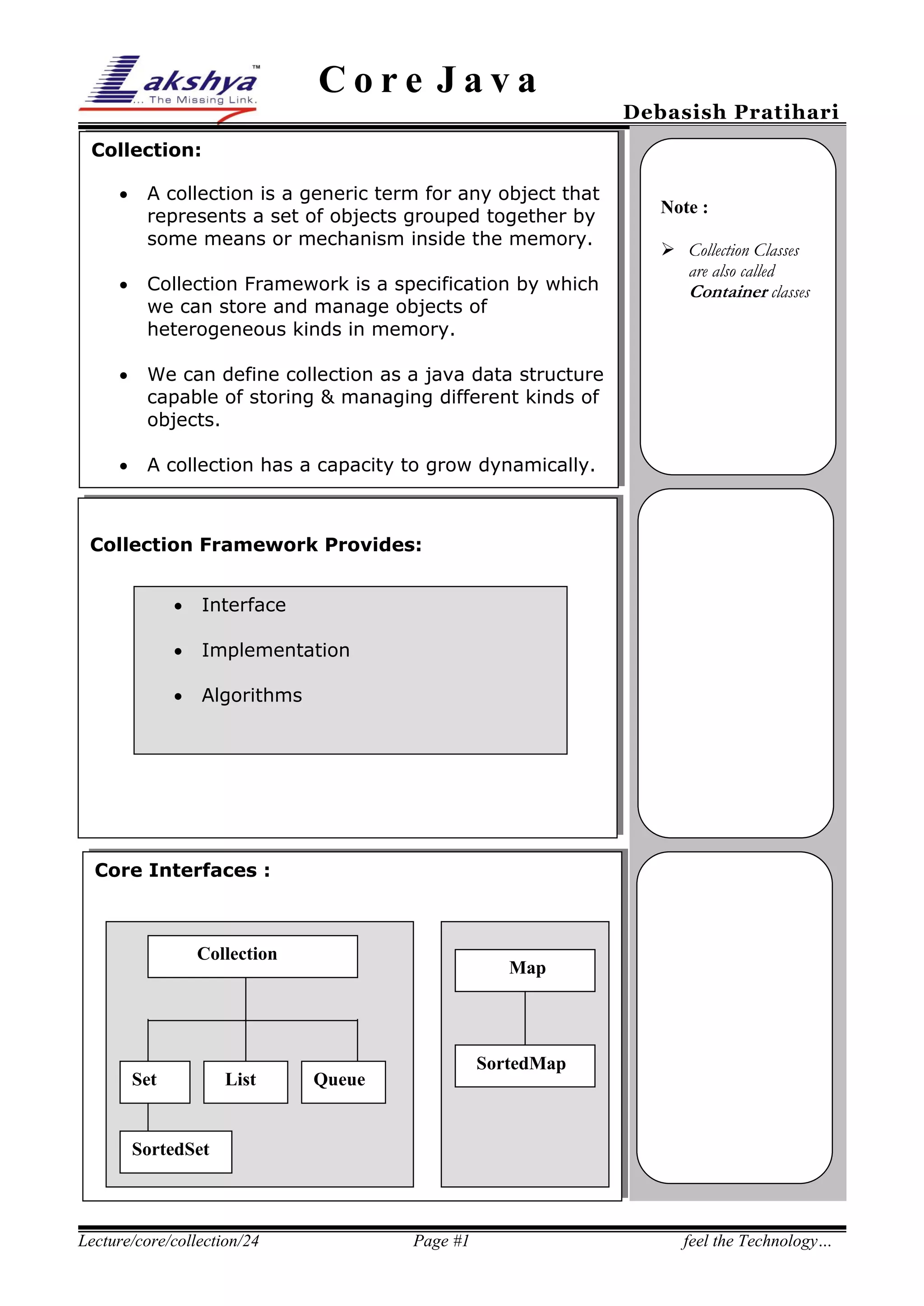
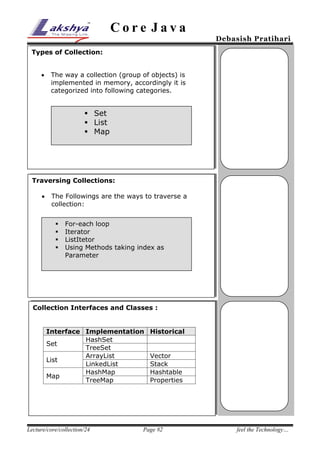
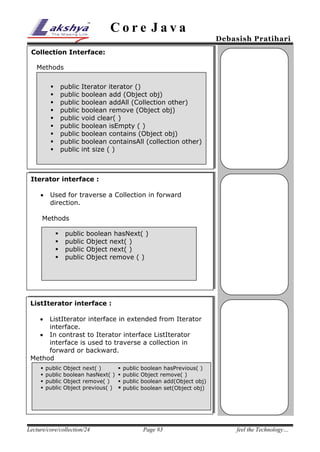
The document discusses Java collection framework. It defines a collection as a data structure capable of storing heterogeneous objects. There are three main types of collections - sets, lists, and maps. Sets cannot contain duplicate elements, lists allow duplicates and positional access, and maps store elements as key-value pairs. The core interfaces provided by the collection framework are Collection, Set, List, and Map. Common implementations of these interfaces include ArrayList, LinkedList, HashSet, TreeSet, HashMap and TreeMap. The document also covers traversing collections using iterators and list iterators, as well as examples of using sets, lists and maps.
![Core Java
Debasish Pratihari
List Interface
Methods
public
public
public
public
public
public
ListIterator listIterator( )
void add(int index, Object obj)
void addAll(int i, Collection list)
Object remove(int indx)
Object set(int indx, Object obj)
int indexOf (Object obj)
Using Set :
25%
Support basic operation of Collection Interface
Can’t contain duplicate elements.
Implementations
HasSet
TreeSet
LinkedHashSet
Example :
import java.util.*;
class SetDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
HashSet <String>set= new HashSet<String>();
set.add("one");
set.add("two");
set.add("three");
set.add("four");
set.add("five");
System.out.println(set);
}
}
Lecture/core/collection/24
Page #4
feel the Technology…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handout-24-131022003942-phpapp02/85/Lecture-24-4-320.jpg)
