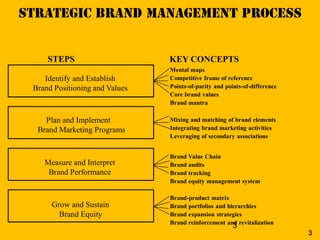
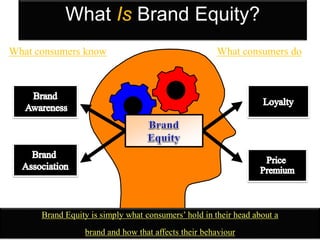
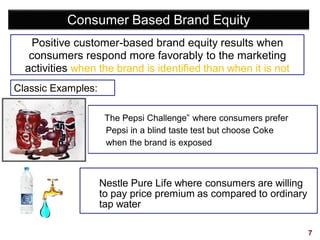
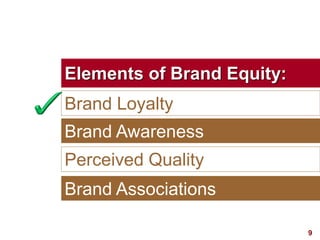
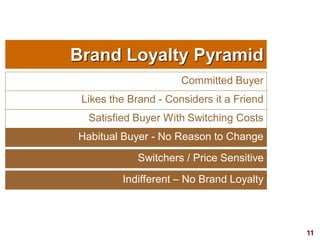
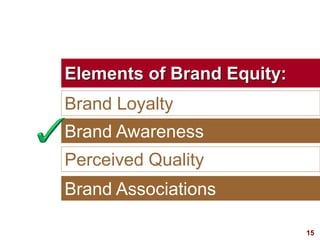
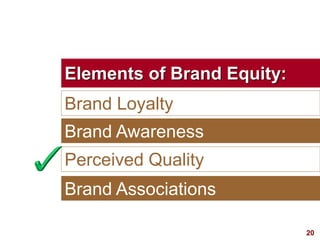
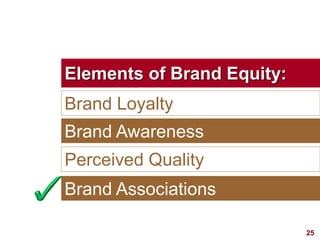
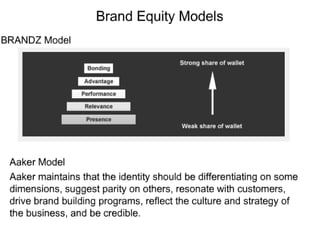
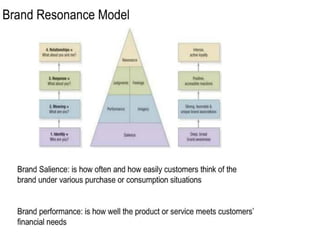
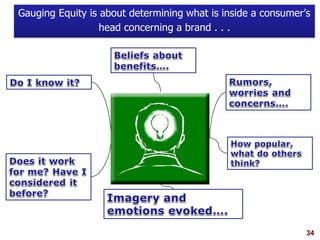
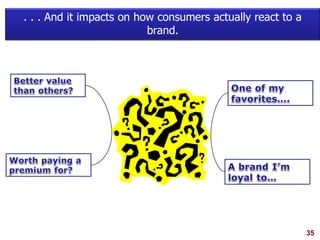
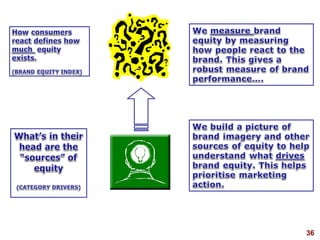
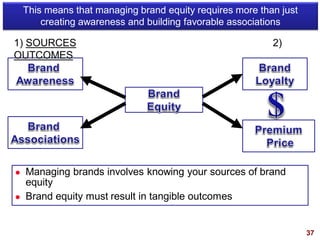
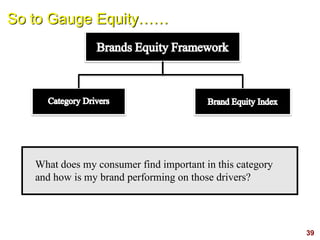
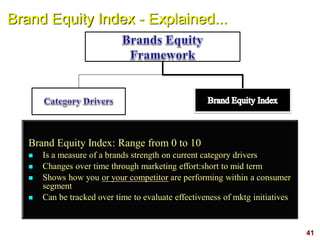
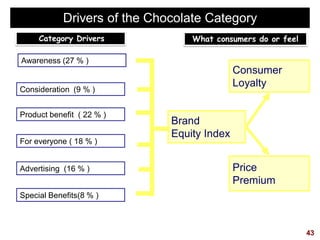
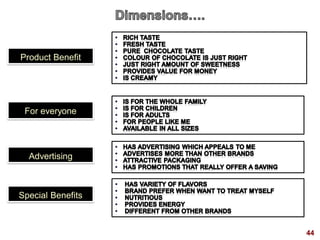
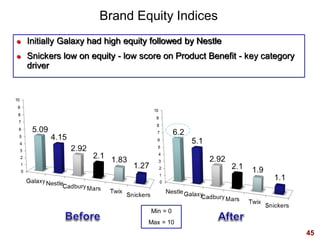
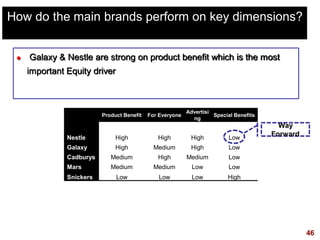
This document discusses strategic brand management concepts and measuring brand equity. It defines brand equity as the differential effect that brand knowledge has on consumer responses. It identifies key elements of brand equity as brand loyalty, brand awareness, perceived quality, and brand associations. The document discusses how to build and measure each element, and the benefits they provide such as loyal customers and ability to charge a price premium. It emphasizes that managing brand equity requires understanding what drives brand equity according to consumers and how the brand performs on those drivers. Methods discussed for measuring equity include calculating a Brand Equity Index to evaluate brand strength over time and against competitors.