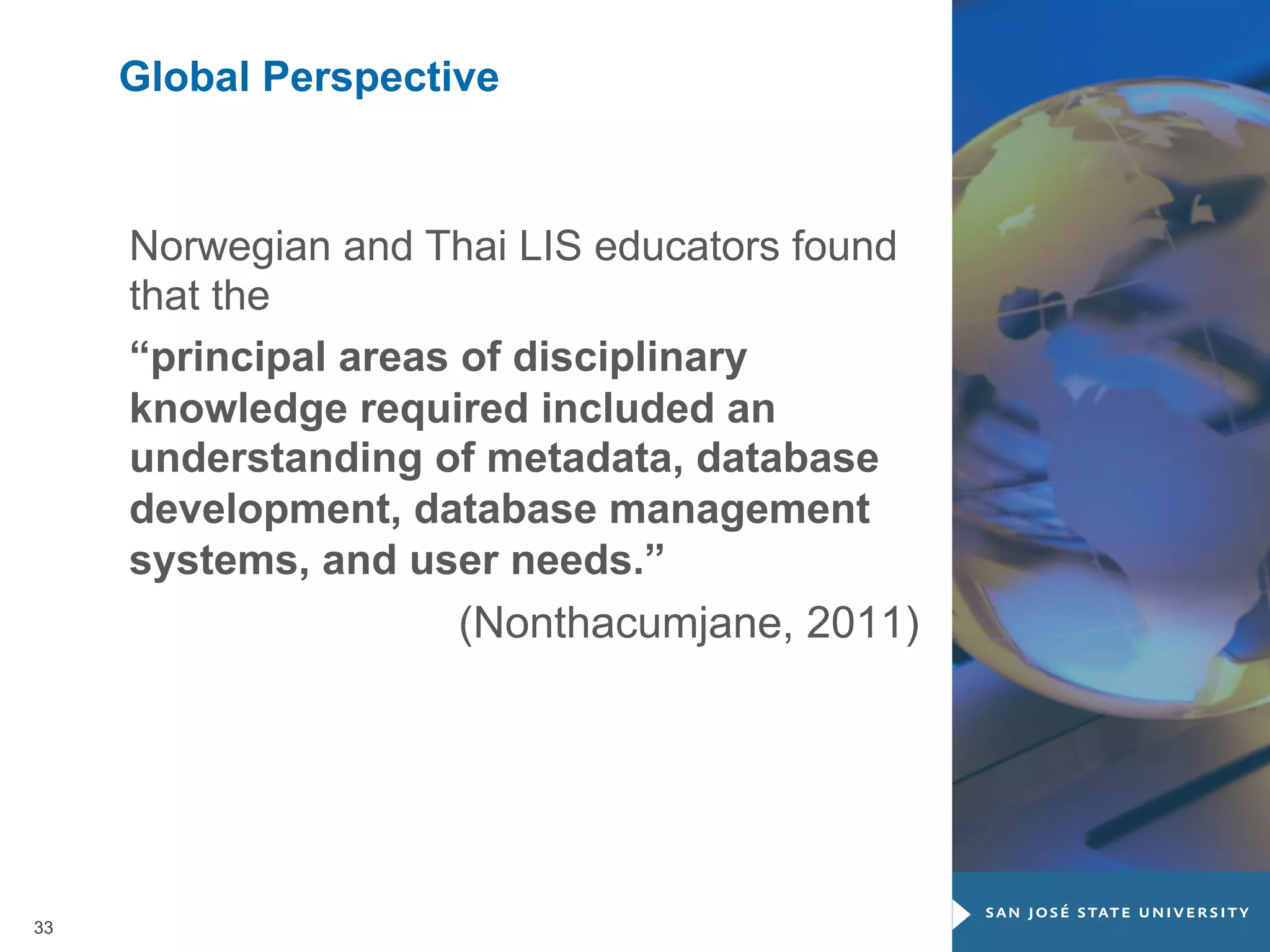
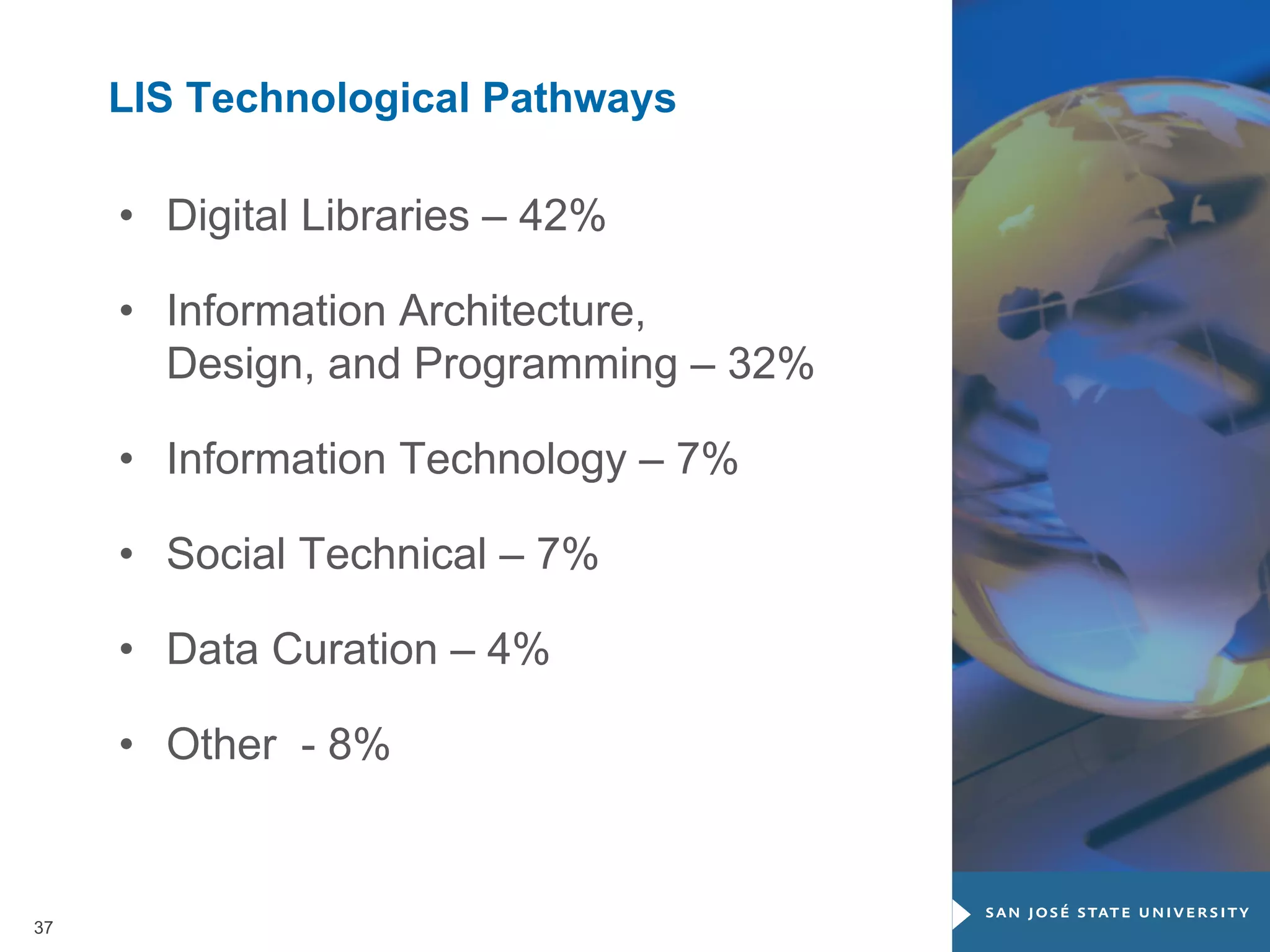
The document outlines the transformative impact of global digital trends on libraries and library science education, highlighting five key trends including democratization of learning and redefined privacy boundaries. It emphasizes the evolving roles of libraries and library professionals, who must adapt to new technologies and develop competencies in areas such as data management and digital content. The necessity for effective communication and a passion for continuous learning is also stressed as essential for future professionals in the library and information science field.