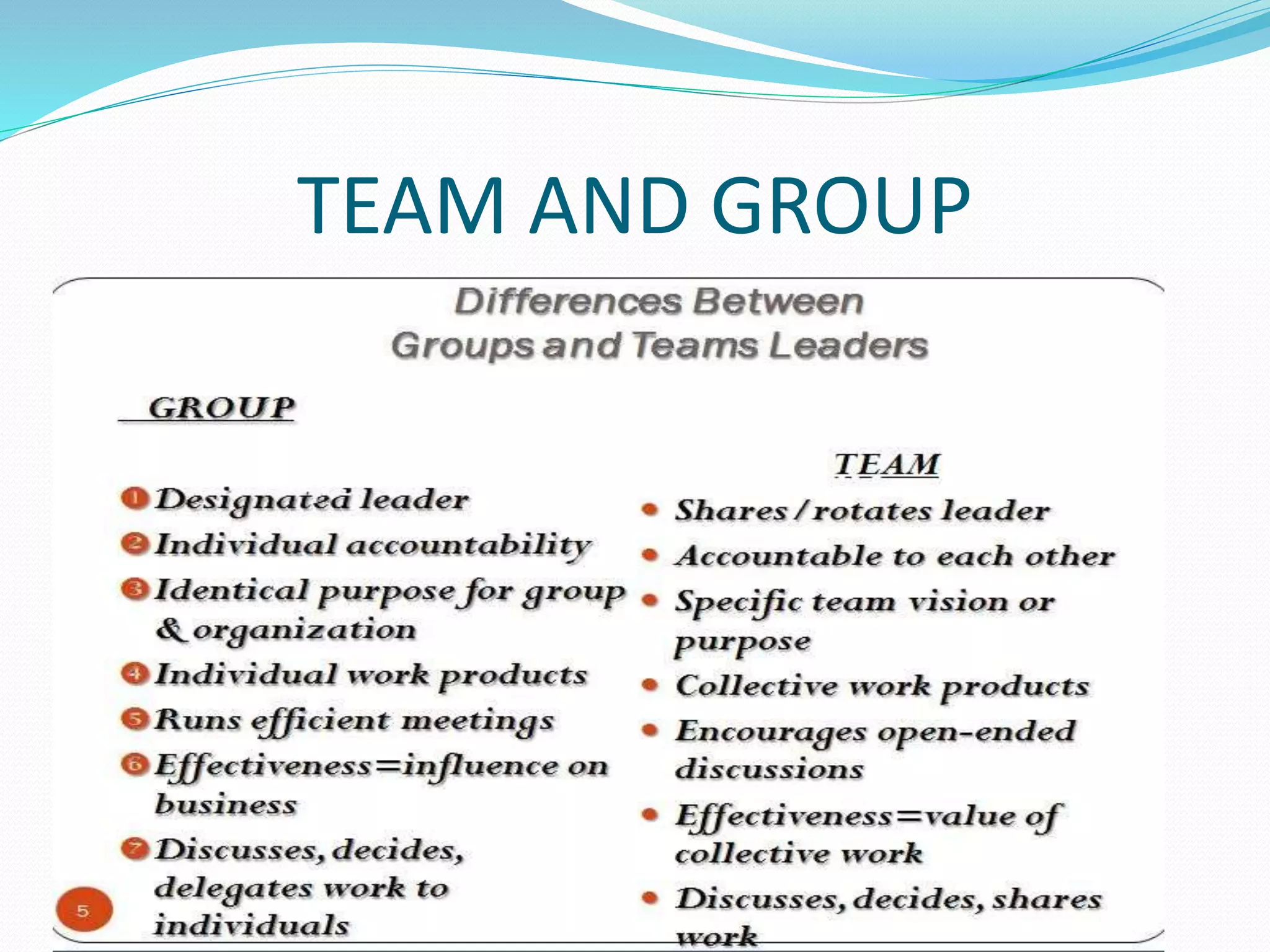
The document outlines a course on leadership and team management, emphasizing the differences between leaders and managers, effective team characteristics, and leadership styles. It describes the stages of team development and stresses the importance of communication within teams, particularly in a competitive and technologically driven environment. Additionally, it highlights the preparation needed for effective teamwork and leadership in various organizational contexts.