Embed presentation
Downloaded 60 times
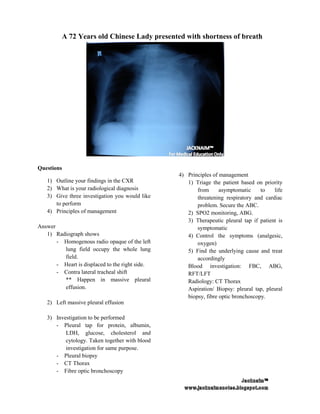

A 72-year-old Chinese lady presented with shortness of breath. Radiograph shows a homogenous radio opaque left lung field occupying the whole lung, displaced heart to the right side, and contra lateral tracheal shift consistent with massive left pleural effusion. Investigations would include pleural tap, pleural biopsy, CT thorax, and fiberoptic bronchoscopy to determine the underlying cause and guide treatment.
