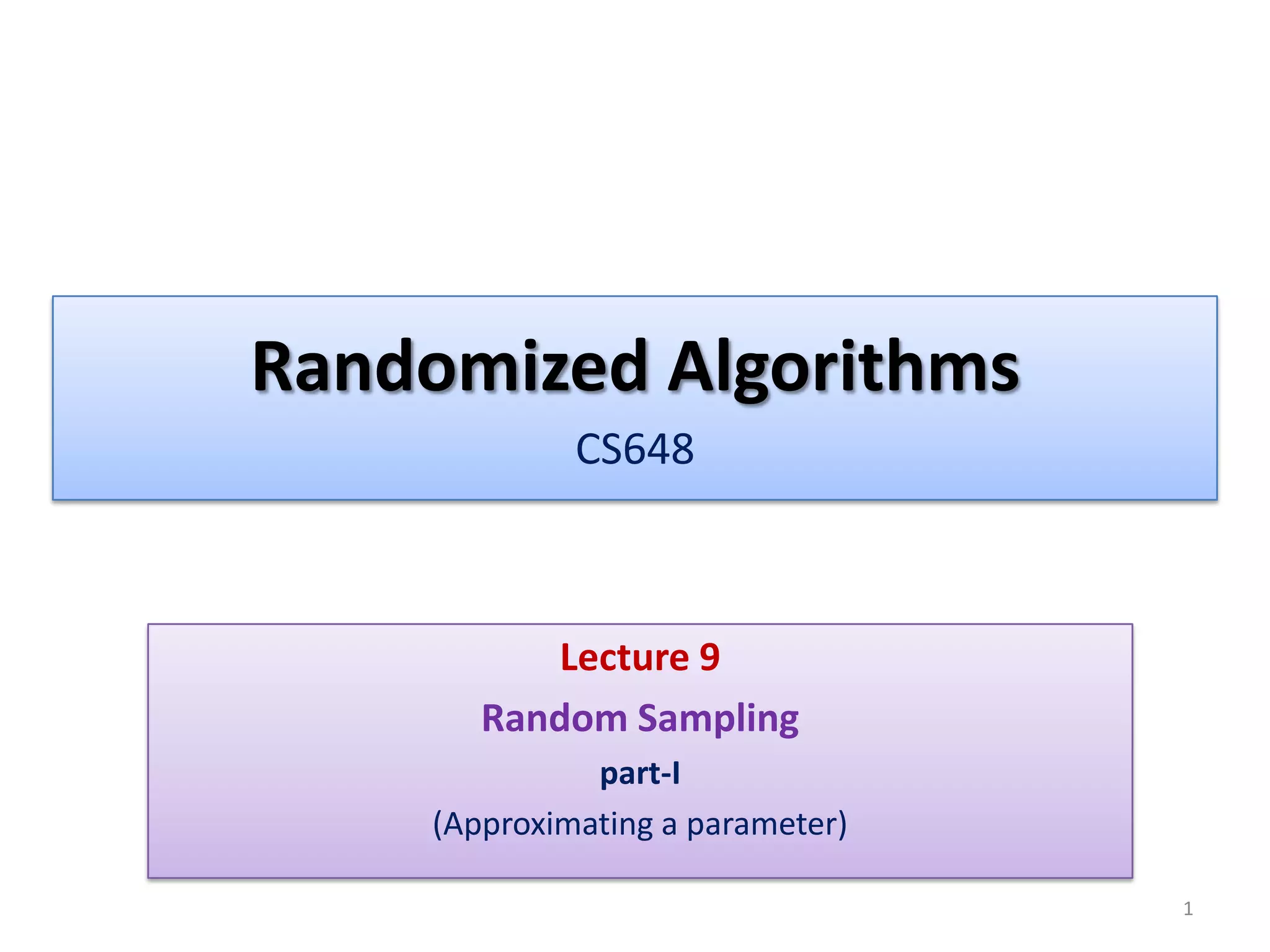
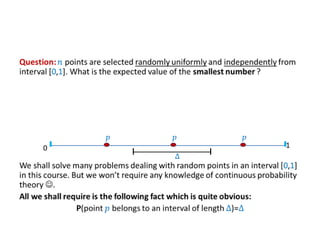
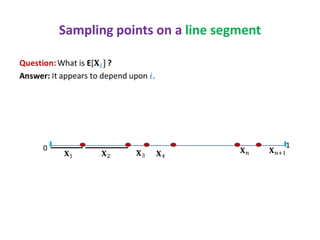
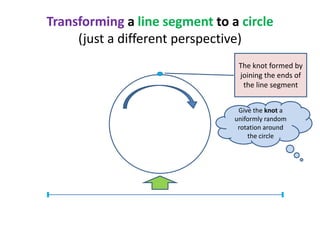
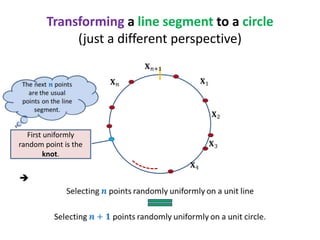
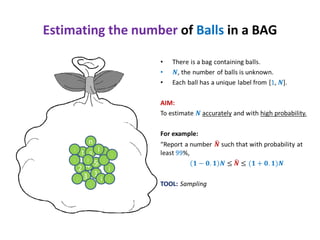
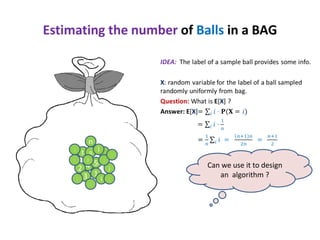
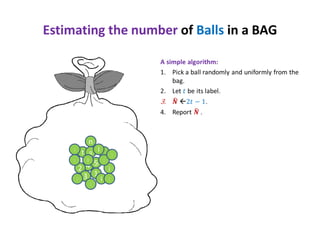
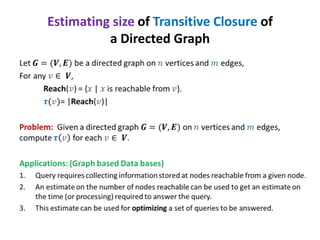
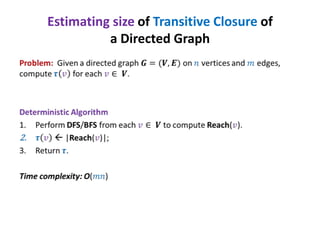
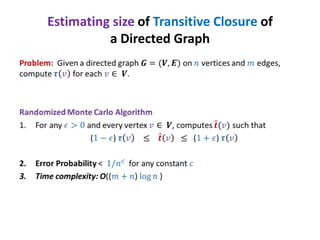
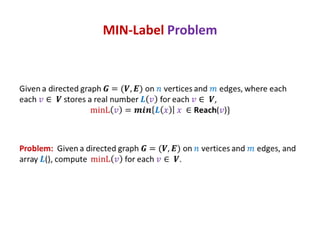
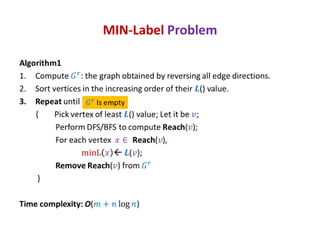
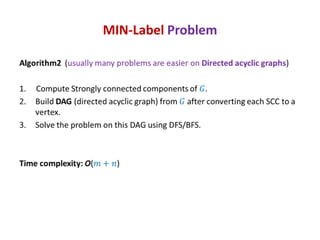
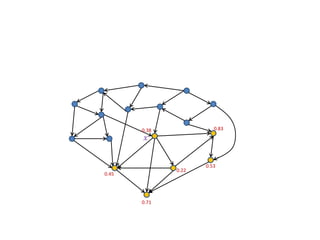
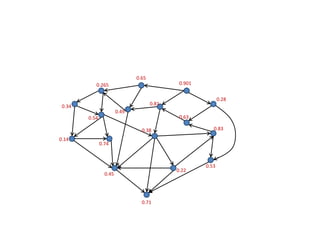
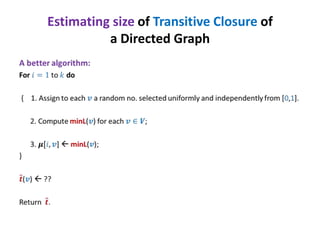
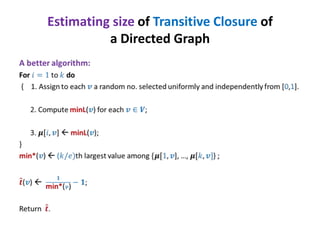
This document discusses random sampling techniques for approximating parameters. It first presents an inspirational problem about using random sampling to estimate the length of a line segment transformed into a circle. Then it discusses using random sampling to estimate the number of balls in a bag by randomly sampling balls, replacing them, and counting the number of unique balls. It suggests extending this to multiple samples to improve accuracy. Finally, it discusses using random sampling to estimate the size of the transitive closure of a directed graph by randomly sampling node pairs and checking connectivity. The document suggests using a Chernoff bound analysis to analyze the error probability of this technique.