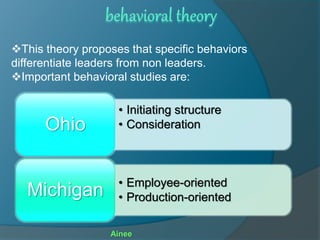
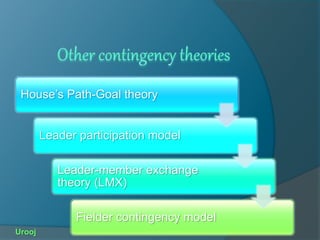
Leadership is guiding others towards collective action for the common good. There are two types of leadership: formal, based on position authority, and informal, based on respect from others. Followership is the process of being guided by a leader at work. Leadership theories include trait theory, behavioral theory, and contingency theory. Contingency theory proposes that leadership effectiveness depends on the environment and follower readiness. A leader's style should match follower readiness to be most effective.