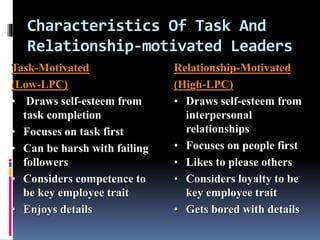
This document discusses different theories and styles of leadership. It defines leadership as the ability to influence a group toward achieving goals. Trait theories focus on personal qualities that make an effective leader, while behavioral theories examine what leaders do. Contingency theories emphasize that leadership effectiveness depends on matching the leader's style to the situation. Fiedler's contingency model identifies leadership styles as task-oriented or relationship-oriented and matches them to levels of situational control. The document also outlines different leadership styles like autocratic, bureaucratic, democratic, and laissez-faire. It briefly discusses transformational, transactional, change, and challenge leadership.