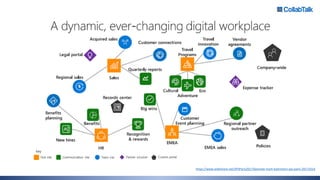
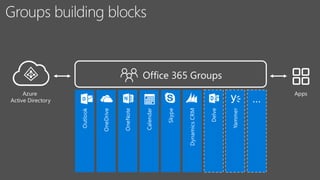
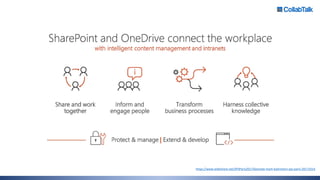
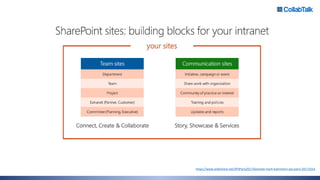
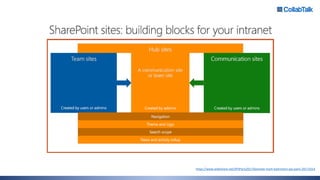
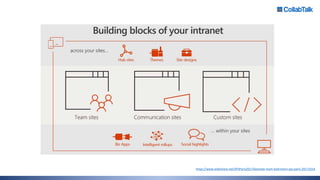
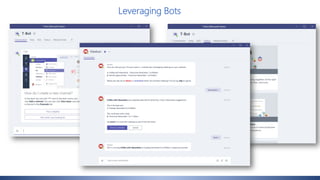
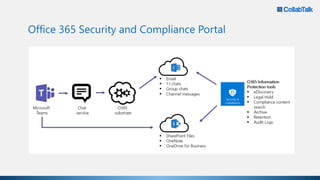
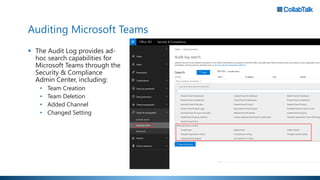
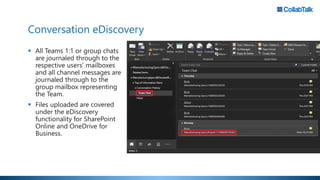
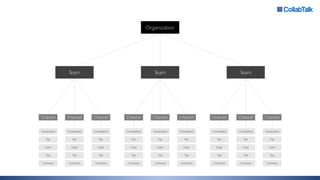
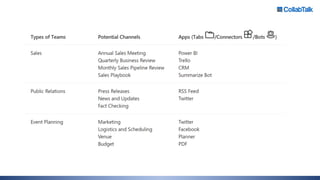
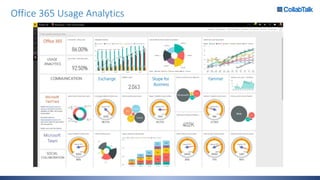
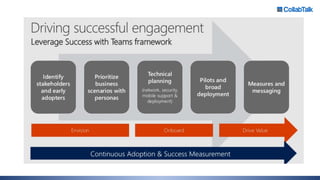
Christian Buckley, founder/CEO of CollabTalk LLC and Microsoft MVP, emphasizes that successful adoption of Microsoft Teams demands a cultural shift within organizations. Various profiles of employees illustrate differing communication styles and needs that must be considered when adopting this collaborative platform. Additionally, the document discusses governance, administration, and best practices for using Microsoft Teams and Office 365 for compliance and efficiency.