This chapter summary covers CSS concepts including the box model, margin, padding, floats, positioning, and layouts. Key points covered include:
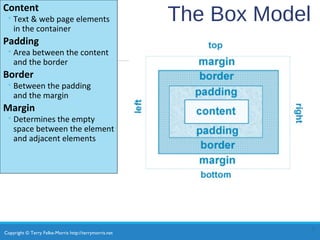
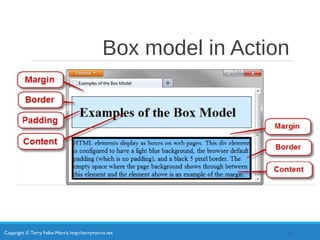
- The box model consists of content, padding, border, and margin areas.
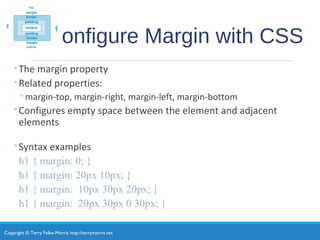
- Margin and padding properties configure spacing around elements.
- The float property positions elements side-by-side, and clear terminates floats.
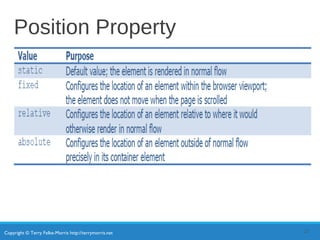
- Positioning includes normal, relative, absolute, and fixed positioning.
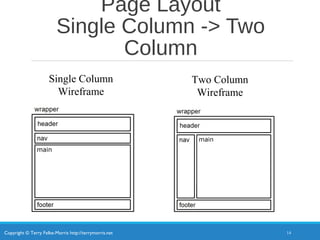
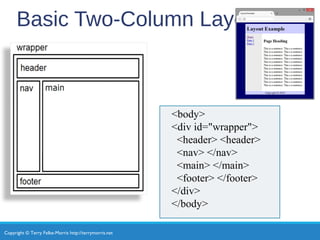
- CSS can create multi-column page layouts including a basic two-column layout.
- Pseudo-classes like hover and link modify anchor element styles during user interactions.
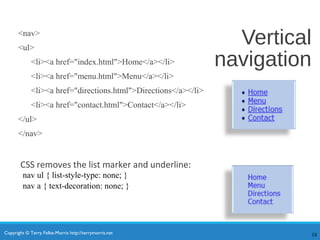
- HTML5 elements like header, nav, main, and aside add






















![Copyright © Terry Felke-Morris http://terrymorris.net
HTML5 Compatibility with
Older BrowsersCSS
header, main, nav, footer, section, article,
figure, figcaption, aside { display: block; }
HTML5 Shim (aka HTML5 Shiv)
<!--[if lt IE 9]>
<script src=" http://html5shim.googlecode.com/svn/trunk/html5.js">
</script>
<![endif]-->
30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter6-170108213052/85/Chapter6-30-320.jpg)