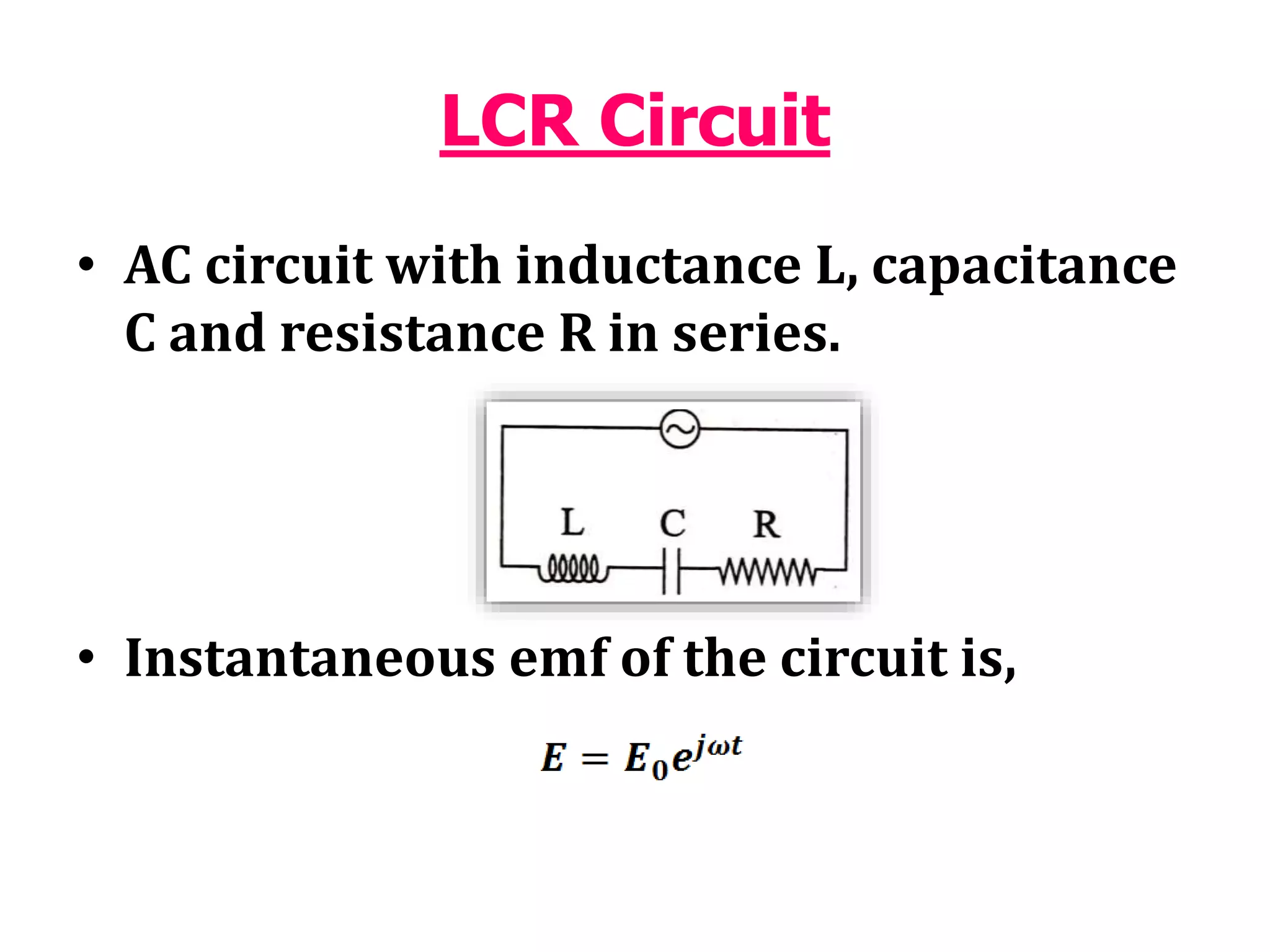
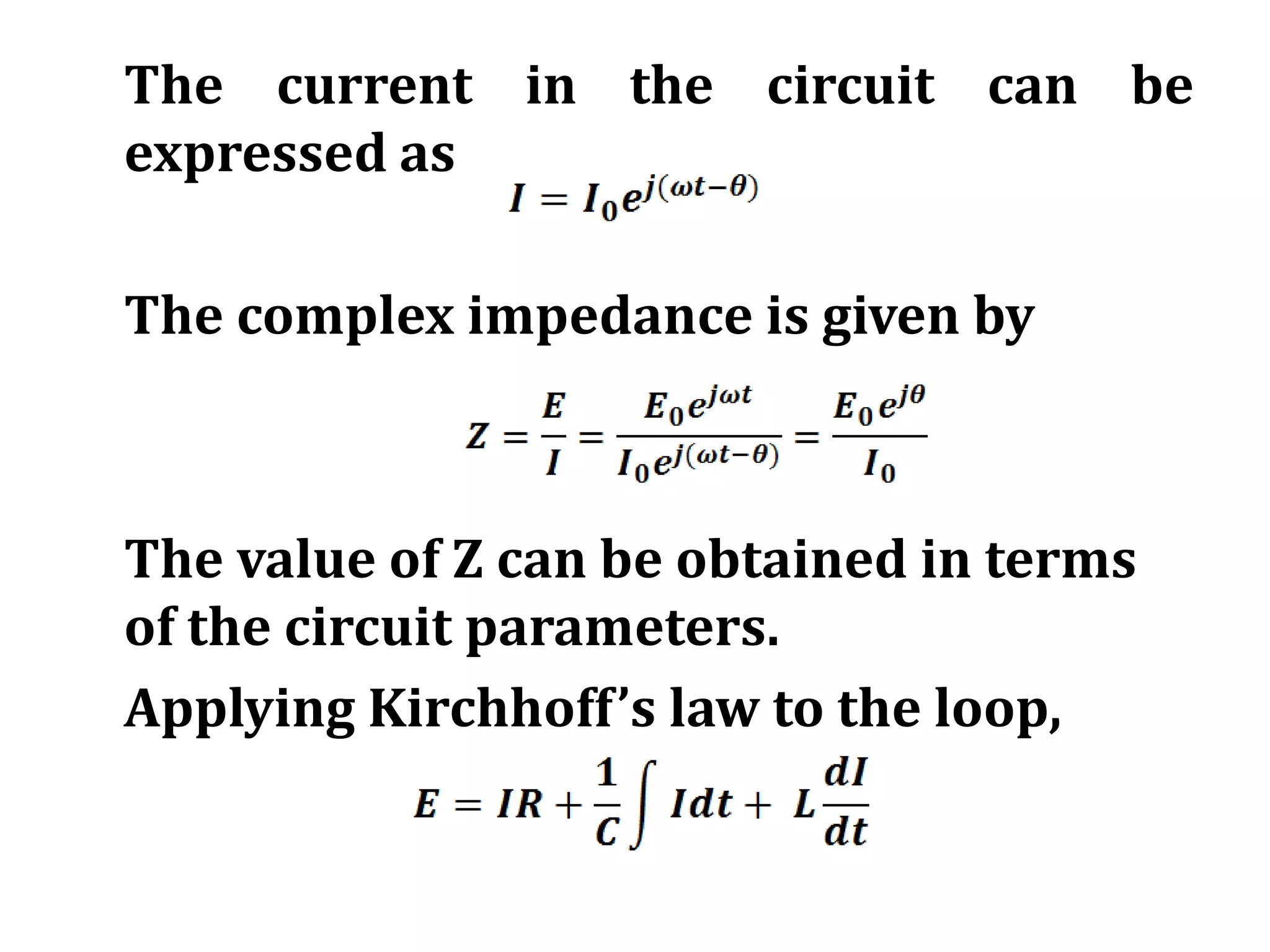
