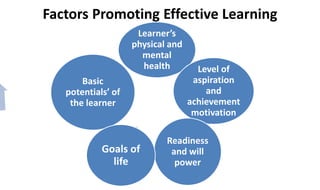
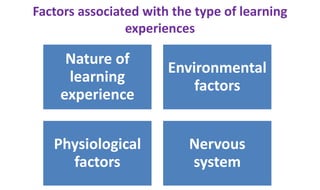
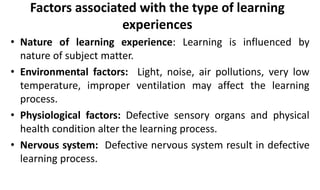
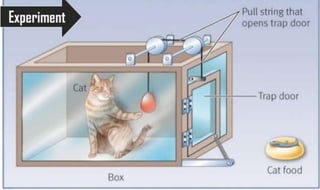
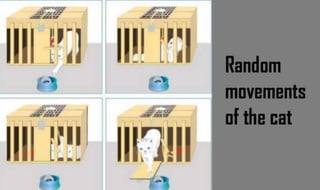
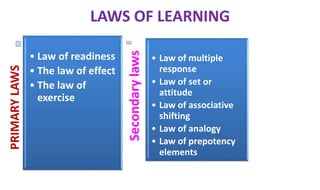
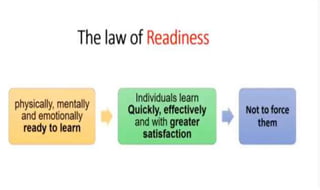
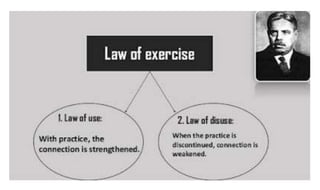
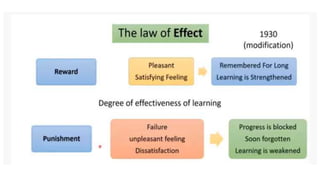
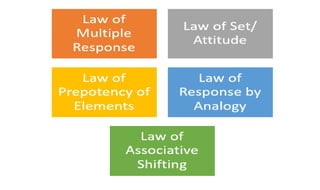
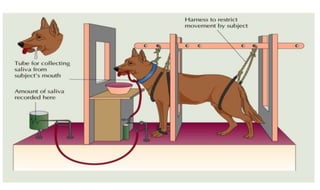
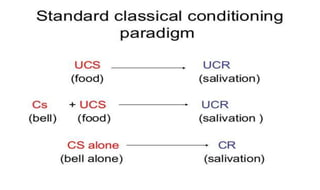
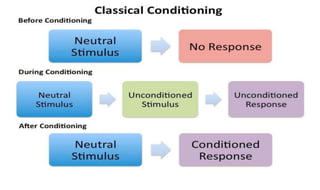
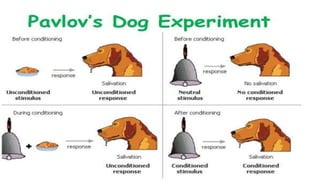
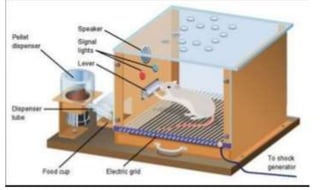
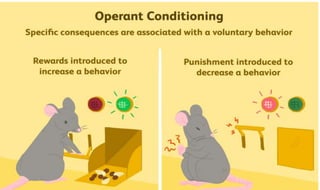
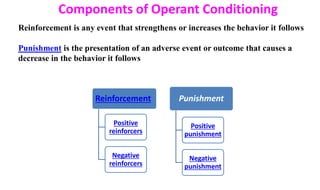
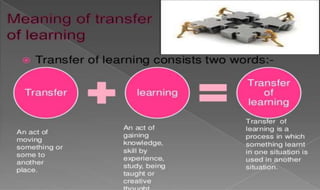
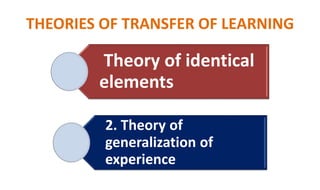
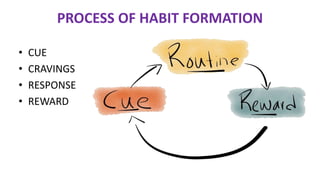
Learning can be defined as a relatively permanent change in behavior resulting from experience. There are several theories and laws of learning. Thorndike's law of effect states that behaviors followed by satisfying consequences are more likely to be repeated, while behaviors followed by unpleasant consequences are less likely to be repeated. Pavlov's classical conditioning theory explains how behaviors can become reflexive through repeated pairing with stimuli. Skinner's operant conditioning theory proposes that behaviors are shaped by their consequences - behaviors followed by reinforcement increase in frequency.