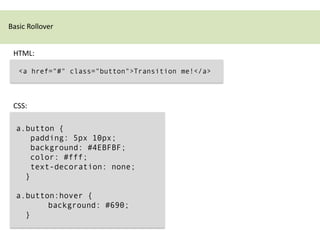
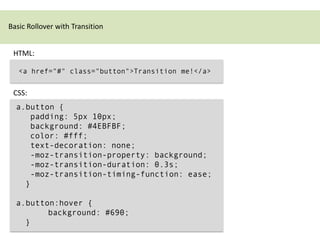
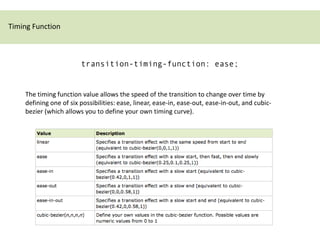
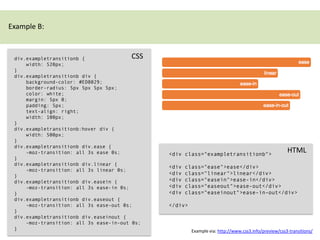
CSS3 transitions allow property values to change smoothly over time during transitions triggered by events like hover or focus. They are defined using transition properties like transition-property, transition-duration, and transition-timing-function. Multiple properties can transition at once or the shorthand "all" can be used. Transition timing functions like ease allow the transition speed to change over its duration. Browser prefixes like -webkit are needed for compatibility. Transitions are useful for hover effects and other interactive transitions.