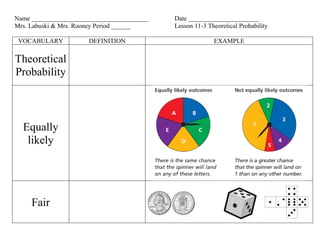
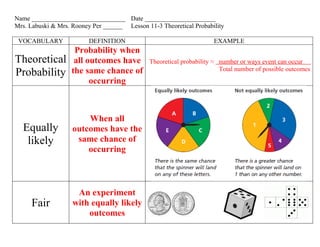
1. The document provides examples of calculating theoretical probabilities using a coin, dice, and other objects. It defines theoretical probability as the probability when all outcomes are equally likely.
2. It also discusses finding the probability of events not occurring by subtracting the probability of the event from 100%.
3. Several examples are worked out calculating probabilities of outcomes from coins, dice, spinners, bags of marbles using the formula for theoretical probability.