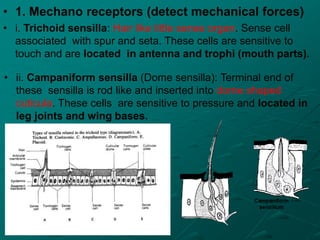
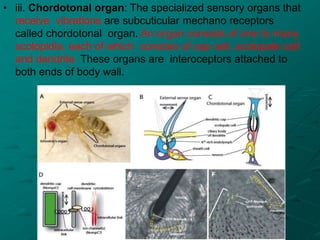
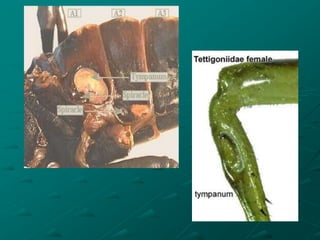
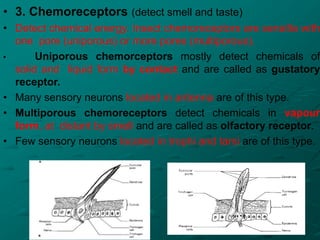
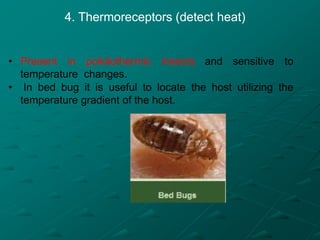
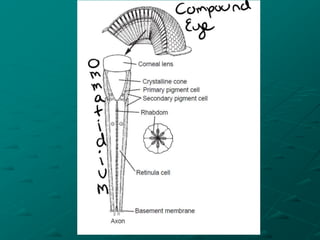
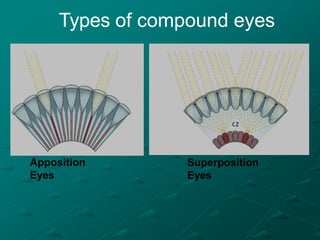
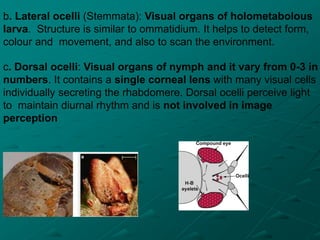
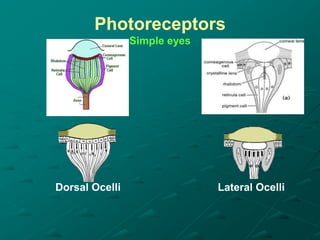
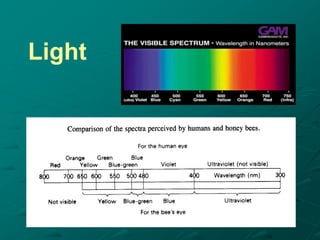
Insects possess five main senses: touch, hearing, smell, taste, and sight. Sensilla are hair-like sensory organs that detect stimuli from the environment and trigger responses. There are several types of sensilla that function as mechanoreceptors, auditory receptors, chemoreceptors, thermoreceptors, and photoreceptors. In particular, compound eyes composed of many ommatidia allow insects to detect light and vision, while antennae and tarsi contain chemoreceptors that detect smells and tastes. Johnston's organs and subgenual organs are examples of chordotonal organs that function as proprioceptors and detect sounds and vibrations.