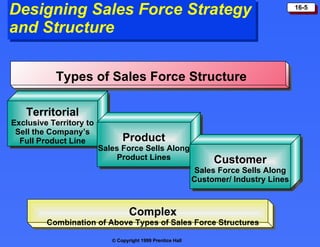
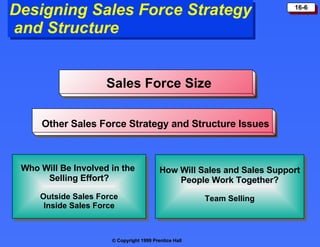
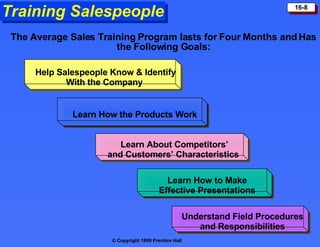
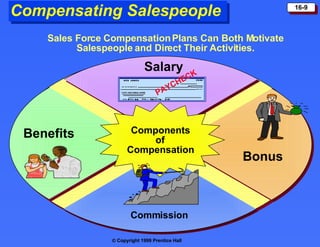
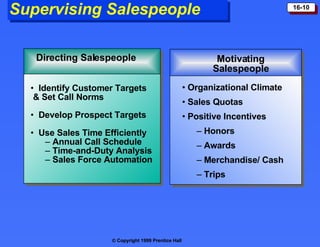
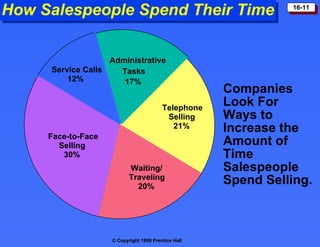
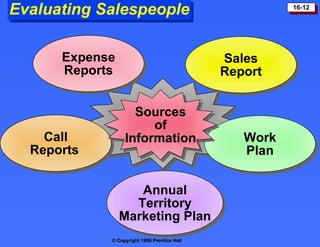
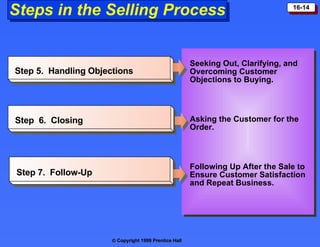
The document discusses personal selling and sales management. It covers the nature of personal selling, the role of the sales force, and how to manage the salesforce. Personal selling involves prospecting, communicating, servicing, and gathering information. The sales force represents the company to customers and customers to the company. Managing the salesforce includes designing strategy and structure, recruiting and selecting salespeople, training, compensating, supervising, and evaluating salespeople.