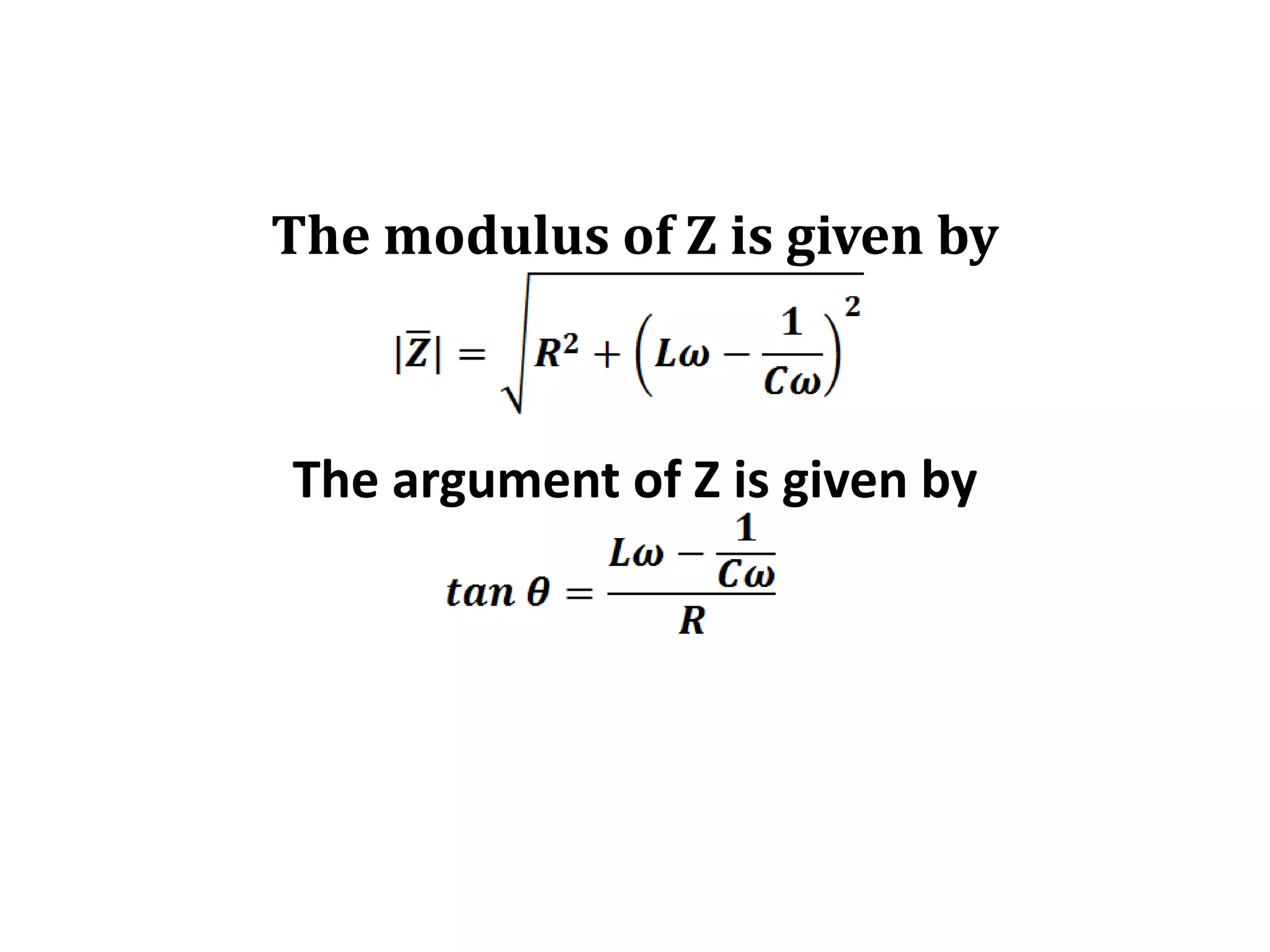
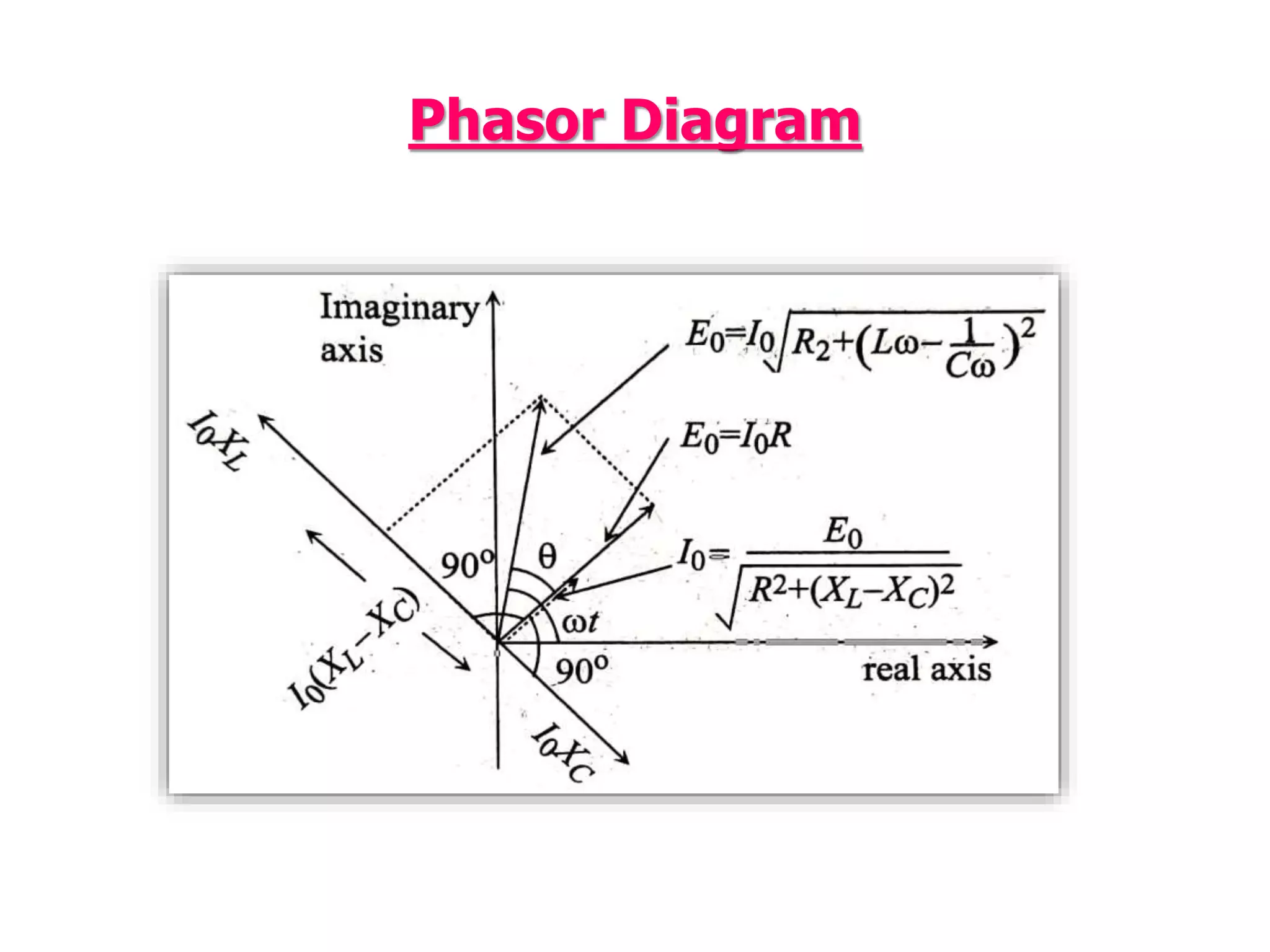
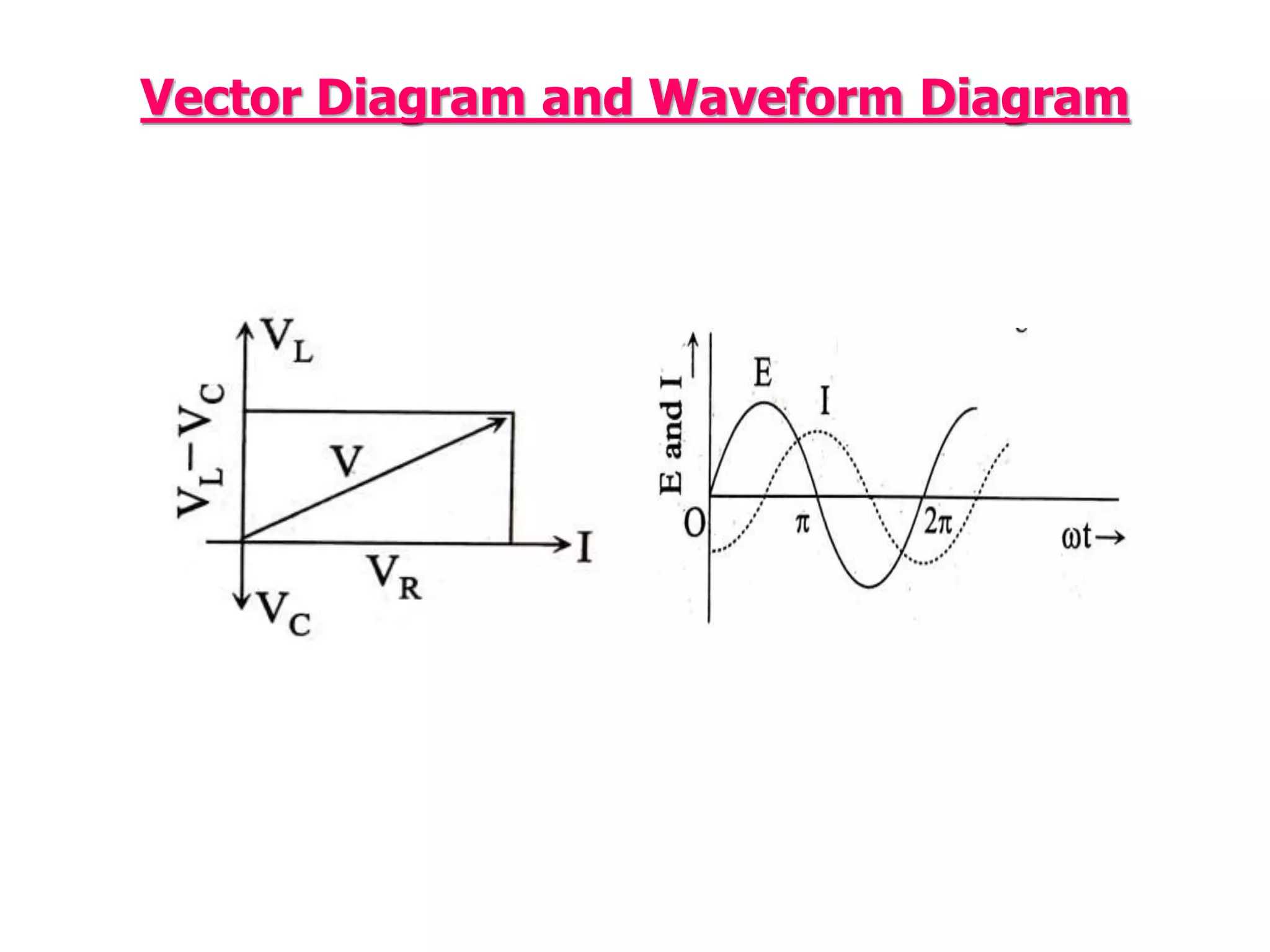
