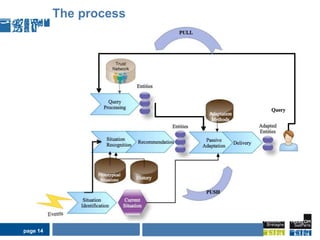
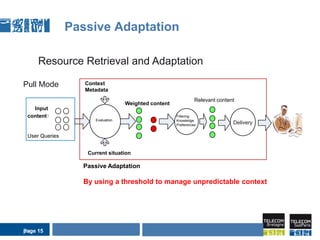
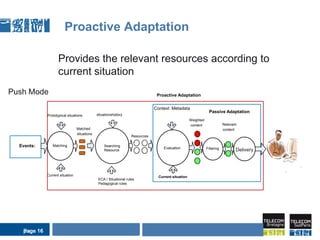
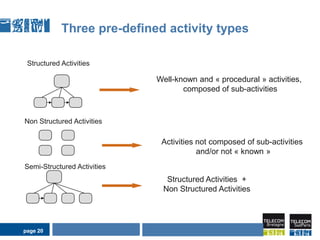
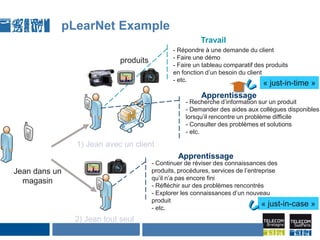
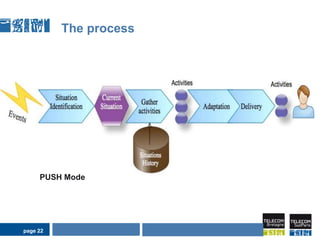
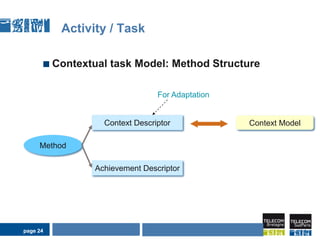
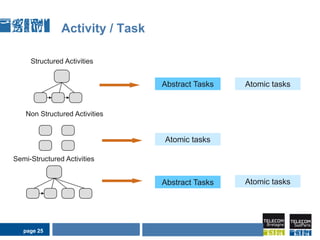
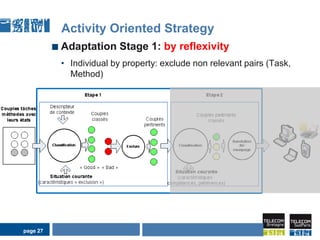
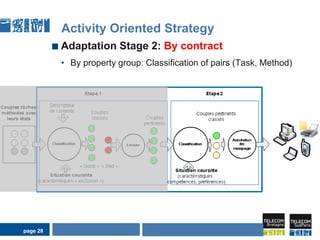
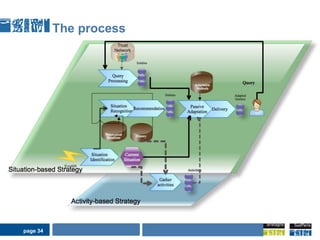
This document discusses pervasive learning at the workplace using a mixed strategy of situation-based and activity-based learning. It proposes combining the two strategies to overcome some of their individual drawbacks and better handle a variety of situations and activities. The key aspects of the mixed strategy are:
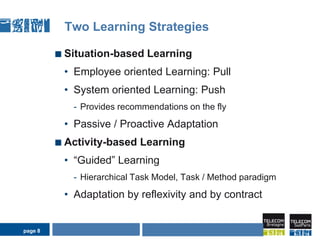
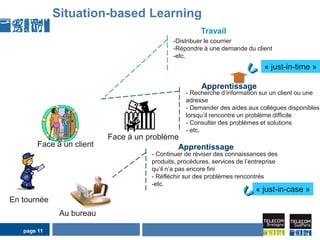
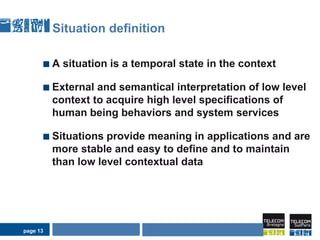
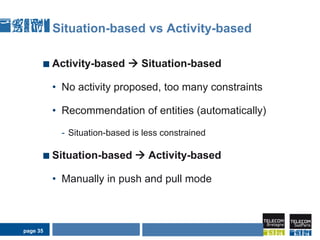
1) Situation-based and activity-based learning strategies are interwoven, with the system able to switch between the two approaches depending on the context.
2) This allows taking advantage of the strengths of both, like linking activities to social contexts, recommendations, clear employee intentions, while compensating for their individual weaknesses.
3) The process involves detecting the current situation or activity, then providing relevant learning resources through either a