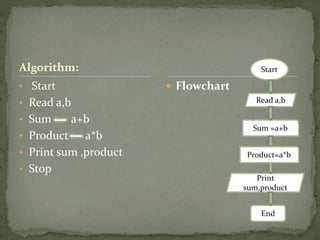
The document outlines the seven stages of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC): 1) problem definition, where the problem is studied to understand requirements, 2) program design, using tools like algorithms and flowcharts, 3) coding, where the program is written, 4) debugging, to detect and correct errors, 5) testing, to verify accuracy, 6) documentation, to guide users, and 7) maintenance, to update the program for changed conditions.