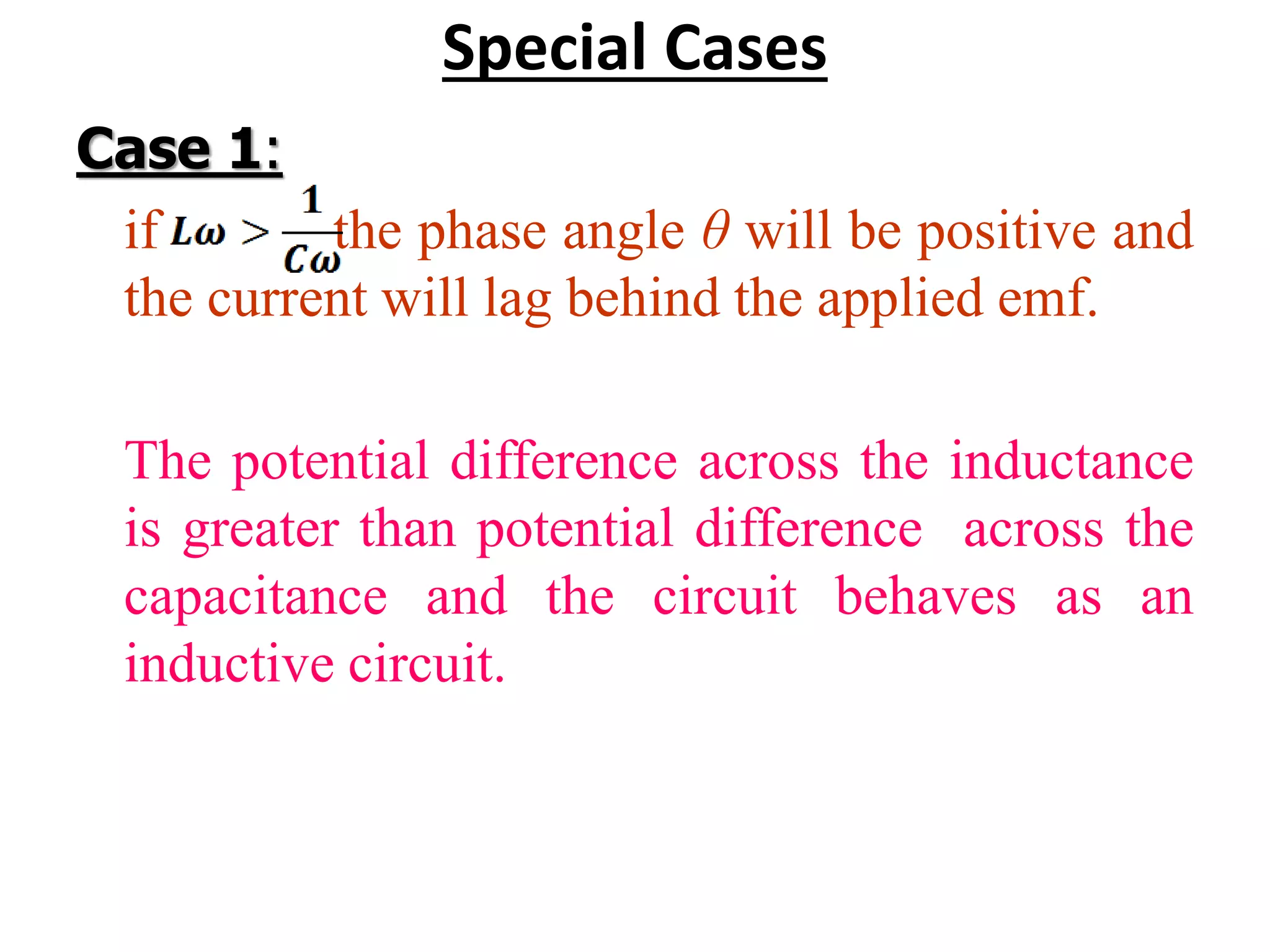
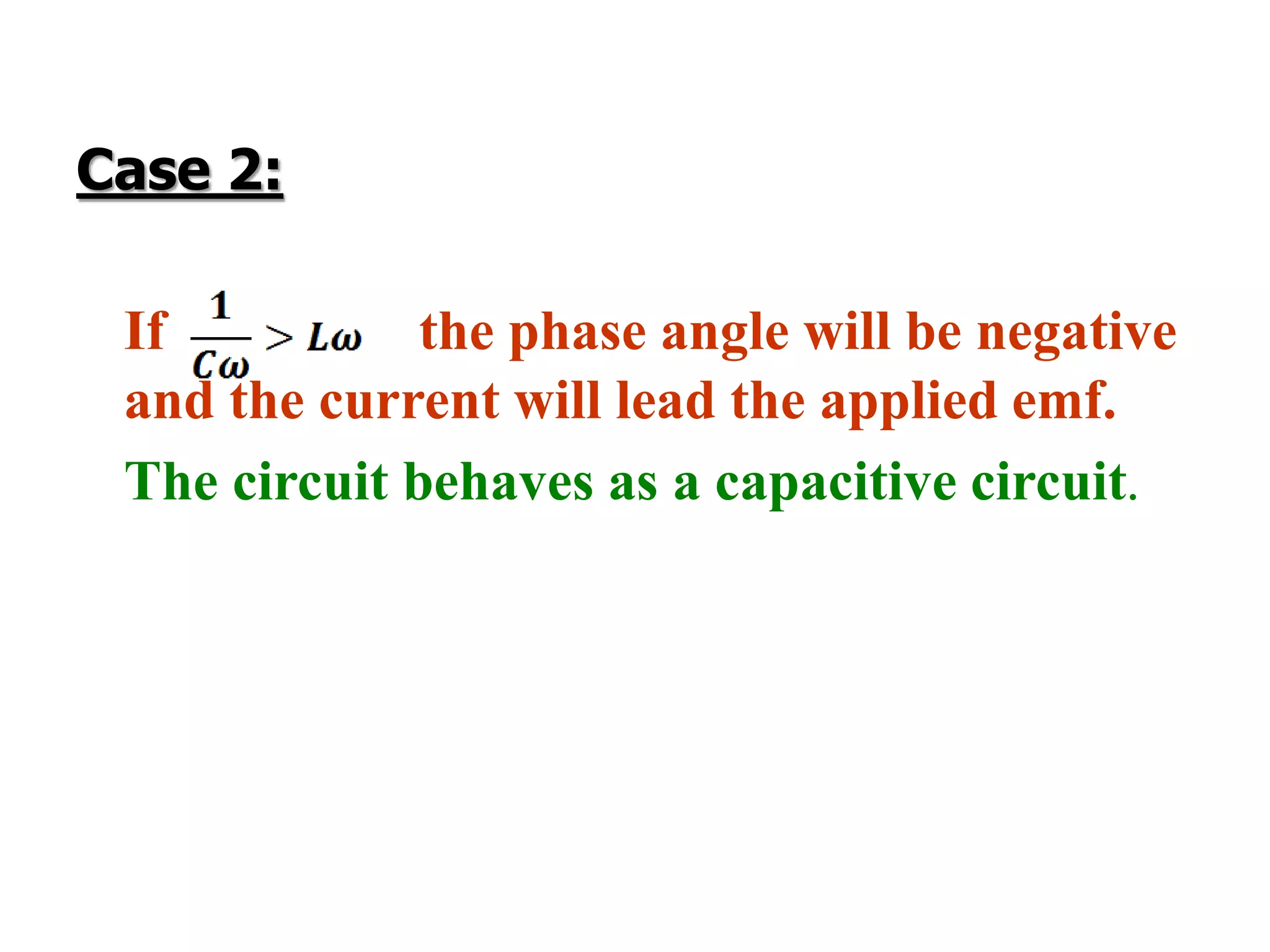
