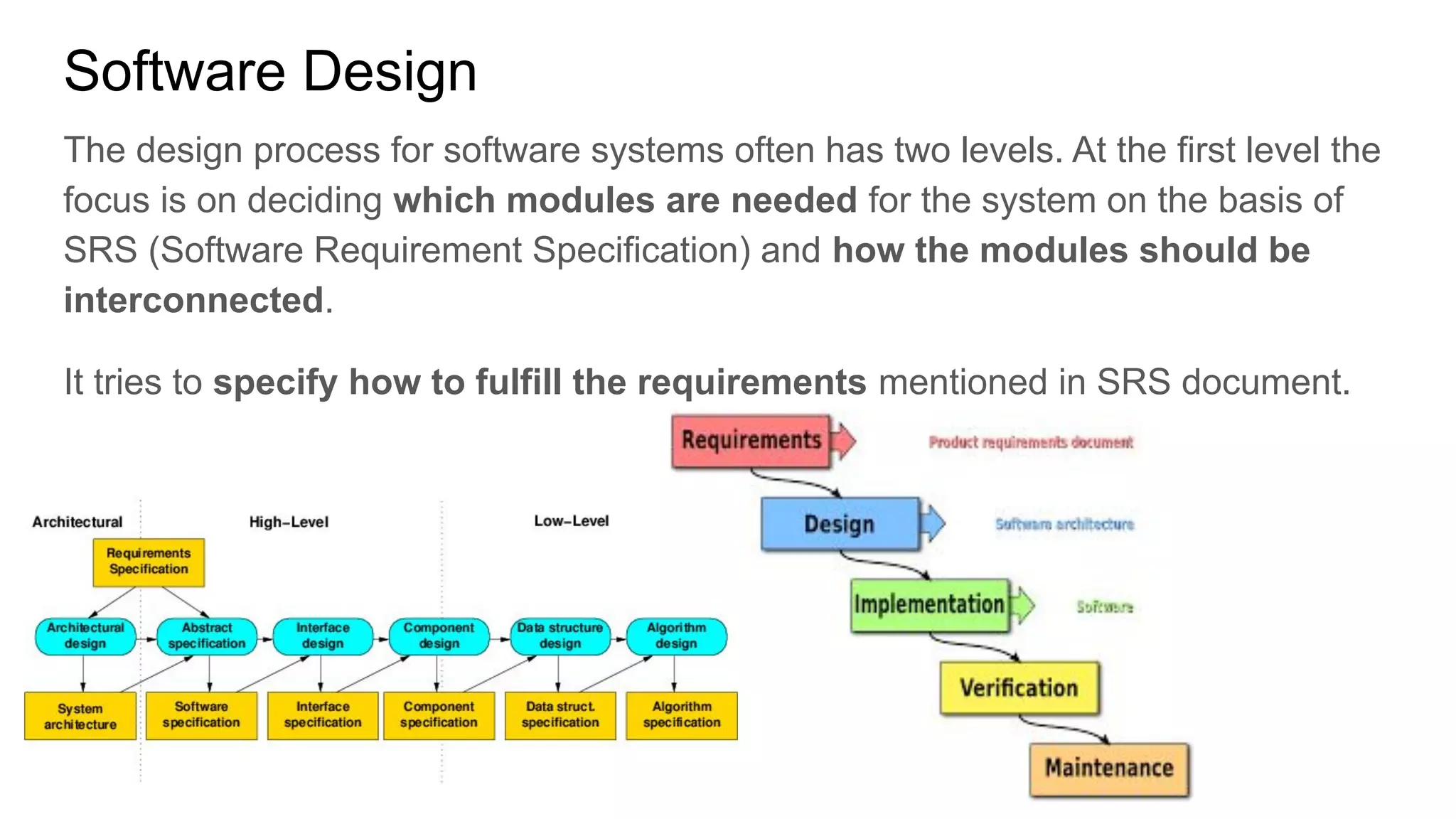
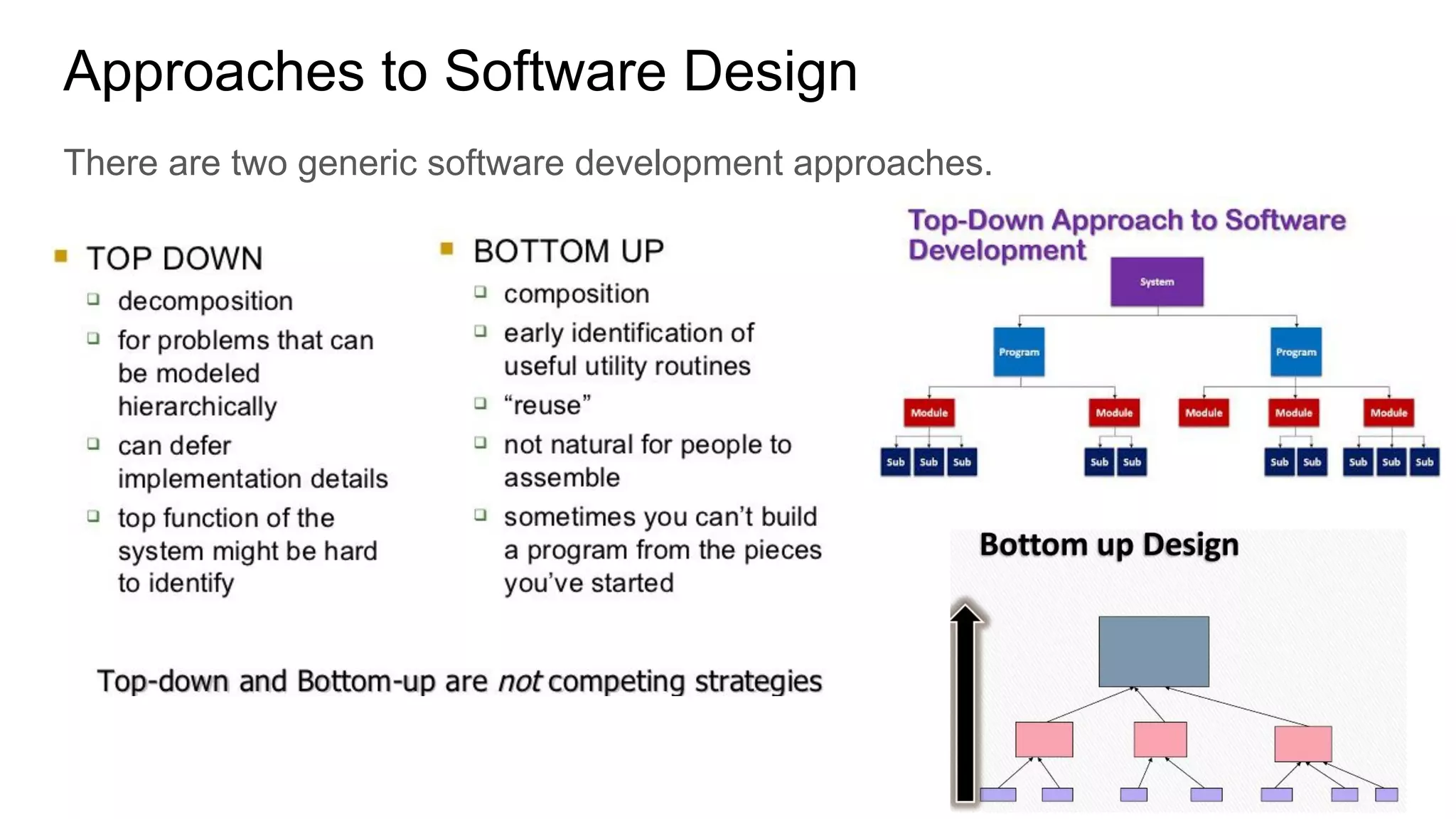
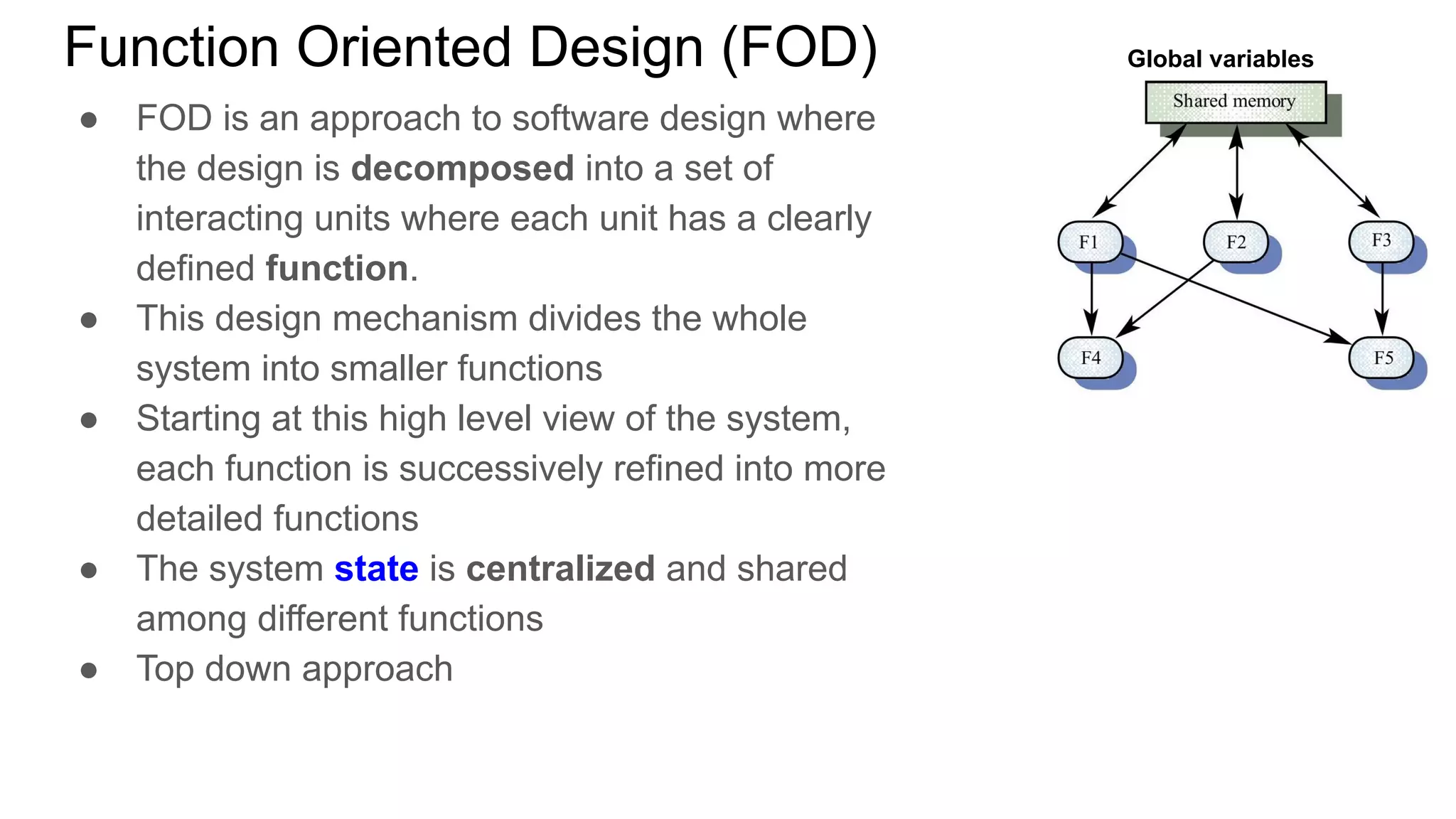
