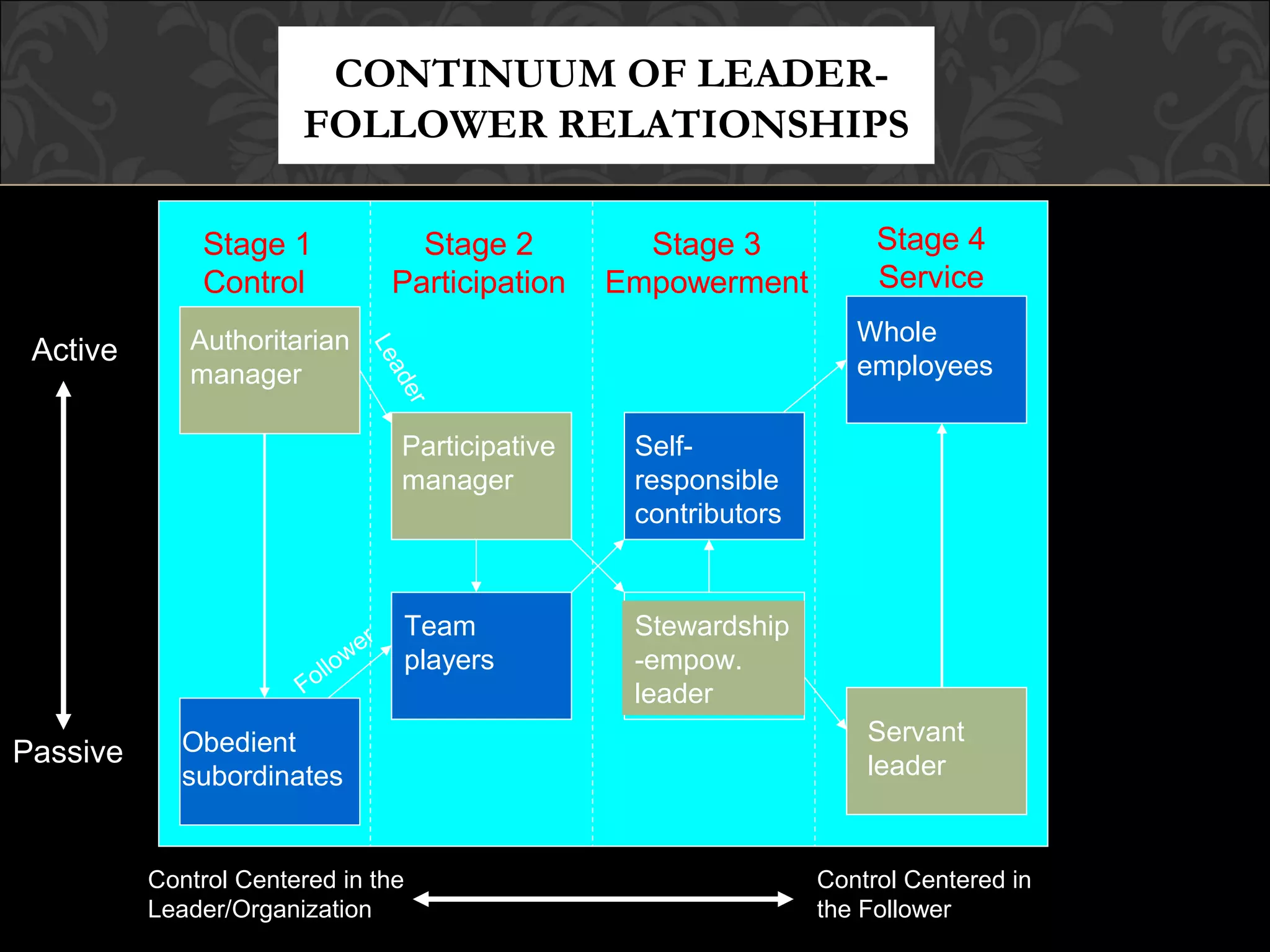
The document discusses various aspects of leadership including definitions of leadership, comparing leadership and management, characteristics of leaders and followers, leadership styles, and developing leadership skills. It provides insights into building effective relationships between leaders and followers as well as developing moral leadership. The document presents a comprehensive overview of leadership concepts through discussions, examples, and frameworks.