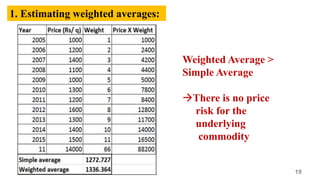
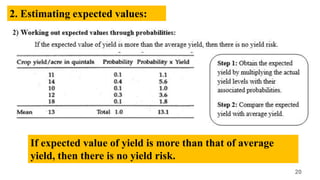
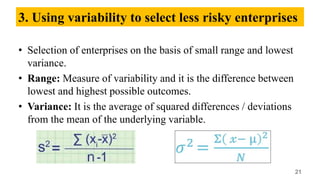
The document discusses the concepts of risk and uncertainty in agriculture, defining risk as a measurable situation with known outcomes and uncertainty as one with unknown outcomes. It outlines various sources of risks such as production, human, market, institutional, financial, and business risks, along with risk management strategies including mitigation, transfer, and coping. It emphasizes the importance of managing risks to maximize opportunities and outlines methods for measurement and reduction of risks in farming.