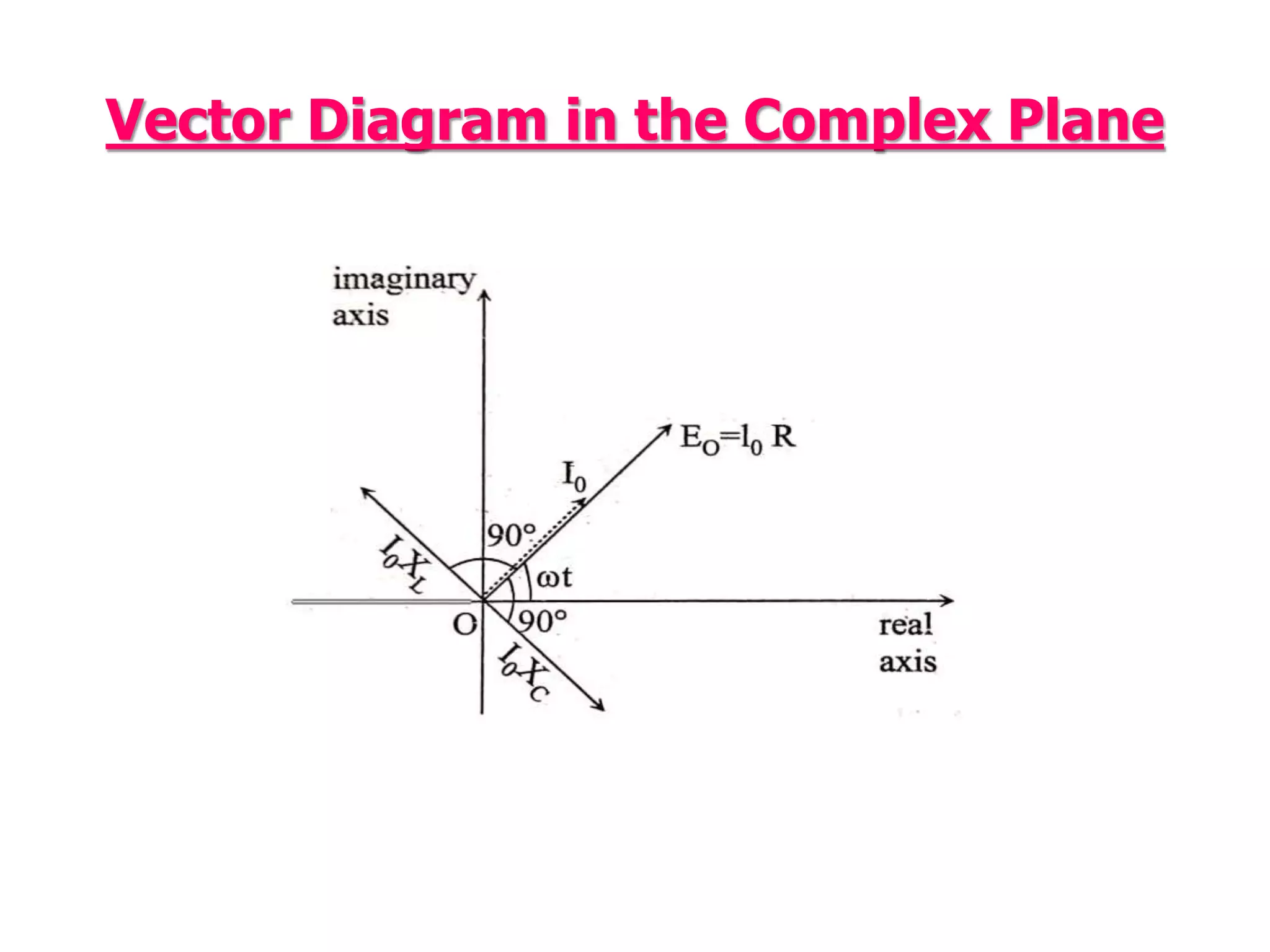
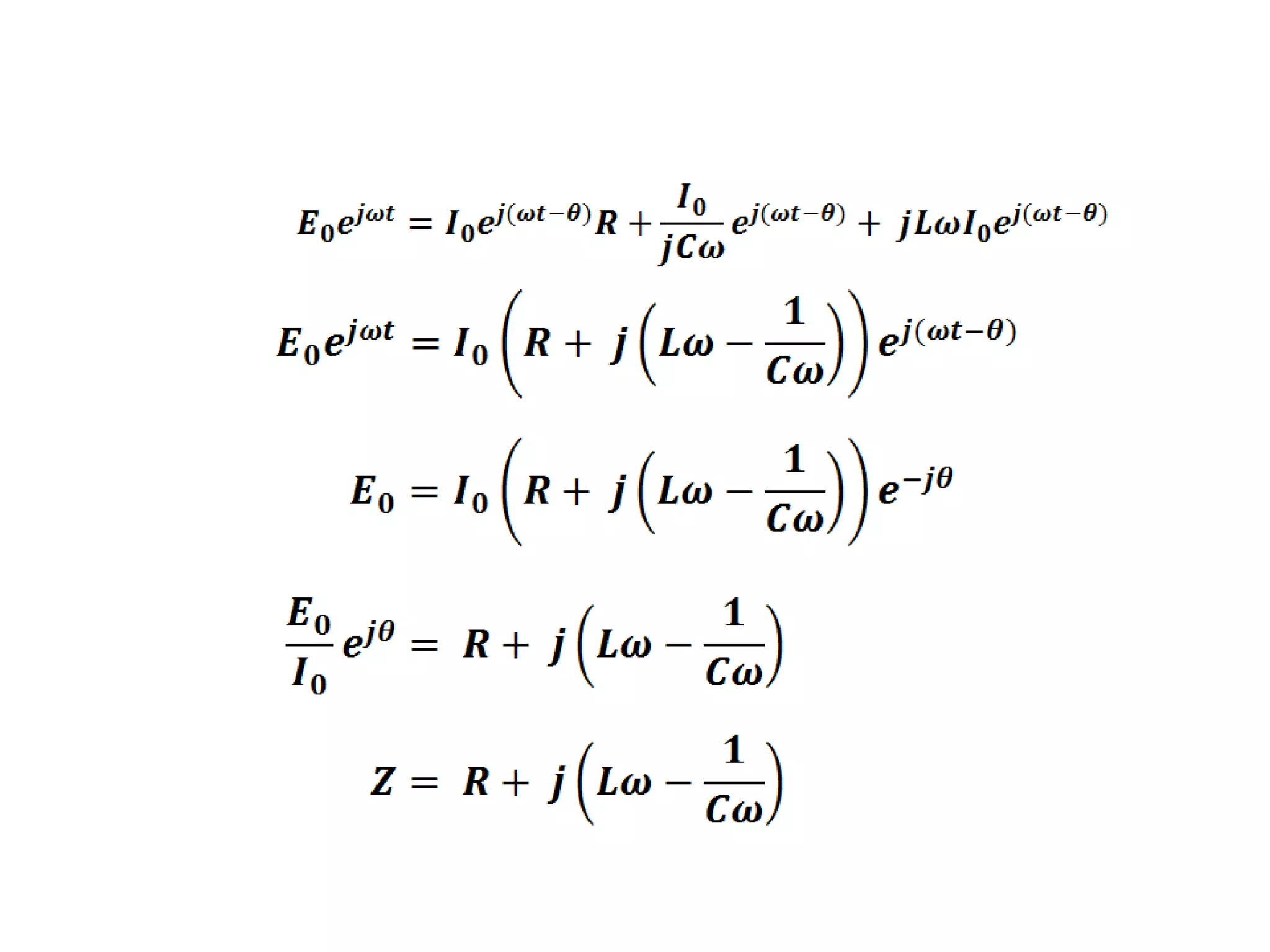This document discusses an AC circuit with inductance, capacitance, and resistance in series. It defines the circuit components and equations for current, impedance, and phase angle. Special cases are described where the circuit behaves as inductive, capacitive, or resistive depending on the phase relationship between current and applied emf. Resonance is explained as the condition when peak current is maximum and phase angle is zero.