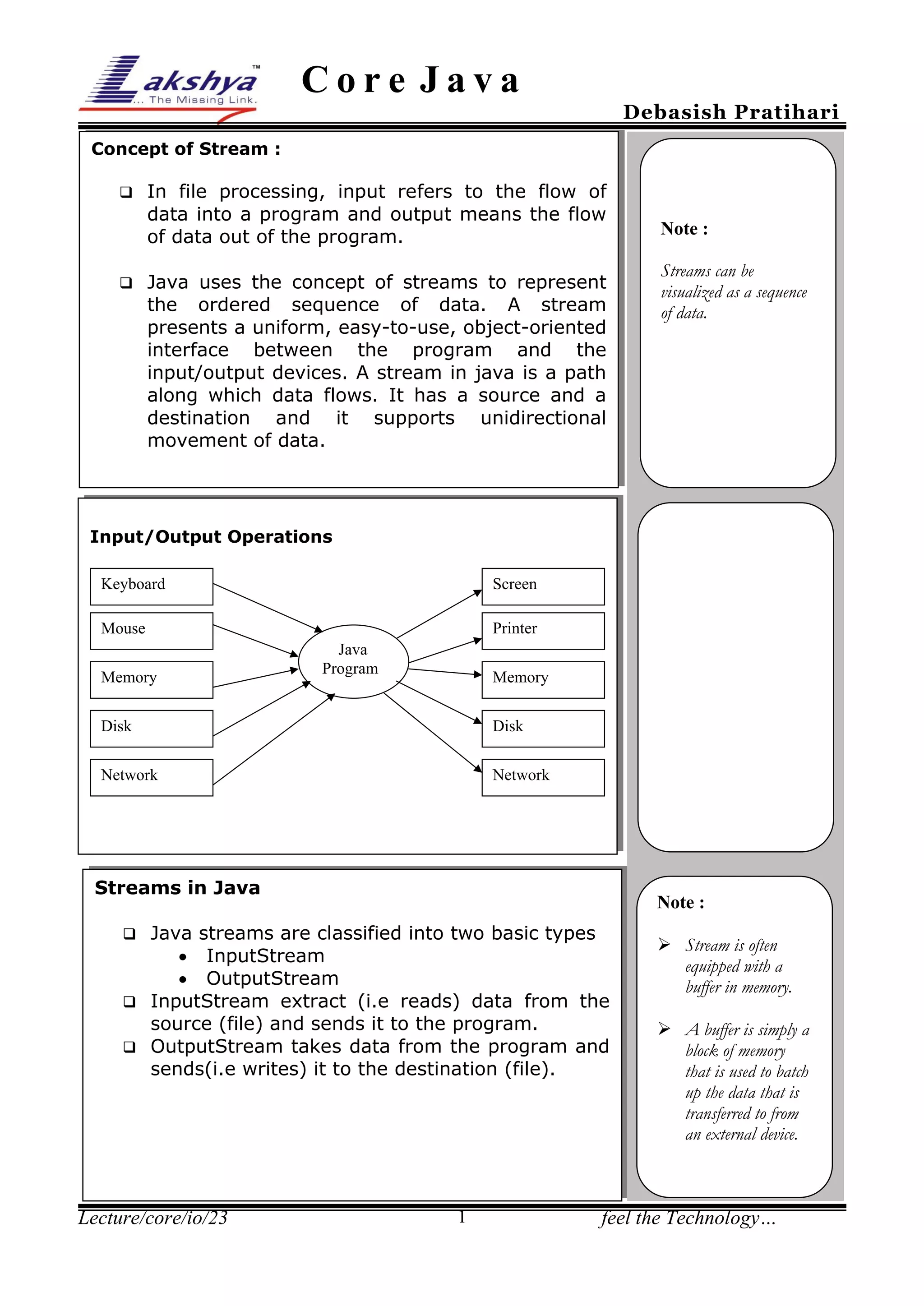
Streams in Java represent an ordered sequence of data and provide a uniform interface between programs and input/output devices. There are two basic types of streams: input streams which read data from a source and output streams which write data to a destination. The java.io package contains classes for processing different data types using byte streams for bytes and character streams for characters. Programs can use input and output streams to copy files, read primitive data types from files, and perform other input/output operations.
![Core Java
Debasish Pratihari
Sample Program-1
Program Objective : To Copy Characters from one File to
another.
File Name : CopyChars.java
import java.io.*;
class CopyChars{
public static void main(String args[]){
File inFile = new File("Input.txt");
File outFile = new File("Output.txt");
FileReader ins= null;
FileWriter outs=null;
try{
ins= new FileReader(inFile);
outs=new FileWriter(outFile);
int ch;
while((ch=ins.read())!= -1)
outs.write(ch);
}catch(IOException e){
System.out.println(e);
System.exit(0);
}
finally{
try{
ins.close();
outs.close();
}catch(IOException e){
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
}
Lecture/core/io/23
3
feel the Technology…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handout-23-131022003920-phpapp01/85/Lecture-23-3-320.jpg)
![Core Java
Debasish Pratihari
Programming Architecture to Deal with Primitive Data type :
Bytes are read
from the file
Bytes are converted
to primitive types
fis
Primitive Types are
read from dis
dis
prim.txt
Program
Screen
primitive
fos
Bytes are written
to the file
dos
Primitives are converted
to a sequence of bytes
Primitive Types are
written to dos
Sample Prohram-2
25%
Program Objective : To deal with primitive Data types
File Name : PrimitiveDemo.java
import java.io.*;
class PrimitiveDemo{
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException{
File primitive = new File("prim.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(primitive);
DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(fos);
dos.writeInt(1234);
dos.writeDouble(34.45);
dos.writeBoolean(false);
dos.writeChar('a');
dos.close();
fos.close();
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(primitive);
DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(fis);
System.out.println(dis.readInt());
System.out.println(dis.readDouble());
System.out.println(dis.readBoolean());
System.out.println(dis.readChar());
dis.close();
fis.close();
}
}
Lecture/core/io/23
4
feel the Technology…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handout-23-131022003920-phpapp01/85/Lecture-23-4-320.jpg)