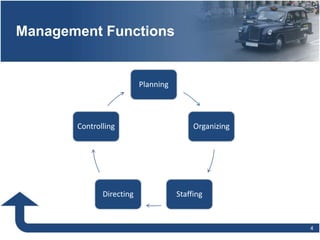
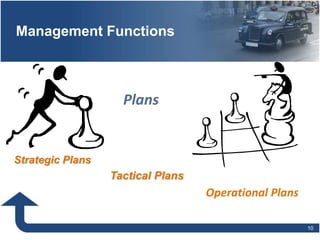
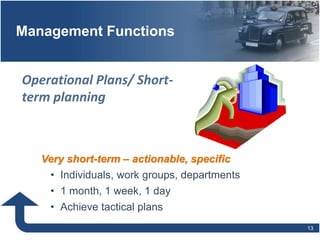
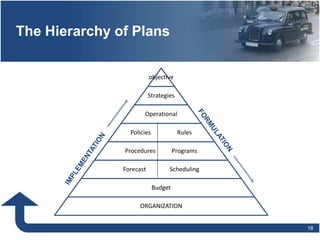
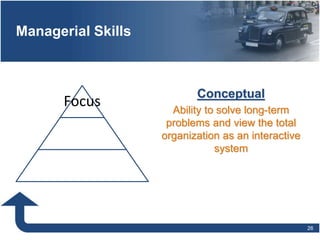
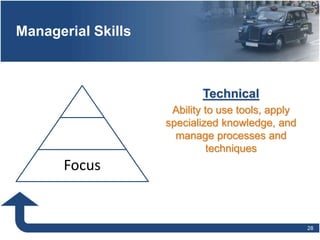
Management involves planning, organizing, directing, and controlling organizational resources to achieve goals efficiently and effectively. The main functions of management are planning, organizing, staffing, directing, and controlling. Planning establishes objectives and strategies, organizing determines how work is grouped and resources allocated, staffing involves hiring and training employees, directing oversees activities and leads people, and controlling monitors progress and ensures goals are met. Effective management requires conceptual, technical, and human relations skills to coordinate resources and activities within an organization.