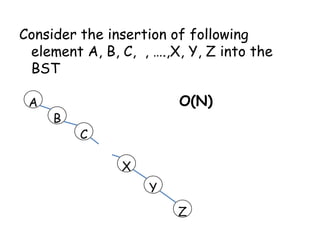
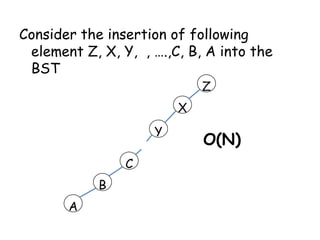
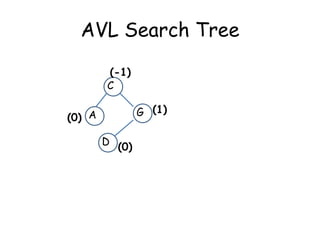
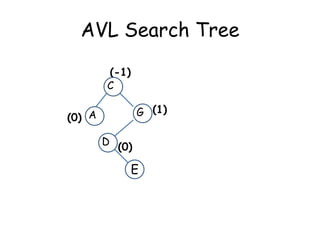
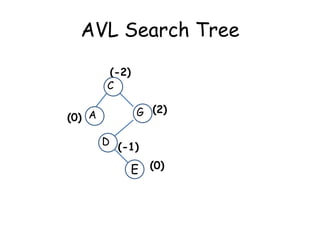
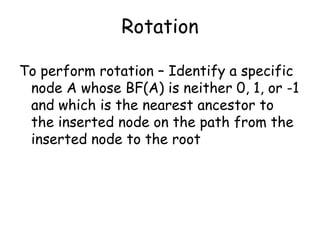
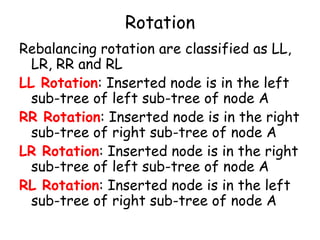
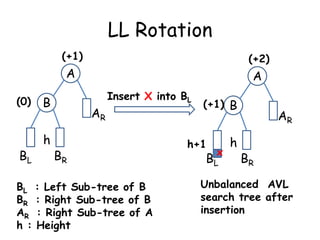
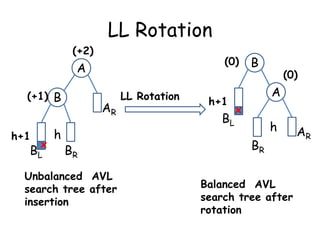
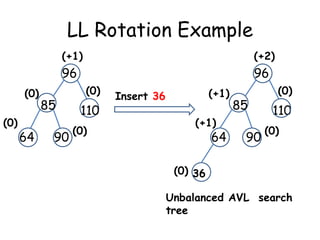
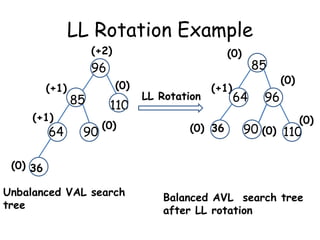
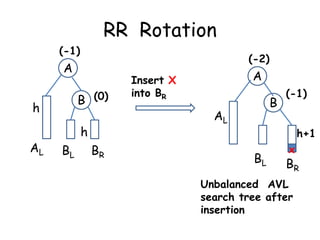
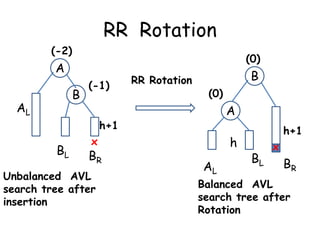
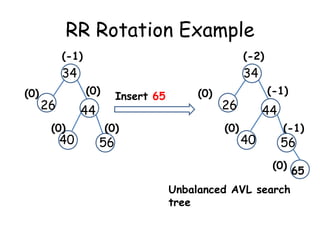
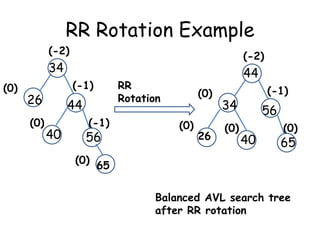
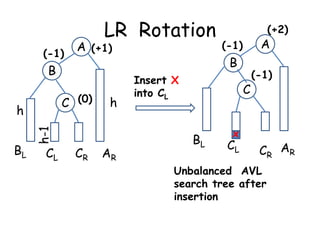
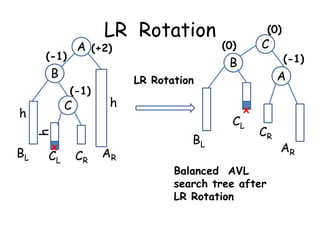
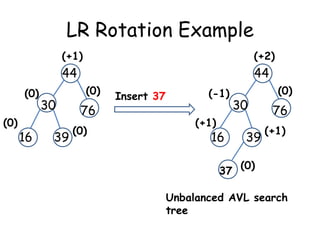
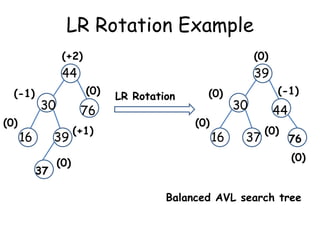
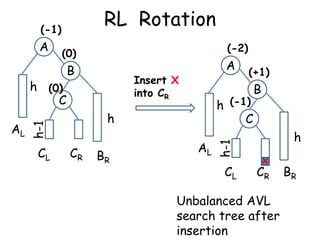
