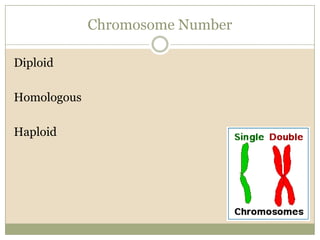
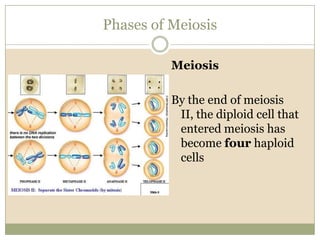
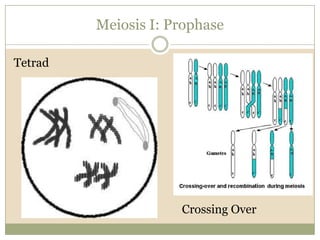
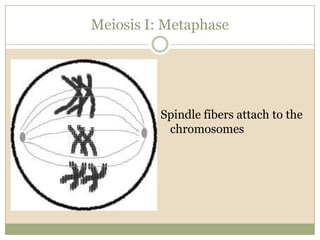
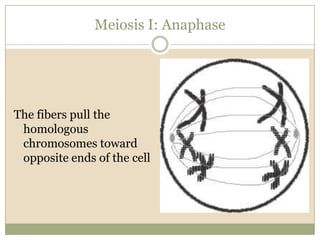
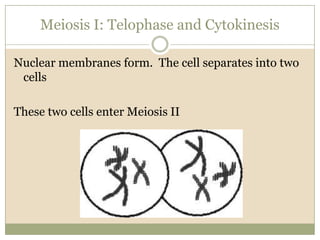
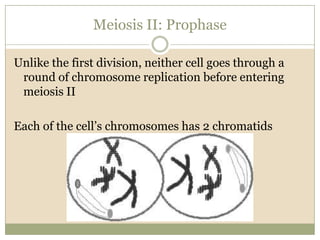
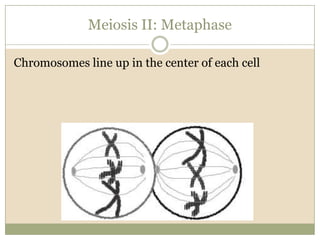
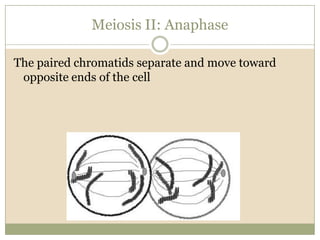
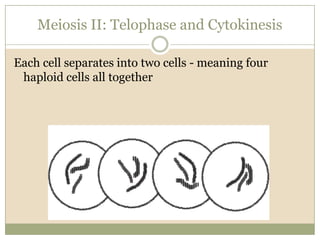
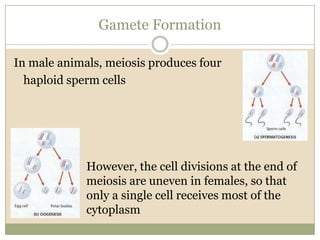
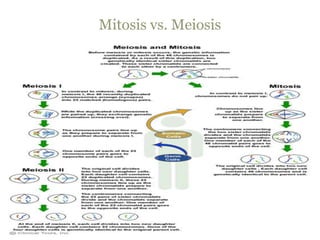
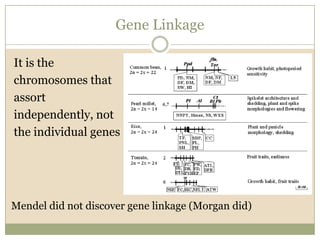
Meiosis involves two cell divisions that result in four haploid cells from one original diploid cell. During the first meiotic division, homologous chromosomes pair up and may exchange genetic material through crossing over. The second meiotic division separates the chromatids so that each of the four resulting haploid cells receives one chromosome from each homologous pair. Gene linkage occurs when genes located near each other on the same chromosome tend to be inherited together.