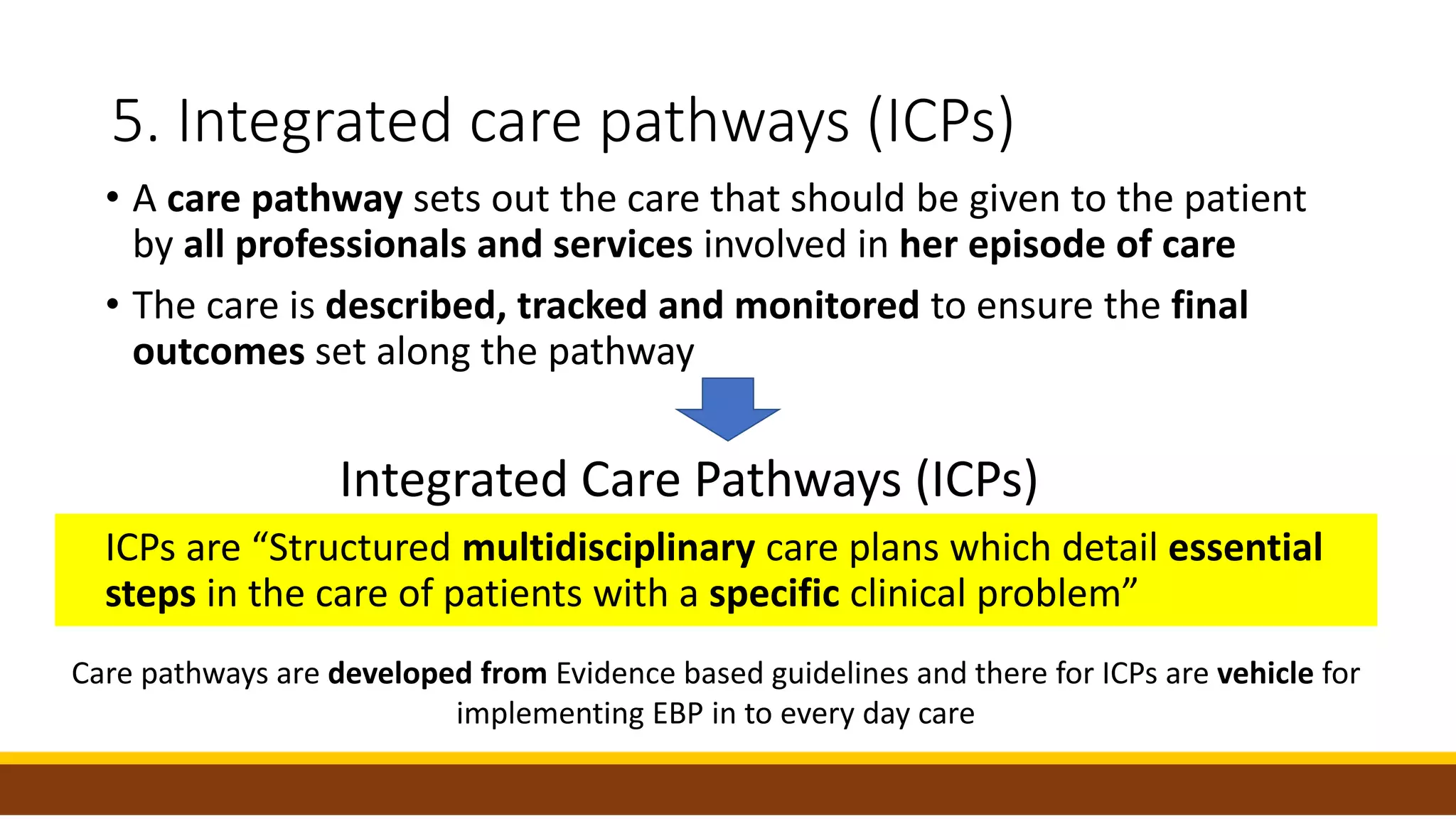
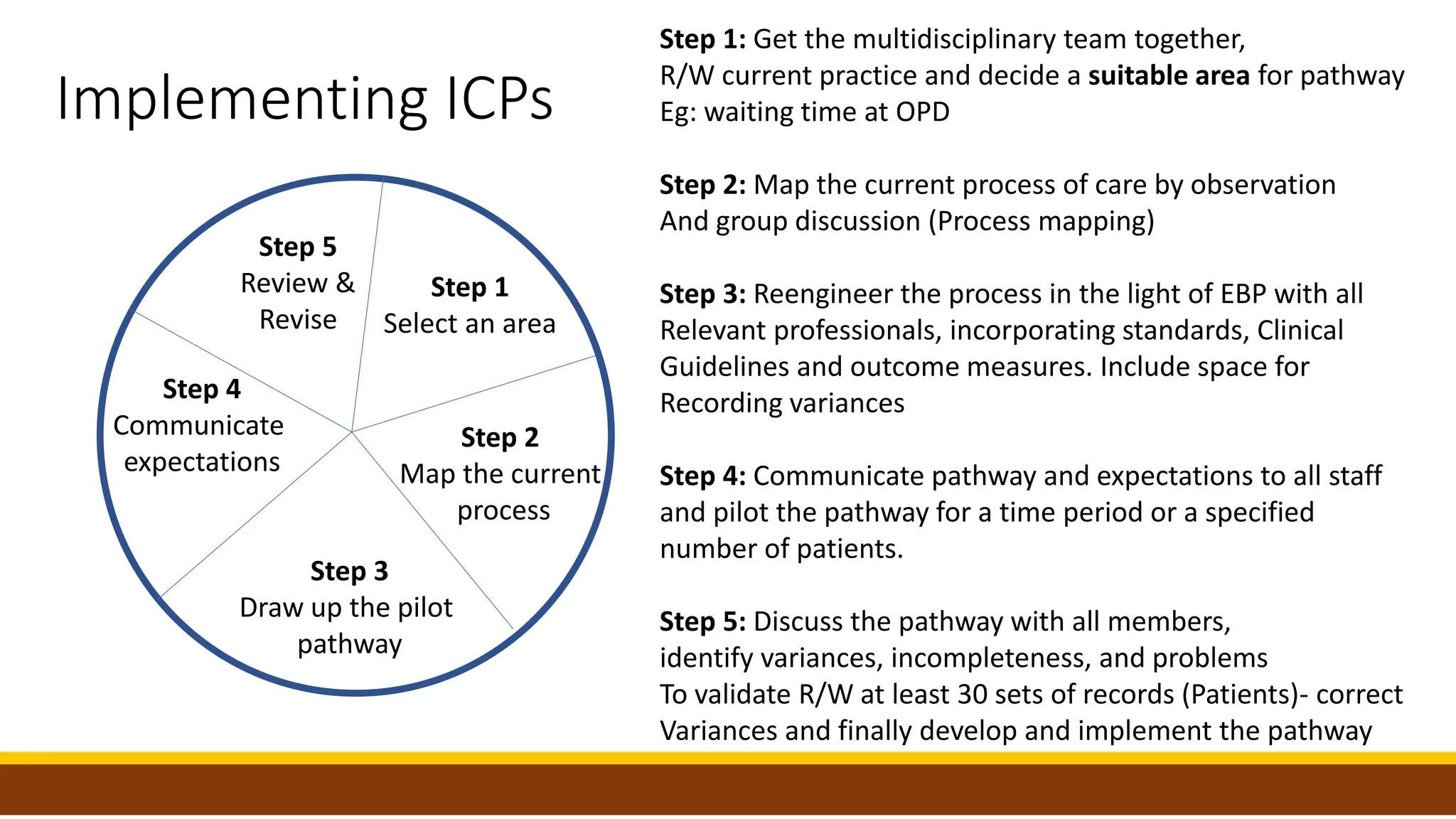
Pillar 6 of clinical governance focuses on clinical effectiveness and ensuring best practices based on evidence. The key elements of clinical effectiveness discussed in the document are: 1) Cost effectiveness analysis to determine value of interventions, 2) Critical appraisal of research evidence before using in decisions, 3) Use of clinical guidelines developed from evidence, 4) Implementation of evidence-based practice through guidelines and evaluation, and 5) Use of integrated care pathways to standardize patient care based on guidelines and monitor outcomes. The document provides details on each of these elements and how organizations can incorporate them to deliver effective, evidence-based clinical care.