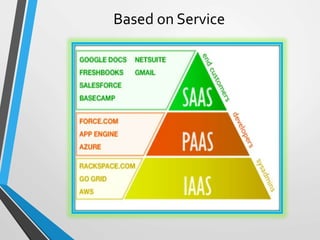
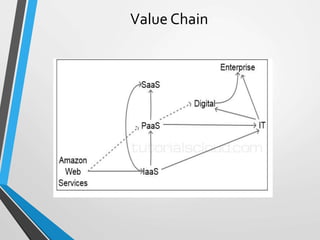
The document discusses cloud computing, including:
- Cloud computing allows users to access computing resources like storage, processing, and security from any location through the internet.
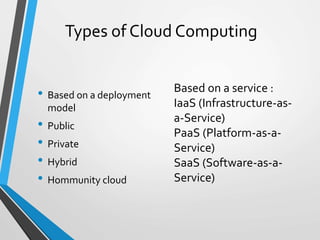
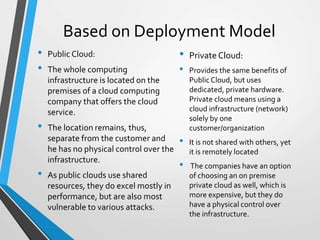
- It works by running applications and storing data on remote servers owned by cloud computing companies, rather than on the user's local machine.
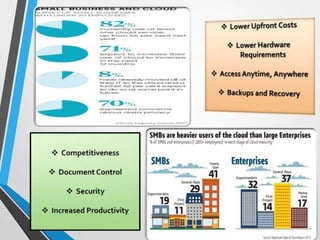
- Over 1 exabyte of data is currently stored in the cloud, and more than 50% of Global 1000 companies are expected to store customer data in the public cloud by the end of 2016.
- The cloud has front-end components like clients and user interfaces, and back-end components like computers, servers, and data storage systems.