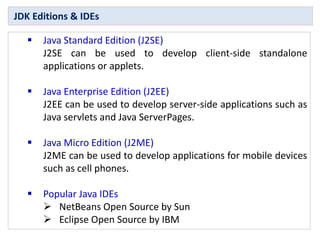
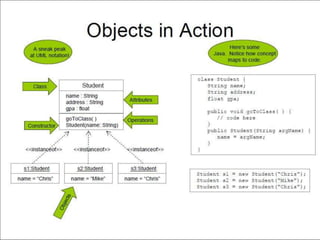
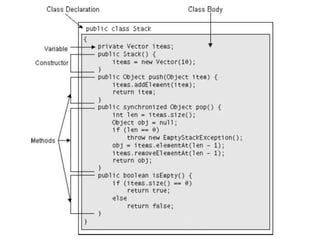
1. Java is an object-oriented, distributed, interpreted, robust, secure, architecture-neutral, and portable programming language.
2. It is interpreted, meaning code is compiled into bytecode that runs on a Java Virtual Machine (JVM) on any system with a JVM.
3. Java incorporates features for object-orientation, networking, security, exception handling and more, making it a powerful yet flexible language for application development.




![//This program prints Welcome to Java!
public class Welcome {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Welcome to Java!");
}
}
A SIMPLE JAVA PROGRAM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect2-characteristicsclasspathcompliation-150219175630-conversion-gate01/85/java-characteristics-classpath-compliation-8-320.jpg)
![//This program prints Welcome to Java!
public class Welcome {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Welcome to Java!");
}
}
PROGRAM EXECUTION – STEP I
Enter main method.
The main method provides the control of program flow. The Java interpreter
executes the application by invoking the main method.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect2-characteristicsclasspathcompliation-150219175630-conversion-gate01/85/java-characteristics-classpath-compliation-9-320.jpg)
![//This program prints Welcome to Java!
public class Welcome {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Welcome to Java!");
}
}
PROGRAM EXECUTION – STEP II
Execute Statement 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect2-characteristicsclasspathcompliation-150219175630-conversion-gate01/85/java-characteristics-classpath-compliation-10-320.jpg)