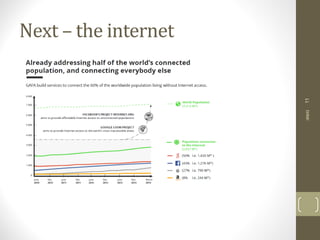
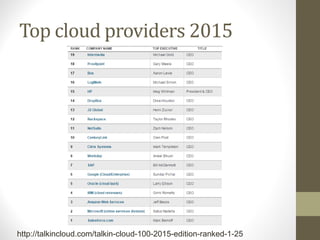
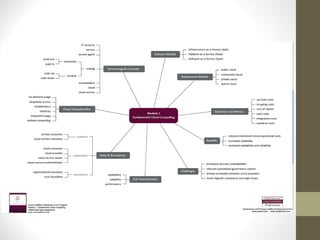
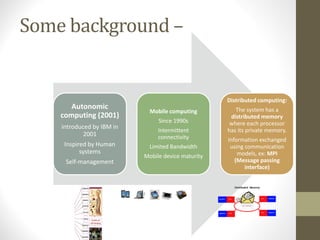
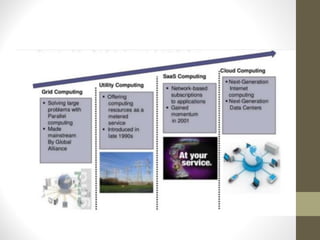
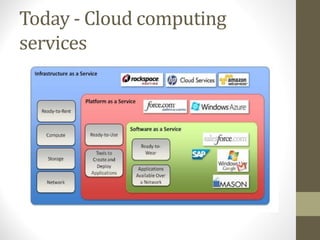
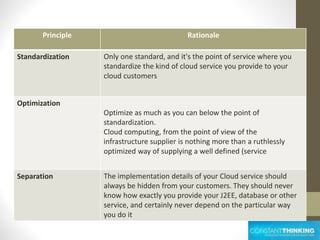
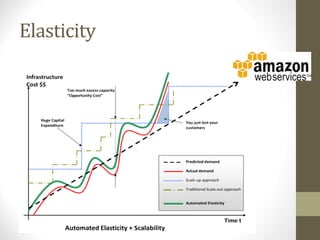
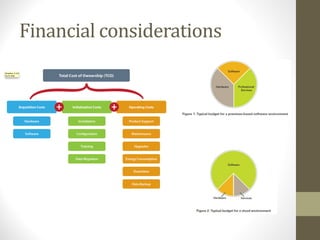
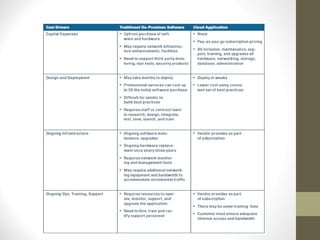
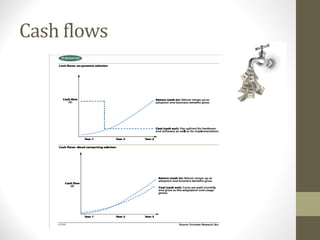
This document provides an overview of cloud computing concepts including definitions of public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, community cloud, and cloud computing models like SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS. Key points covered include:
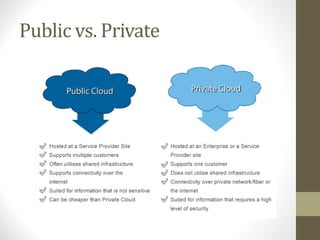
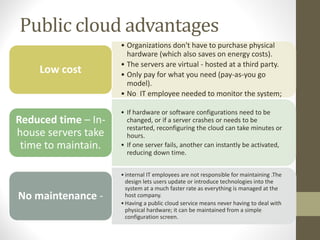
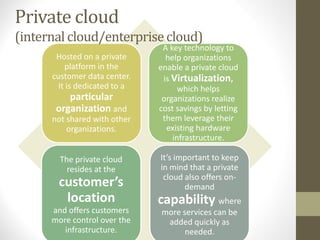
- Public cloud is hosted by a third party and accessed over the internet, while private cloud is hosted internally or on-site.
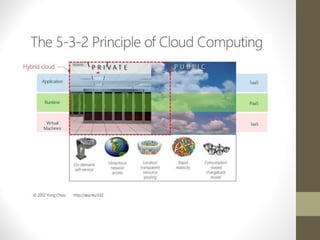
- Hybrid cloud combines public and private cloud models.
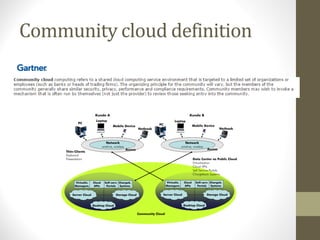
- Community cloud is shared by several organizations with common interests.
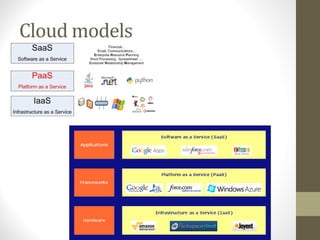
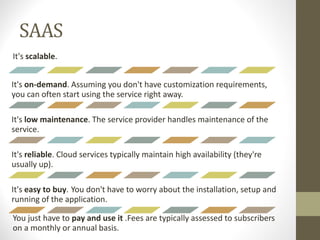
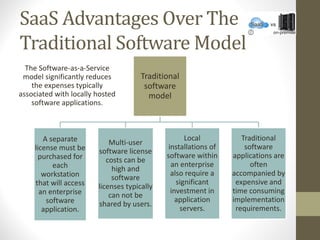
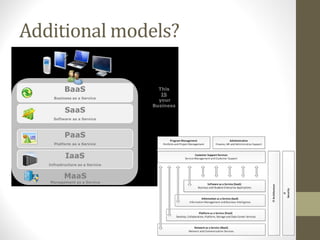
- SaaS provides applications delivered as a service, IaaS provides infrastructure resources, and PaaS provides platforms for application development.
- Advantages and disadvantages of public and private clouds are discussed.