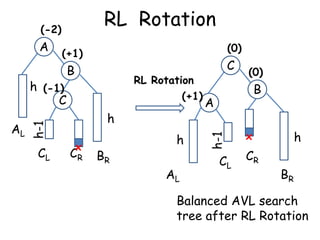
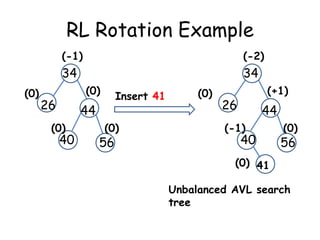
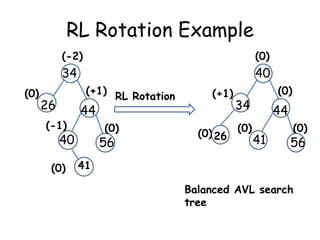
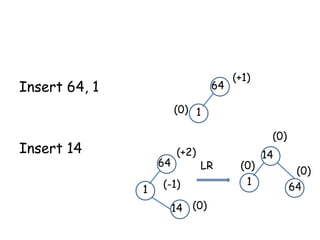
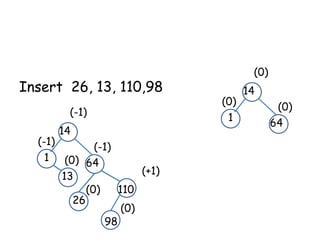
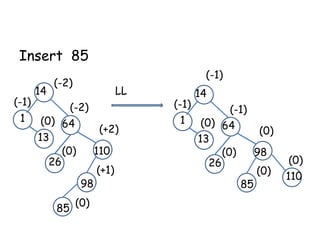
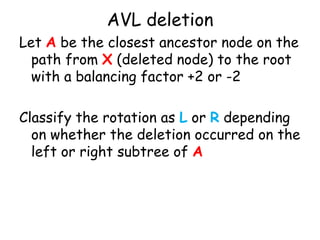
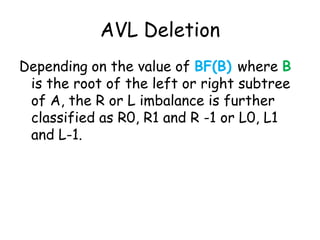
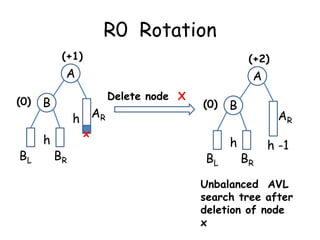
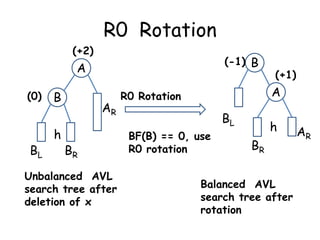
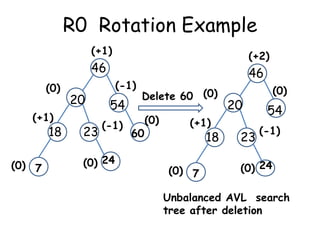
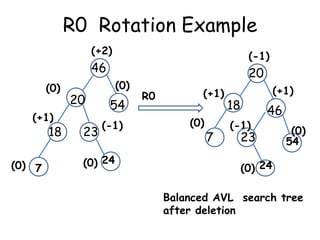
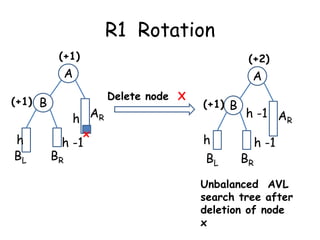
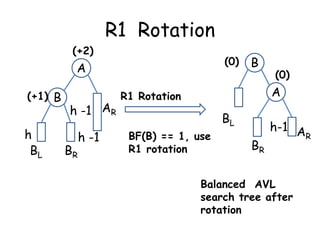
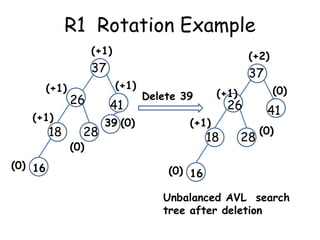
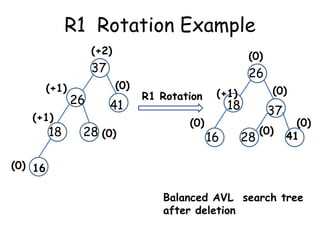
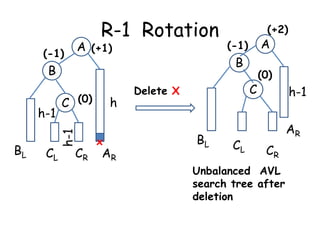
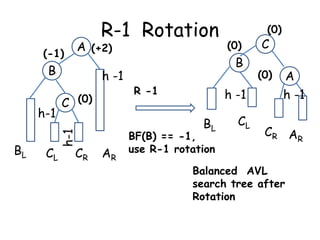
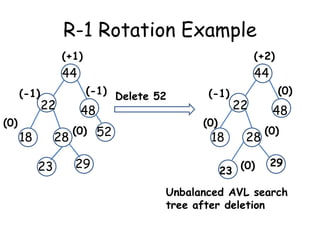
