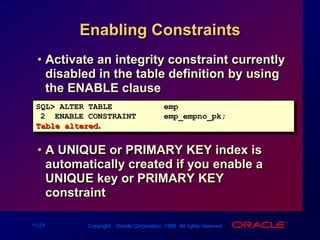
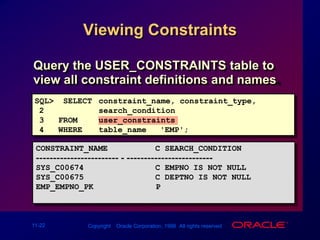
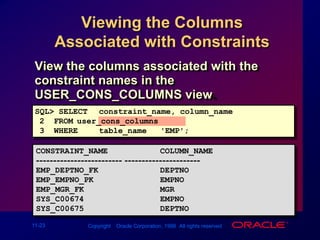
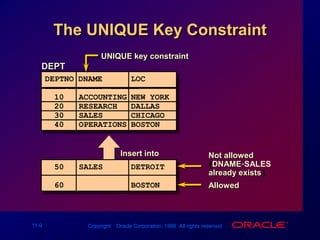
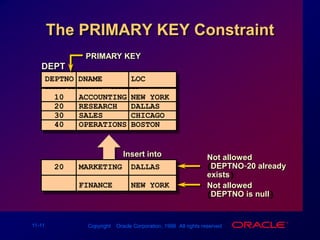
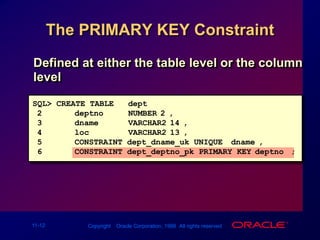
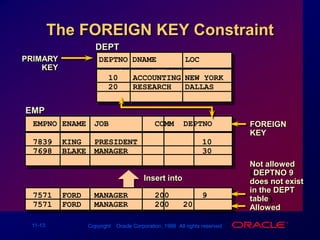
Constraints enforce rules at the table level to maintain data integrity. The main types are NOT NULL, UNIQUE, PRIMARY KEY, FOREIGN KEY, and CHECK. Constraints can be created at the column or table level and are defined using SQL's CREATE TABLE and ALTER TABLE statements. User can view existing constraints and their properties in data dictionary views like USER_CONSTRAINTS and USER_CONS_COLUMNS.




![Defining ConstraintsCREATE TABLE [schema.]table (columndatatype [DEFAULT expr] [column_constraint], ... [table_constraint][,...]);CREATE TABLE emp( empno NUMBER(4), ename VARCHAR2(10), ... deptno NUMBER(7,2) NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT emp_empno_pk PRIMARY KEY (EMPNO));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/les11includingconstraints-090827015132-phpapp01/85/Les11-Including-Constraints-5-320.jpg)
![Defining ConstraintsColumn constraint levelTable constraint levelcolumn [CONSTRAINT constraint_name] constraint_type,column,...[CONSTRAINT constraint_name] constraint_type (column, ...),](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/les11includingconstraints-090827015132-phpapp01/85/Les11-Including-Constraints-6-320.jpg)
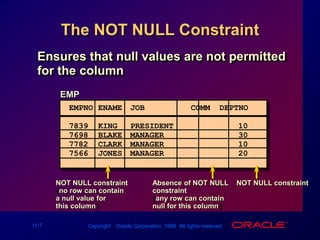





![Adding a Constraint ALTER TABLEtable ADD [CONSTRAINT constraint] type (column);Add or drop, but not modify, a constraintEnable or disable constraintsAdd a NOT NULL constraint by using the MODIFY clause](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/les11includingconstraints-090827015132-phpapp01/85/Les11-Including-Constraints-17-320.jpg)