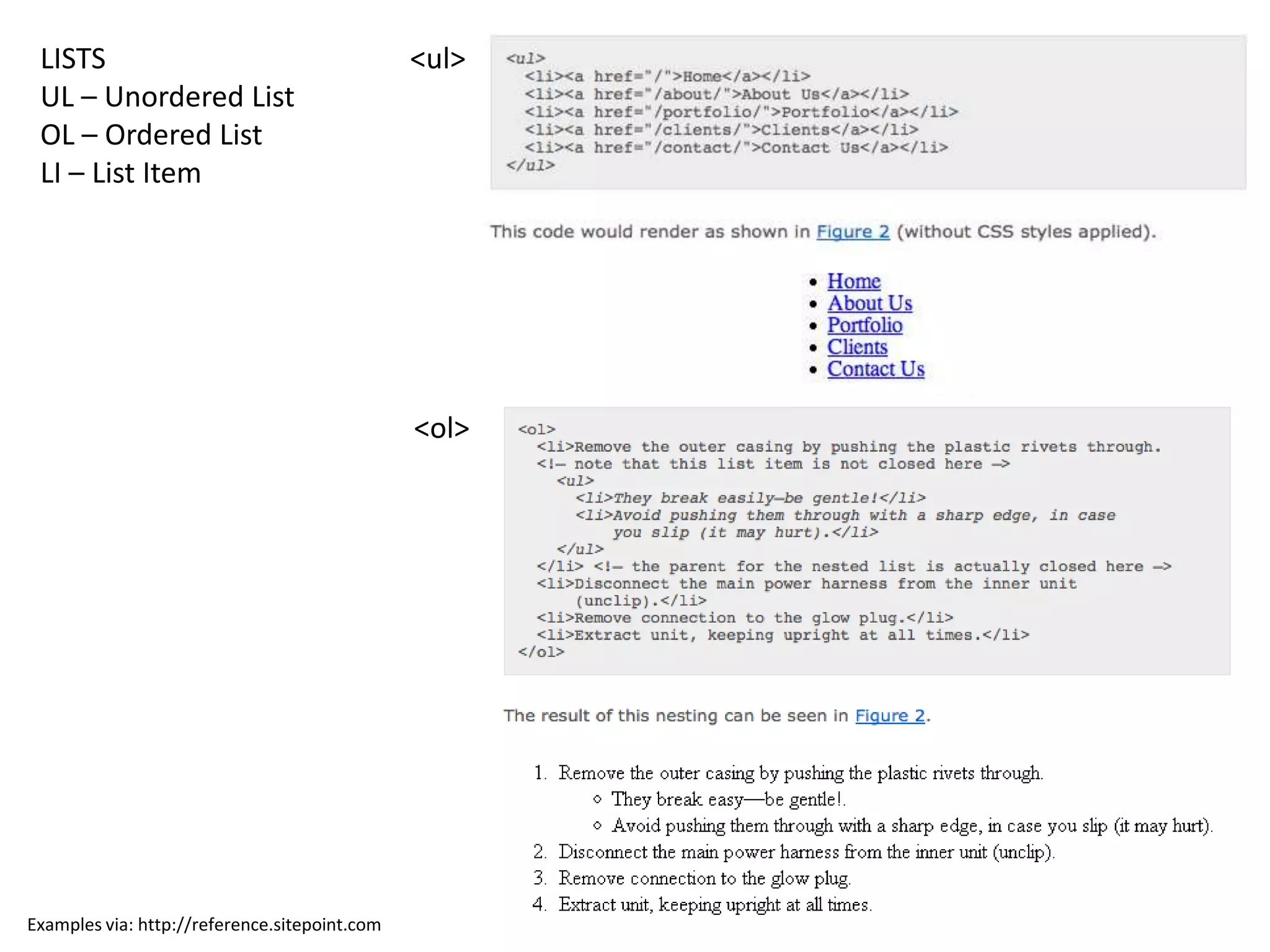
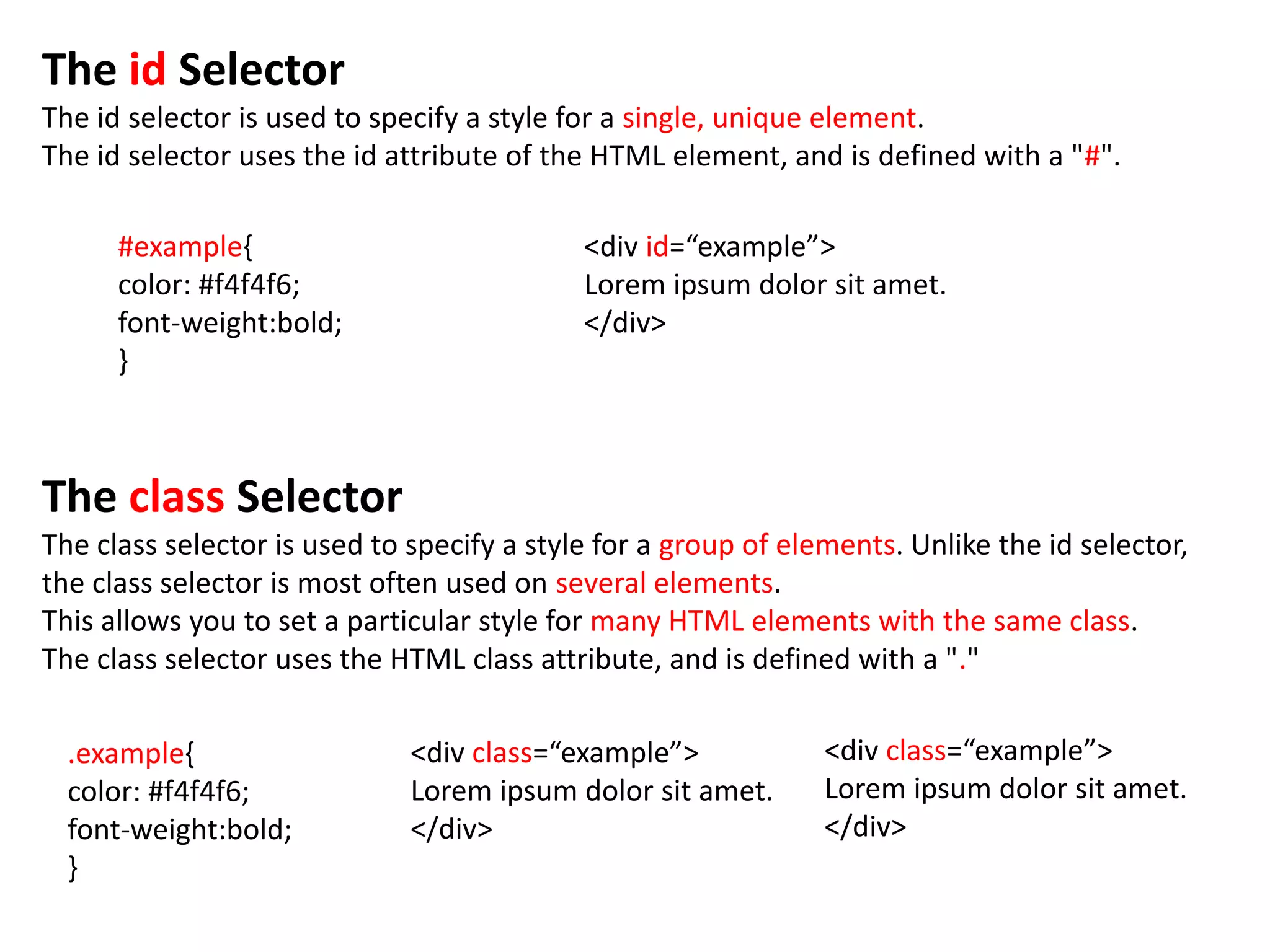
The document discusses various CSS properties including lists, selectors like id and class, display types, positioning, float, and clear. It provides examples of how to use ul, ol, and li elements to create lists. It also demonstrates using id and class selectors to style specific elements or groups of elements. Common display types like block and inline are defined. Positioning options like relative, absolute, and their use of properties like top and left are outlined. The float property is described for shifting elements left or right, and clear is used to avoid elements flowing around floated items.