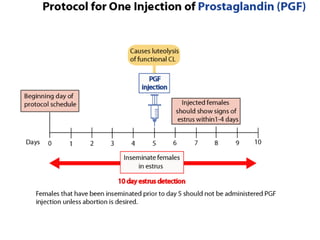
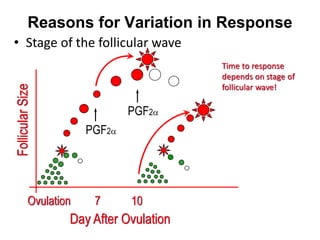
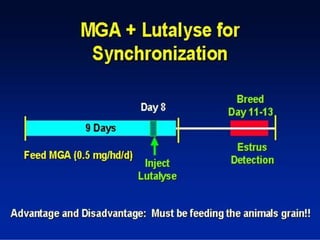
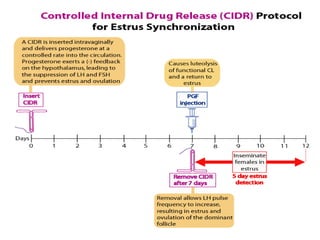
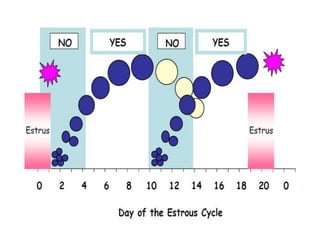
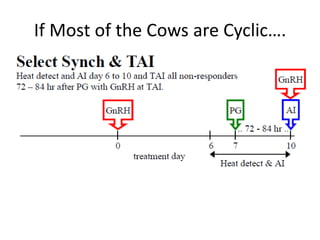
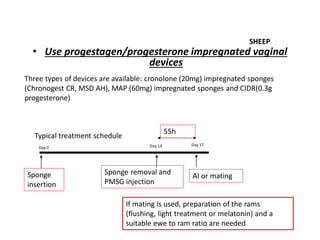
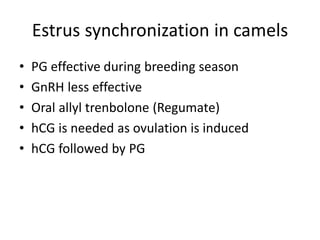
This document summarizes estrus synchronization techniques in various domestic farm animals. It discusses the benefits of estrus synchronization such as labor savings and planned breeding. It describes the structures that regulate estrus cycles and various approaches used, including extending or terminating the luteal phase using progestins or prostaglandins. Specific synchronization methods and protocols are outlined for cattle, buffalo, sheep, goats, sows, mares, and camels. Prostaglandin, progesterone, and gonadotropin treatments as well as considerations for optimal management are covered.