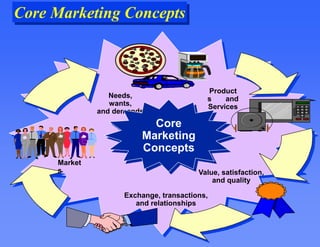
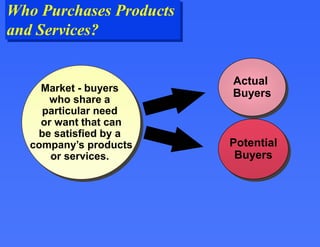
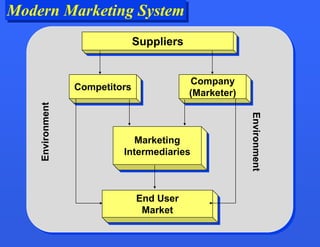
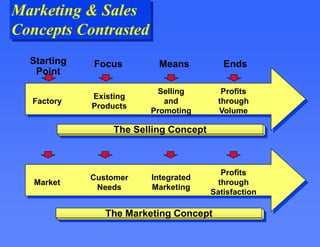
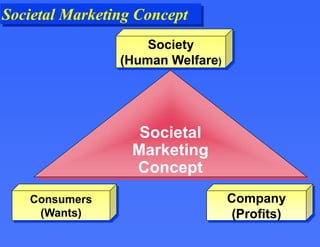
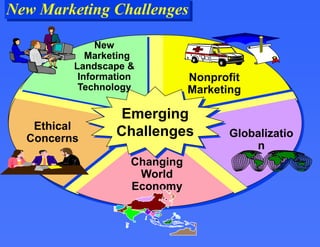
This document provides an overview of key marketing concepts. It defines marketing as the process of satisfying customer needs through the exchange of products and services. The core concepts discussed are the marketing mix of product, price, place and promotion. It also examines what motivates consumer behavior in terms of needs, wants and demands. Additional topics covered include how value and satisfaction influence customer choice, and how modern marketing systems facilitate exchanges between suppliers, marketers and end users.