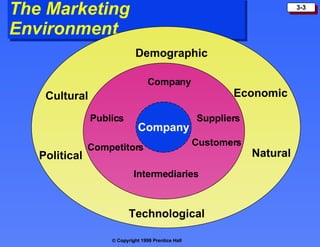
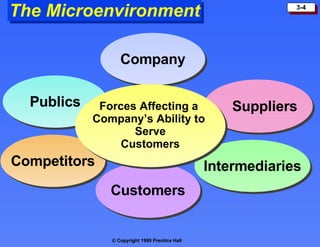
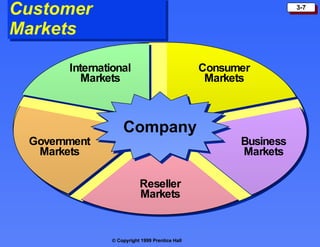
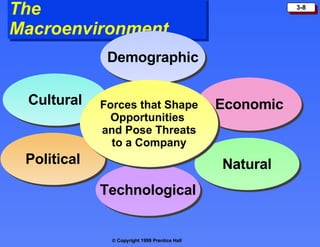
The document discusses the marketing environment, which includes the microenvironment and macroenvironment.
The microenvironment comprises forces close to the company that influence its ability to do business, such as suppliers, marketing intermediaries, customers, competitors, and publics.
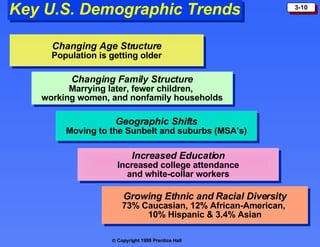
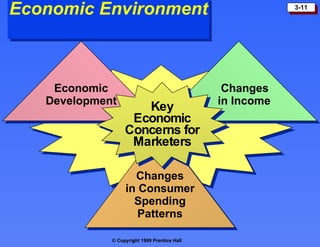
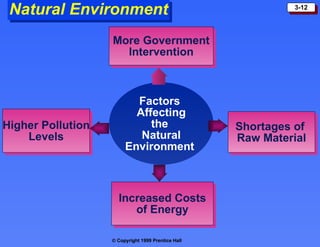
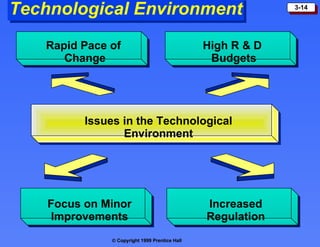
The macroenvironment consists of larger societal forces in the demographic, economic, natural, technological, political, and cultural environments that affect whole industries. Understanding these environments helps companies respond strategically to opportunities and threats.