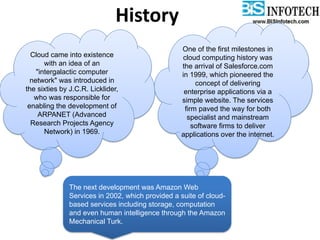
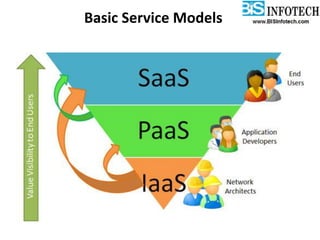
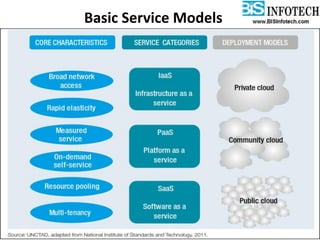
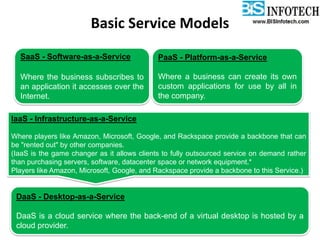
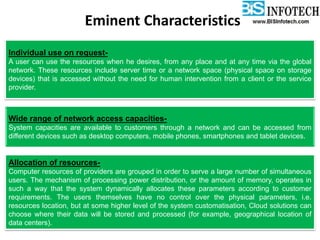
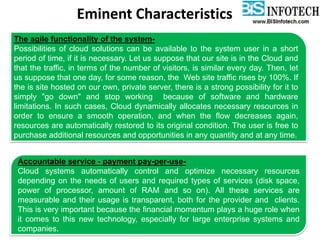
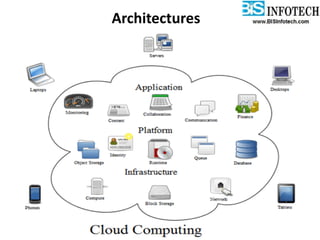
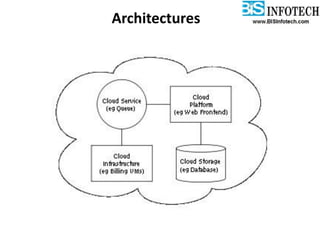
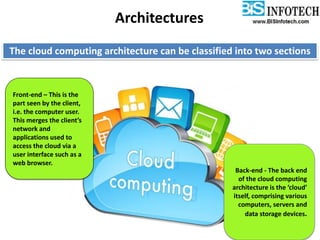
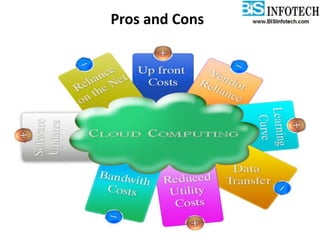
The document provides a comprehensive overview of cloud computing, including its history, definitions, basic service models (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS), and pros and cons. It highlights the growth of the cloud services market, which is projected to expand significantly, driven by innovations and increased adoption in various sectors. Additionally, it discusses the challenges faced in cloud computing, such as security requirements and reliability, while emphasizing the need for reputable service providers.