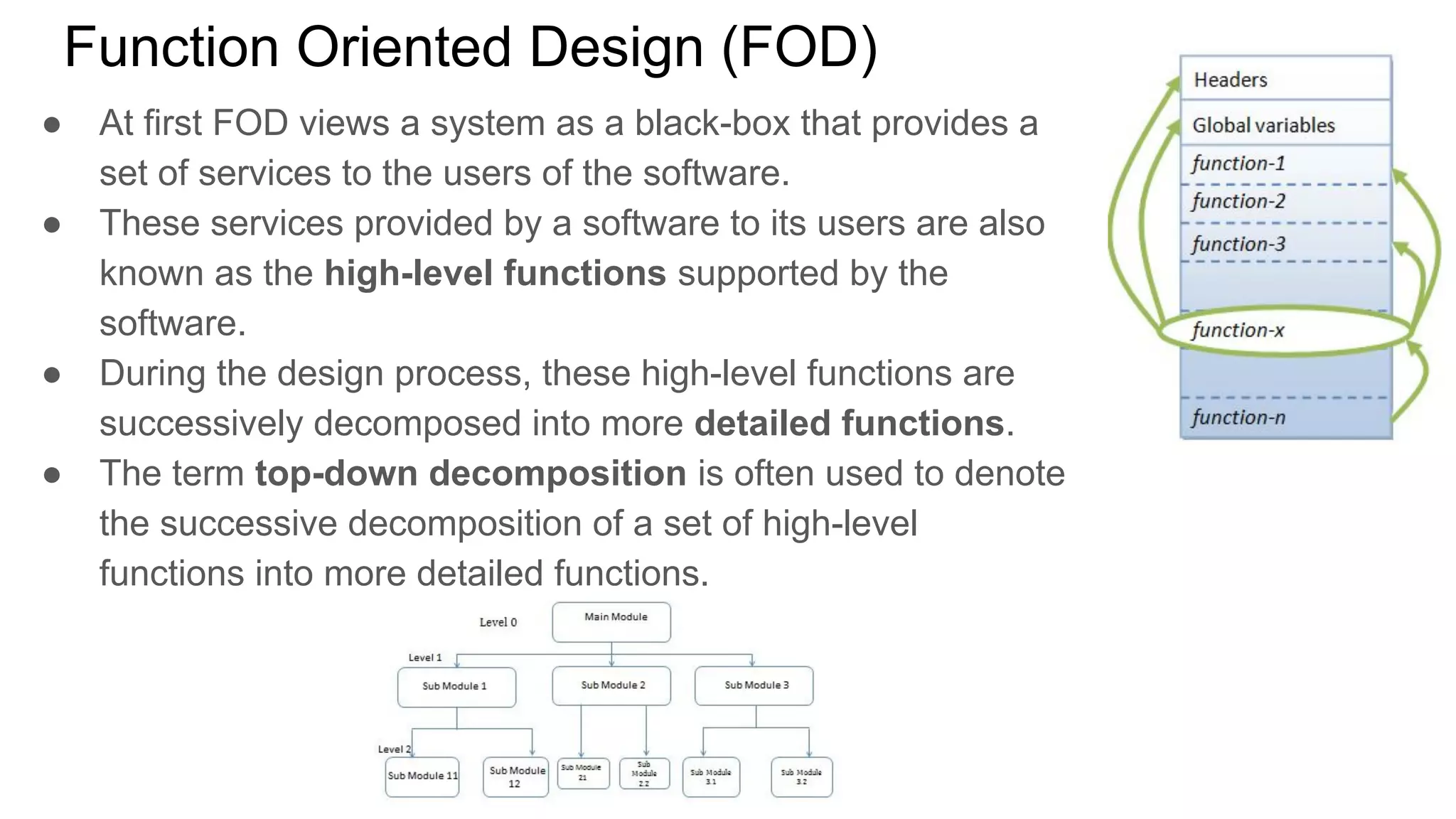
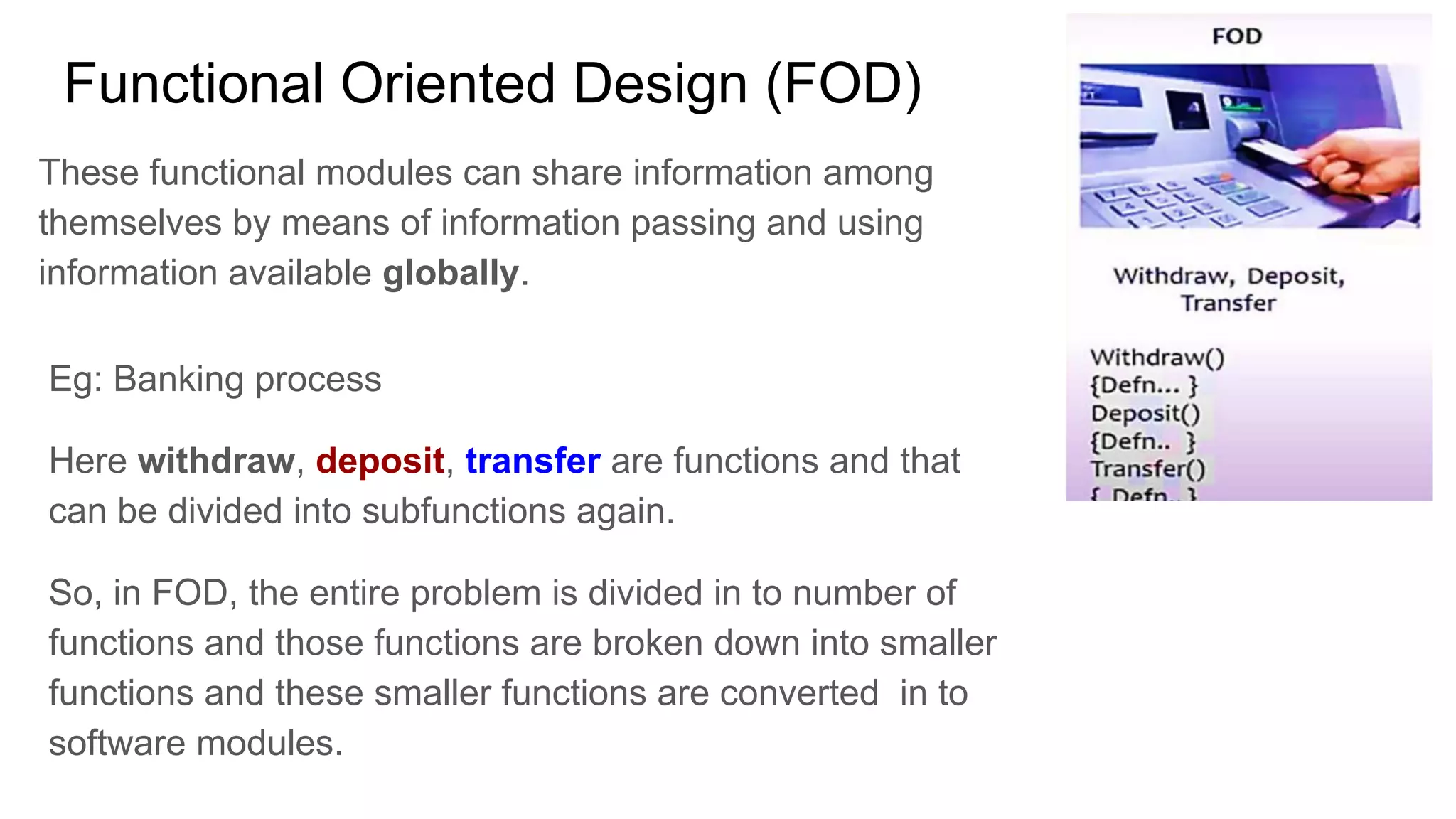
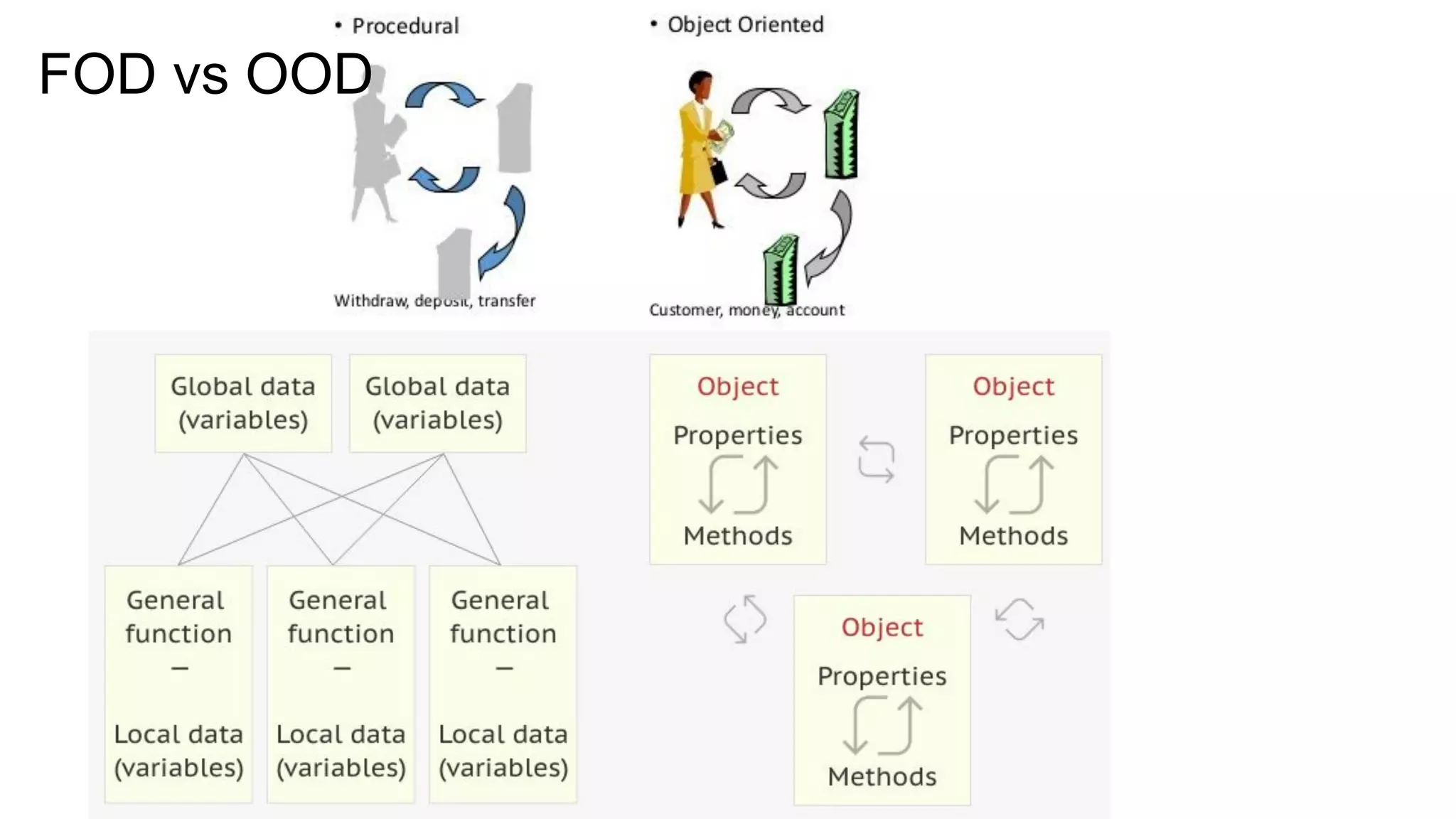
This document provides an overview of the topics that will be covered in the CST 205 Object Oriented Programming using Java course. It discusses approaches to software design like functional oriented design and object oriented design. It provides examples of each approach like an automated fire alarm system. It also discusses object modeling using UML diagrams and provides an introduction to Java programming concepts like environment, platforms, bytecode and program structure.