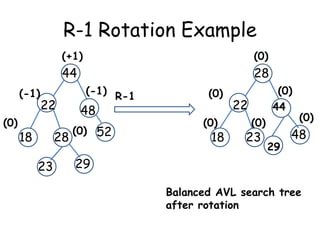
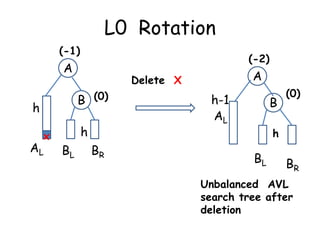
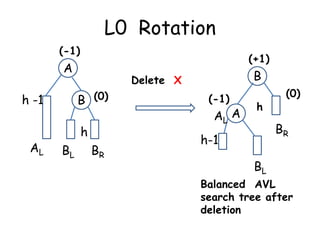
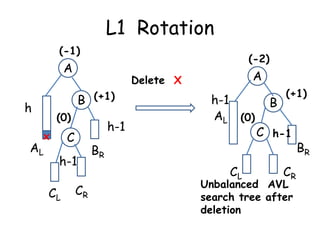
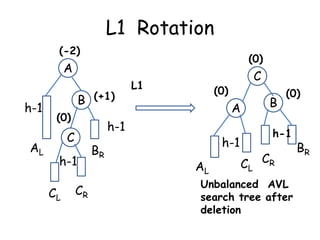
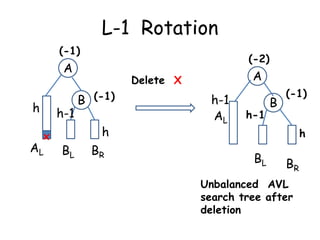
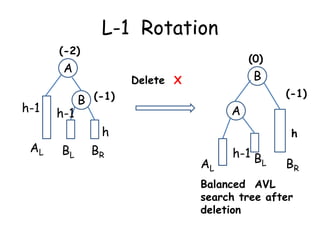
This document discusses balanced binary search trees (BSTs), specifically AVL trees. It explains that AVL trees ensure insertions and deletions are O(log N) by keeping the height difference between left and right subtrees no more than 1. It covers the four types of rotations (LL, RR, LR, RL) used to rebalance the tree after insertions or deletions. Deletions can also cause imbalance and require L, R, L0, L1, R0, R1, L-1, R-1 rotations depending on the balancing factors. Examples are provided for each type of rotation.