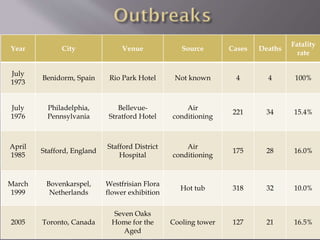
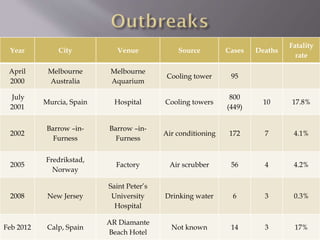
This document discusses Legionnaires' disease, caused by Legionella pneumophila bacteria. It is a type of atypical pneumonia that does not show up on normal sputum tests. Risk factors include age, smoking, lung disease, and immunosuppression. Outbreaks are linked to sources that allow bacterial growth in warm, stagnant water that becomes aerosolized, such as cooling towers, hot tubs, and plumbing systems. Symptoms include fever, cough, and pneumonia. Diagnosis involves culture, urinary antigen testing, and antibody tests. Treatment is with macrolides or fluoroquinolones. Prevention focuses on controlling bacterial growth in water systems.