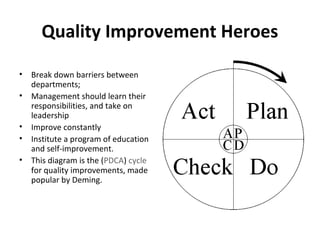
This document discusses continuous quality improvements in hospital management. It covers three main topics: continuous quality improvement and patient safety/satisfaction, improving quality through nursing, and improving quality by risk management. The key points are that continuous quality improvement aims to consistently assess and improve service delivery. Improving nursing quality focuses on staffing levels, education, and giving nurses more autonomy over their work. Risk management identifies risks and develops strategies like risk avoidance, reduction, retention, and transfer to prevent risks and improve quality of care.