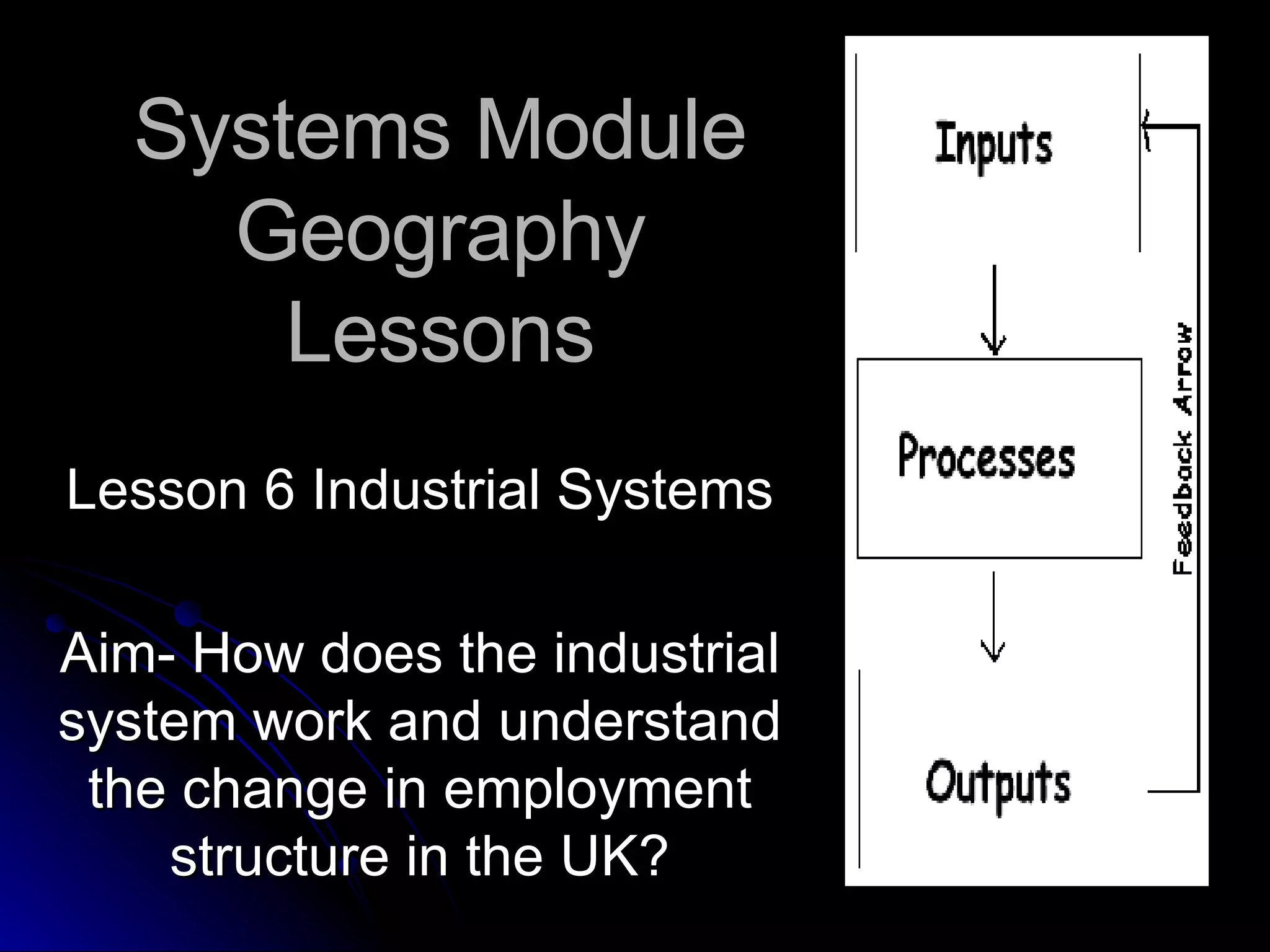
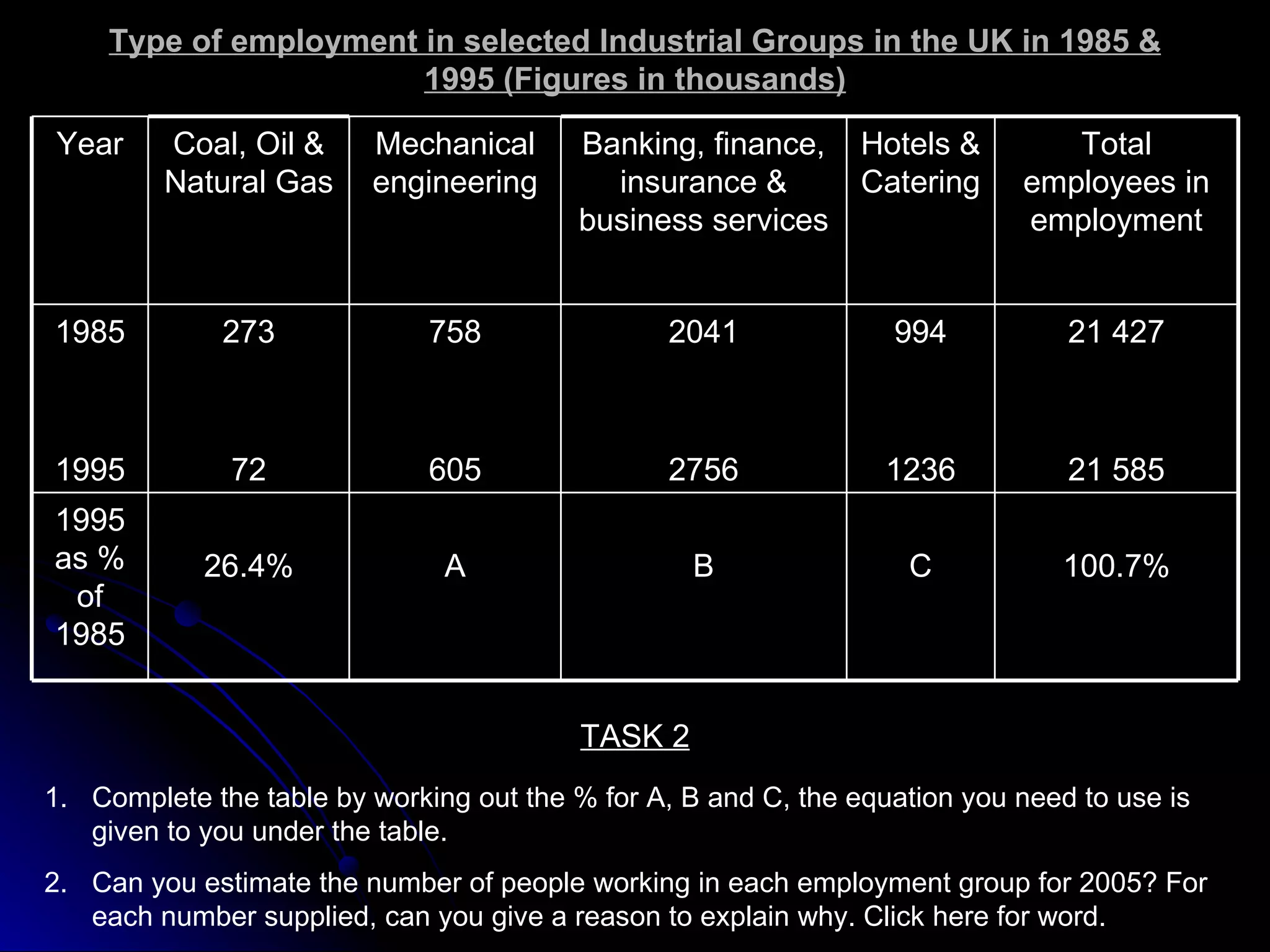
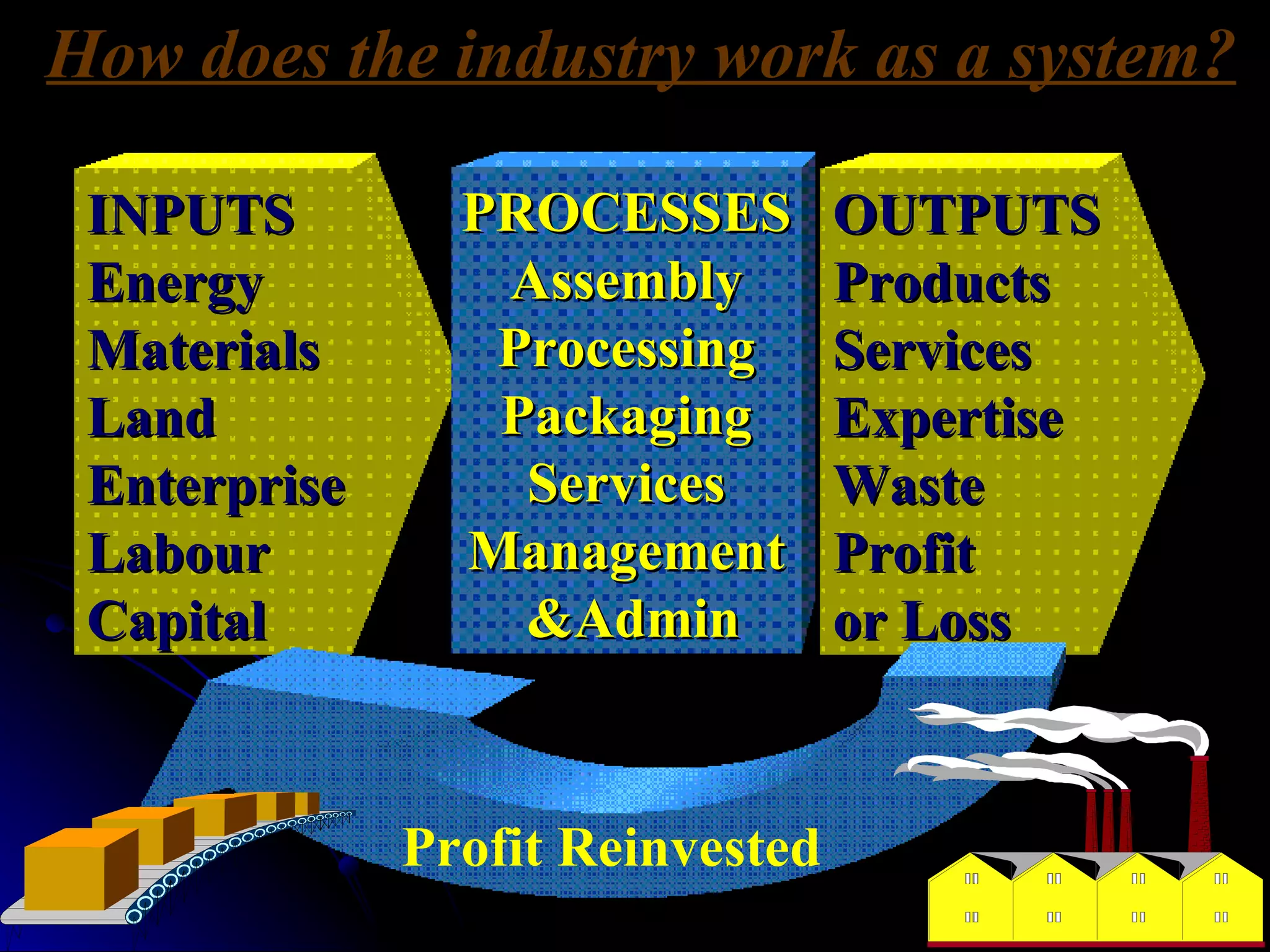
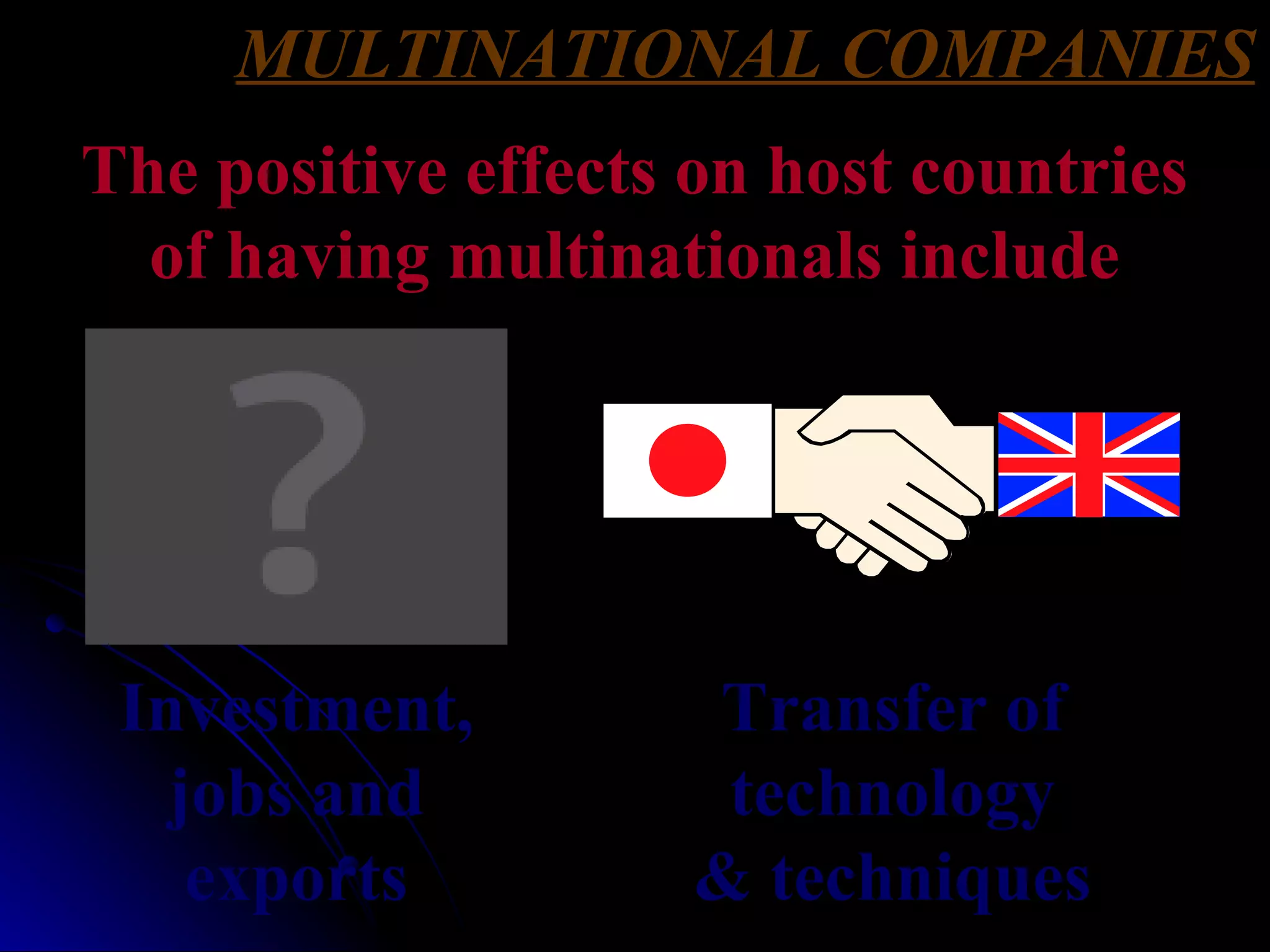
The document discusses industrial systems and changes in employment structure in the UK. It describes the four types of industrial activity - primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary. Over time, as the UK industrialized and mechanized, employment shifted from primary industries like farming to secondary industries like manufacturing, and more recently to tertiary service industries. The document also discusses multinational companies and some positive and negative effects they can have on host countries.