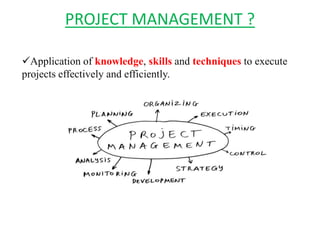
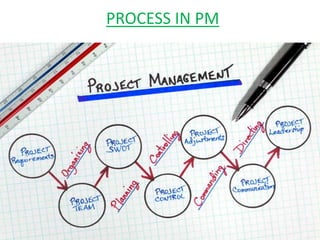
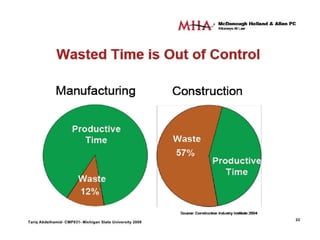
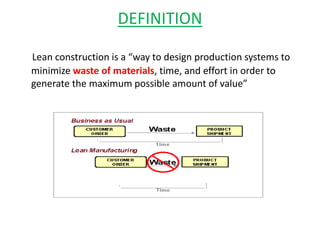
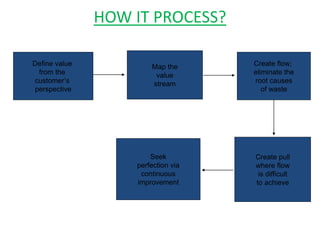
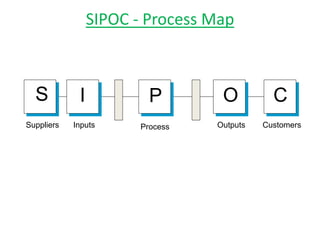
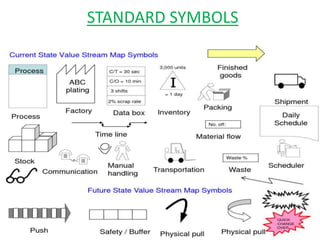
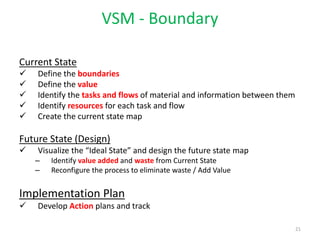
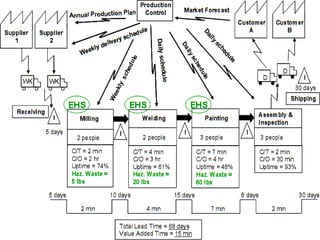
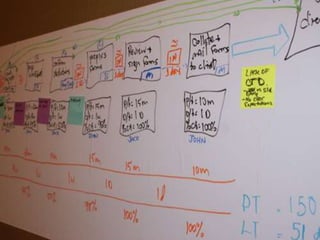
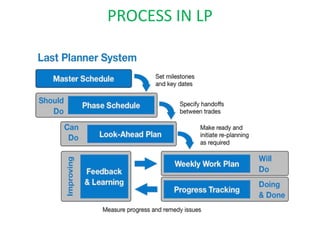
This document discusses lean practices for effective project management. It describes lean construction as taking inspiration from the Toyota Production System to minimize waste of materials, time, and effort in order to maximize value. Key lean tools for reducing waste in construction projects are identified as value stream mapping, which is used to identify waste by mapping the current and future states of processes, and the Last Planner System, which aims to minimize waste by improving the predictability and reliability of construction schedules.