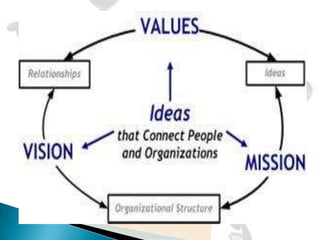
I. Leaders play a key role in establishing organizational values and setting the direction of the organization. Values guide leader's decisions and perceptions.
II. Values can be terminal or instrumental, and shape beliefs, attitudes, and personality. Terminal values are desirable end goals like accomplishment or friendship, while instrumental values are means to achieve goals, like courage or honesty.
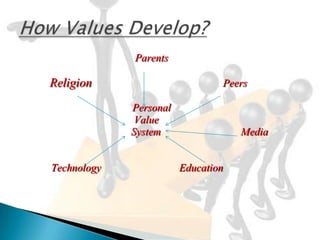
III. Cultural dimensions from the GLOBE study, like assertiveness and future orientation, distinguish societies and impact management. Values are learned from multiple influences like parents, religion, peers, media, and education.