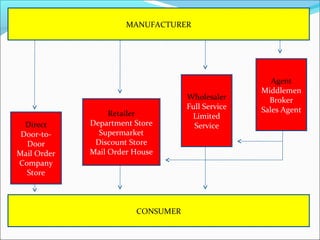
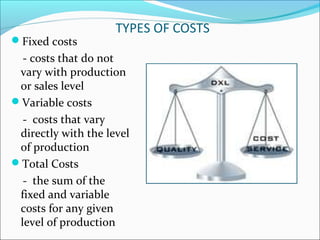
The document outlines key marketing concepts, including market definition, marketing activities, and segmentation. It elaborates on the marketing mix, focusing on product, promotion, and distribution channels, as well as various promotional strategies such as personal selling, advertising, and sales promotion. Additionally, it discusses pricing strategies and factors influencing pricing decisions, such as costs and competition.