![Core Java
Debasish Pratihari
Using List :
Supports basic operations of Collection
Interface.
Facilitate positional access and Searching.
Supports range operation.
Implementations:
ArrayList
LinkedList
Example:
import java.util.*;
class ListDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
LinkedList<Integer> list= new LinkedList<Integer>();
list.add(10);
list.add(20);
list.add(30);
System.out.println(list);
ListIterator itr= list.listIterator();
while(itr.hasNext())
System.out.println(itr.next());
while(itr.hasPrevious())
System.out.println(itr.previous());
}
}
Lecture/core/collection/24
Page #5
feel the Technology…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handout-24-131022003942-phpapp02/85/Lecture-24-5-320.jpg)
![Core Java
Debasish Pratihari
Using Map :
Elements are stored as key-value pair
A map can’t contain duplicate keys
Accept null as key value.
Implementations:
HashMap
TreeMap
LinkedHashMap
Example :
import java.util.*;
class MapDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
HashMap<String,String> map
= new HashMap<String,String>();
map.put("one","java");
map.put("two","j2ee");
map.put("three","struts");
map.put("four","hibernate");
map.put("","EJB");
System.out.println(map);
}
}
HashTable vs HashMap :
HashTable
Synchronized
Doesn’t accept null
Order is maintained
Lecture/core/collection/24
vs
HashMap
Un-synchronized
Accept null
No guarantee of
order
Page #6
feel the Technology…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handout-24-131022003942-phpapp02/85/Lecture-24-6-320.jpg)